Conglomerate rocks, fascinating sedimentary formations composed of rounded gravel-sized clasts cemented together, offer a glimpse into Earth’s ancient environments. At rockscapes.net, we’ll explore where you can discover these geological treasures and how they can enhance your landscape design. Whether you’re envisioning a stunning rock garden or a durable pathway, understanding conglomerate rocks is key. Let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of these captivating stones.
1. What Exactly Are Conglomerate Rocks?
Conglomerate rocks are sedimentary rocks primarily composed of rounded or semi-rounded clasts (fragments of other rocks or minerals) that are larger than 2 millimeters in diameter, cemented together by a matrix of finer particles like sand, silt, or clay. These rocks tell stories of ancient riverbeds, shorelines, and glacial deposits.
1.1 What Defines a Conglomerate Rock?
A conglomerate rock is defined by its composition, which includes rounded clasts (gravel-sized or larger) held together by a matrix. According to the University of Arizona’s Department of Geosciences, the rounding of the clasts indicates significant transport and abrasion, often in a fluvial (river) or coastal environment.
1.2 What is the Composition of Conglomerate Rocks?
Conglomerate rocks consist of two main components:
-
Clasts: These are the larger, rounded fragments within the rock. They can be composed of various materials, including:
- Mineral particles like feldspar or quartz.
- Fragments of metamorphic or igneous rocks.
- Common rock types such as quartzite, sandstone, limestone, granite, or basalt.
-
Matrix: This is the finer-grained material that fills the spaces between the clasts and binds them together. It typically consists of:
- Sand
- Silt
- Clay/mud
- Chemical cement (e.g., silica, calcium carbonate, iron oxide)
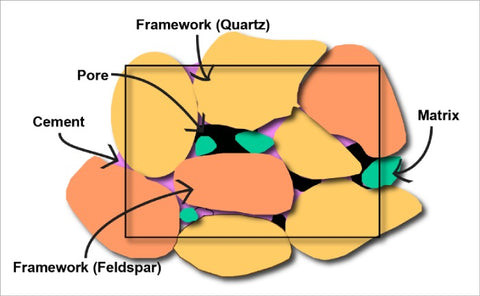 Conglomerate rock composition of clasts and matrix
Conglomerate rock composition of clasts and matrix
1.3 How Do Conglomerate Rocks Differ From Breccia?
Conglomerate rocks differ from breccia primarily in the shape of their clasts; conglomerate rocks contain rounded clasts, indicating significant abrasion and transport, while breccia contains angular clasts, suggesting minimal transport and local origin.
1.4 How Old is the Oldest Conglomerate Rock?
The oldest known conglomerate rocks are found in the Jack Hills of Australia, with meta-conglomerate layers dating back over four billion years, containing the planet’s oldest zircon crystals.
2. Where Can You Find Conglomerate Rocks?
Conglomerate rocks are found in locations with abundant water sources, such as lakes, rivers, beaches with strong currents, and glacial environments. These environments facilitate the erosion, transportation, and deposition of the clasts that form conglomerate rocks.
2.1 What Geographical Regions Are Known for Conglomerate Deposits?
Conglomerate rocks are found worldwide, including:
- Asia: China, India, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, Russia, Uzbekistan.
- Africa: Namibia, Nigeria, South Africa.
- Europe: Austria, Denmark, Germany, Great Britain, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom.
- North America: Canada, USA.
- South America: Brazil.
- Australia: New South Wales, New Zealand.
- Other: Greenland.
2.2 What Specific Locations in the USA Have Significant Conglomerate Formations?
Notable conglomerate deposits in the USA include:
- Crestone, Colorado (San Luis Valley): Known for its distinctive Crestone Conglomerate.
- Pennsylvania: Various locations across the state, indicating ancient river systems and depositional environments.
2.3 What Role Do Water Bodies Play in Conglomerate Formation?
Water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and oceans are essential for the formation of conglomerate rocks, as they provide the necessary energy to erode, transport, and deposit the clasts that make up these rocks. According to a study by the Geological Society of America, fluvial (river) environments are particularly effective at rounding clasts through abrasion during transport.
2.4 How Do Glaciers Contribute to Conglomerate Formation?
Glaciers contribute to conglomerate formation by plucking sediments and rocks during ice formation, transporting them within the glacial mass, and depositing them as “glacial till” upon melting. This process often results in poorly sorted, coarse-grained conglomerate deposits.
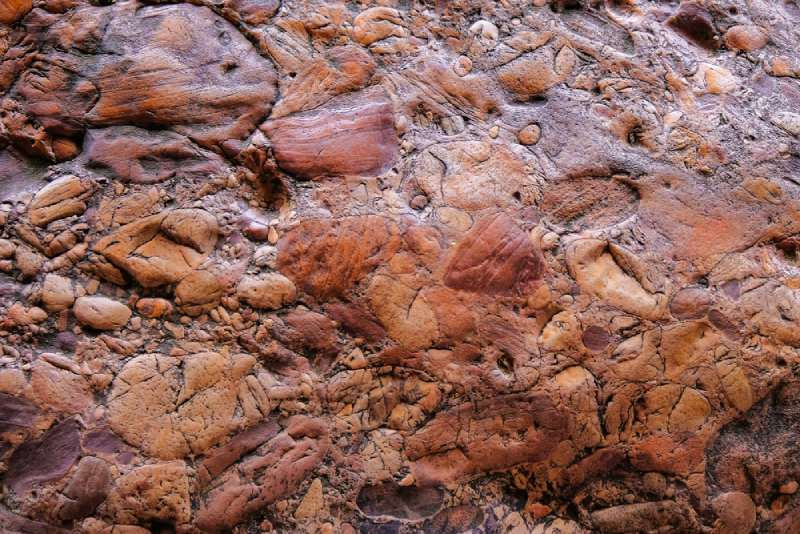 Conglomerate rocks found in different locations
Conglomerate rocks found in different locations
3. Understanding Conglomerate Rock Texture, Classification, and Types
Conglomerate rocks exhibit a clastic texture due to their formation from fragments of other rocks. Their classification depends on the composition of the clasts and the matrix.
3.1 What is the Texture of Conglomerate Rocks?
Conglomerate rocks have a clastic texture, characterized by the presence of visible, rounded clasts cemented together in a matrix.
3.2 How Are Conglomerates Classified Based on Cement Percentage?
Conglomerates are classified based on the percentage of cement (matrix) as follows:
- Paraconglomerate: Matrix-supported conglomerate with at least 15% matrix. Further classified into laminated (cemented clasts) and non-laminated types. Examples include tillites and tilloids.
- Orthoconglomerate: Clast-supported conglomerate with less than 15% matrix, where clasts dominate the mass.
3.3 What is the Difference Between Petromict and Oligomict Conglomerates?
The difference lies in the resistance of the clasts to weathering:
- Petromict Conglomerate: Contains clasts with low weathering resistance (e.g., limestone, dolomite, shale).
- Oligomict Conglomerate: Contains clasts with high weathering resistance (e.g., quartz, chert, basalt).
3.4 What Are Intraformational and Extraformational Conglomerates?
- Intraformational Conglomerate: Clasts and matrix originate from the same environment, having similar compositions (e.g., siliceous matrix with quartz and jasper clasts).
- Extraformational Conglomerate: Clasts and matrix have different origins, with clasts transported from a different rock type area than the matrix (e.g., basalt clasts in a calcareous matrix).
3.5 How Do Monomictic, Diamictic, and Polymictic Conglomerates Differ?
These classifications are based on the variation in parent material:
- Monomictic Conglomerate: Contains clasts of the same rock type or parent material.
- Diamictic Conglomerate: Contains clasts consisting of two types of parent rocks (e.g., quartz and jasper clasts).
- Polymictic Conglomerate: Contains clasts of numerous types of parent rocks (e.g., quartz, basalt, limestone, and chert clasts).
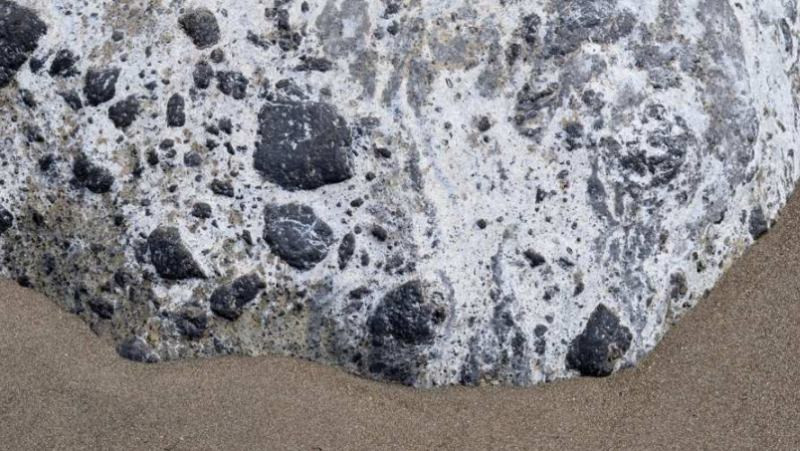 Conglomerate classification of different types
Conglomerate classification of different types
4. Exploring Conglomerate Rock Colors and Their Significance
The colors of conglomerate rocks depend on the colors of the clasts and the matrix, with common colors including beige, black, brown, gray, orange, rust, white, and yellow. These colors can significantly influence their aesthetic appeal in landscaping applications.
4.1 What Factors Determine the Color of Conglomerate Rocks?
The color of conglomerate rocks is determined by the composition and color of both the clasts and the matrix. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the presence of iron oxides can result in reddish or brownish hues, while silica-rich matrices may produce lighter colors.
4.2 What Common Colors Are Found in Conglomerate Rocks?
Common colors include:
- Beige
- Black
- Brown
- Buff
- Light to Dark Gray
- Orange
- Rust
- White
- Yellow
4.3 How Does Color Affect the Use of Conglomerate in Landscaping?
The color of conglomerate rocks greatly impacts their use in landscaping, influencing the overall aesthetic and blending with other elements in the design. Lighter colors can brighten up a space, while darker colors can add contrast and depth.
5. The Formation Process of Conglomerate Rocks
Conglomerate rocks form through the erosion, transportation, deposition, and cementation of rounded clasts, typically in environments with significant water activity. The rounding of clasts indicates they have been tumbled and transported over considerable distances.
5.1 What Are the Key Stages in Conglomerate Formation?
The key stages are:
- Erosion: Weathering and erosion break down rocks into smaller fragments (clasts).
- Transportation: Clasts are transported by water, wind, or ice, becoming rounded through abrasion.
- Deposition: Clasts are deposited in environments such as riverbeds, shorelines, or glacial areas.
- Cementation: Over time, minerals precipitate from groundwater and cement the clasts together, forming solid rock.
5.2 How Does the Environment Influence Conglomerate Formation?
Different environments produce conglomerate rocks with varying characteristics:
- Shallow Water Marine Environment: Tidal waves tumble gravels and pebbles, forming well-rounded clasts. Deposition occurs with sands, silts, and mud.
- Deep Water Marine Environment: Clasts flow with river flood currents and settle in deep sea areas, resulting in smaller, rounded clasts rich in silt, clay, and sand.
- Glacial Environment: Sediments falling on glacial ice are plucked and carried, depositing coarse-grained, poorly sorted clasts upon melting.
- Alluvial Environment: Streams moving from mountains deposit large and small clasts as water slows and disperses.
- Fluvial Environment: River floods transport and sort clasts, resulting in graded bedding of conglomerate deposits.
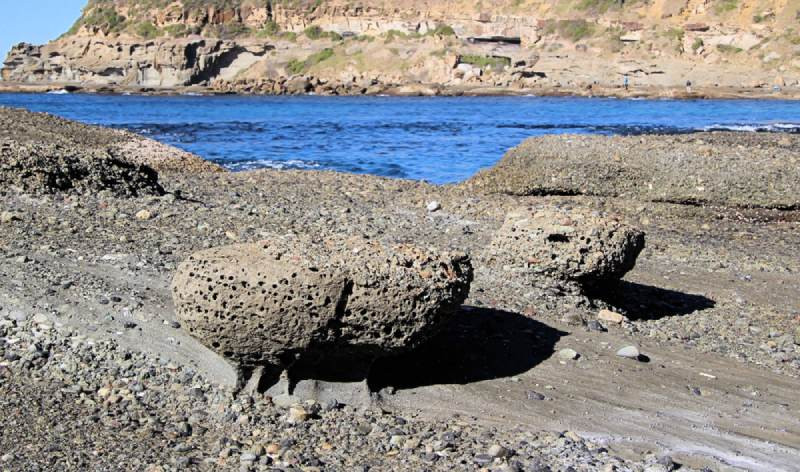 Conglomerate rock formation process
Conglomerate rock formation process
6. Diverse Uses of Conglomerate Rock
Conglomerate rock, while limited in some industrial applications due to its variable properties, finds its primary use as an aggregate raw material in road and building construction.
6.1 What Are the Main Applications of Conglomerate Rock in Construction?
The main applications include:
- Construction Aggregate: Crushed conglomerates are used as aggregate in road and building construction.
- Cement Manufacturing: Conglomerates are used as a raw material in the cement manufacturing industry.
6.2 How is Conglomerate Rock Used in Landscaping and Decoration?
Conglomerate rocks are used:
- Dimension Stones: Smaller clast conglomerates are cut into specific shapes for flooring, wall veneers, and roof tiles.
- Decorative Material: Different clast parent materials provide various colors and textures for interior and exterior decoration.
6.3 Are There Any Historical or Architectural Uses of Conglomerate?
Yes, examples include:
- Santa Maria de Montserrat Abbey (Spain): Constructed using conglomerate rocks from Montserrat.
- Curbing: Conglomerates offer unique options for entrance front curbing to create appealing designs.
6.4 What Other Commercial Applications Exist for Conglomerate Rock?
Other applications include:
- Antiquity Material: Used for artifacts, monuments, sculpture formation, and small figurines.
- Cemetery Markers and Tombstones: Historically used for these purposes.
- Aquifers: Used in the construction of aquifers.
 Conglomerate rock for pebble tiles
Conglomerate rock for pebble tiles
7. Why Choose Conglomerate Rocks for Your Landscaping Project?
Conglomerate rocks offer a unique combination of aesthetic appeal and practical benefits, making them an excellent choice for various landscaping projects. Their natural variations in color and texture add visual interest, while their durability ensures long-lasting performance.
7.1 What Are the Aesthetic Benefits of Using Conglomerate?
Aesthetic benefits include:
- Natural Variation: The diverse clasts provide unique colors, textures, and styles.
- Visual Appeal: When cut properly, conglomerates can enhance interior and exterior designs.
- Curbing Appeal: Offers unique options for entrance front curbing.
7.2 How Durable Are Conglomerate Rocks in Outdoor Applications?
The durability of conglomerate rocks depends on the strength of the cementing material and the resistance of the clasts to weathering. Properly cemented conglomerates with durable clasts can withstand harsh weather conditions and heavy use.
7.3 What Design Styles Complement Conglomerate Rocks?
Conglomerate rocks complement a variety of design styles, including:
- Rustic: Their natural, rugged appearance fits well with rustic designs.
- Naturalistic: They blend seamlessly with natural landscapes.
- Eclectic: Their diverse colors and textures make them suitable for eclectic designs.
7.4 How Can Conglomerate Be Used to Create Unique Landscape Features?
Conglomerate can be used to create:
- Rock Gardens: Use various sizes and colors to create visually appealing rock gardens.
- Pathways: Use dimension stone for durable and attractive pathways.
- Water Features: Integrate conglomerates into water features for a natural look.
8. Sourcing Conglomerate Rocks for Your Project
Sourcing high-quality conglomerate rocks is essential for ensuring the success of your landscaping project. Choosing a reputable supplier ensures you get the right type of stone for your specific needs.
8.1 What Should You Consider When Choosing a Conglomerate Supplier?
Consider the following:
- Quality of Stone: Ensure the stone is durable and has the desired aesthetic.
- Variety of Options: Look for a supplier with a wide range of colors, sizes, and textures.
- Reputation and Reviews: Check online reviews and ask for references.
- Pricing and Availability: Compare prices and ensure the supplier can meet your project timeline.
8.2 How Can Rockscapes.Net Help You Find the Perfect Conglomerate?
At rockscapes.net, we offer:
- Extensive Selection: A wide variety of conglomerate rocks to suit any design.
- Expert Advice: Our team can help you choose the right stone for your project.
- High-Quality Materials: We source only the best conglomerate rocks.
- Competitive Pricing: We offer competitive prices to fit your budget.
8.3 What Questions Should You Ask a Conglomerate Supplier?
Ask the following questions:
- What is the source of the conglomerate rocks?
- What is the cementing material?
- What is the resistance of the clasts to weathering?
- What sizes and colors are available?
- What is the price per ton or square foot?
- What is the lead time for delivery?
9. Installation and Maintenance Tips for Conglomerate Landscapes
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for preserving the beauty and longevity of your conglomerate landscape. Following these tips will help ensure your project remains stunning for years to come.
9.1 What Are the Best Practices for Installing Conglomerate Rocks?
Best practices include:
- Proper Base Preparation: Ensure a stable base for pathways and rock gardens.
- Appropriate Spacing: Allow for drainage and prevent overcrowding.
- Professional Installation: Consider hiring a professional for complex projects.
9.2 How Can You Maintain the Appearance of Conglomerate Over Time?
Maintenance tips include:
- Regular Cleaning: Remove dirt, debris, and stains with a brush and water.
- Sealing: Apply a sealant to protect against weathering and staining.
- Weed Control: Regularly remove weeds to prevent them from taking over.
9.3 What Are Common Issues and How Can You Address Them?
Common issues and solutions include:
- Discoloration: Clean with a mild detergent and water.
- Cracking: Repair cracks with epoxy or mortar.
- Settling: Add additional base material to level settled areas.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Conglomerate Rocks
Here are some frequently asked questions about conglomerate rocks to help you better understand their properties and applications:
10.1 What is Conglomerate Rock?
Conglomerate rock is a sedimentary rock composed of rounded gravel-sized clasts cemented together by a matrix of finer particles.
10.2 Where Can I Find Conglomerate Rocks?
Conglomerate rocks are found in areas with abundant water sources, such as riverbeds, shorelines, and glacial environments, across the globe.
10.3 How Are Conglomerate Rocks Formed?
Conglomerate rocks are formed through the erosion, transportation, deposition, and cementation of rounded clasts.
10.4 What Are the Main Uses of Conglomerate Rock?
The main uses include construction aggregate, cement manufacturing, dimension stones, and decorative material in landscaping.
10.5 How Durable Is Conglomerate Rock?
The durability depends on the strength of the cementing material and the resistance of the clasts to weathering.
10.6 What Colors Do Conglomerate Rocks Come In?
Common colors include beige, black, brown, gray, orange, rust, white, and yellow.
10.7 How Do I Choose the Right Conglomerate Supplier?
Consider the quality of stone, variety of options, reputation, pricing, and availability.
10.8 How Do I Install Conglomerate Rocks in My Landscape?
Ensure proper base preparation, appropriate spacing, and consider professional installation for complex projects.
10.9 How Do I Maintain Conglomerate Rocks?
Regularly clean, seal, and control weeds to maintain their appearance.
10.10 Can Conglomerate Rocks Be Used in Water Features?
Yes, conglomerates can be integrated into water features for a natural look.
Final Thoughts: Discover the Beauty of Conglomerate with Rockscapes.net
Conglomerate rocks offer a unique and versatile option for enhancing your landscape. From their diverse colors and textures to their practical applications, these geological treasures can transform your outdoor space into a stunning and durable environment. At rockscapes.net, we are dedicated to helping you find the perfect conglomerate rocks for your project.
Ready to explore the beauty and potential of conglomerate rocks? Visit rockscapes.net today to discover our extensive selection, get expert advice, and start creating the landscape of your dreams. Let us help you bring your vision to life with the timeless appeal of natural stone.
Address: 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States
Phone: +1 (480) 965-9011
Website: rockscapes.net
Don’t wait—transform your landscape with the enduring beauty of conglomerate rocks. Contact us now and let rockscapes.net be your trusted partner in creating exceptional outdoor spaces.