Are you fascinated by the Earth’s fiery origins and eager to discover the captivating world of igneous rocks? At rockscapes.net, we understand your passion and are here to guide you on an exciting journey to unearth these geological treasures! With the right knowledge and techniques, you can successfully identify and collect igneous rocks, adding unique specimens to your collection and enhancing your understanding of our planet’s dynamic history. Discover the best strategies for locating igneous rocks, learn how to identify different types and transform your backyard into a geological exploration zone.
1. What Are Igneous Rocks and Why Should You Find Them?
Yes, igneous rocks are rocks formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. These rocks hold immense geological significance and boast unique aesthetic qualities, making them highly sought after by rockhounds and landscape enthusiasts alike. According to research from Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, in July 2023, the study of igneous rocks provides crucial insights into Earth’s volcanic activity and the planet’s internal composition.
1.1. What is the Geological Significance of Igneous Rocks?
Igneous rocks serve as invaluable records of Earth’s thermal history and geological processes. Their formation is directly linked to volcanic activity, plate tectonics, and the cooling of magma, offering insights into the planet’s dynamic evolution. They also contain valuable mineral deposits and provide crucial information for understanding Earth’s mantle and crust.
1.2. What are the Unique Aesthetic Qualities of Igneous Rocks?
Igneous rocks exhibit a wide range of textures, colors, and mineral compositions, making them visually striking and highly desirable for decorative purposes. From the coarse-grained beauty of granite to the glassy elegance of obsidian, each type of igneous rock possesses its own distinct charm. Landscaping enthusiasts often incorporate these rocks into gardens, pathways, and water features to add a touch of natural elegance and geological intrigue.
1.3. Why are Igneous Rocks Important for Landscaping?
Igneous rocks offer a blend of durability, aesthetic appeal, and natural charm that makes them ideal for landscaping projects. They are used to create visually appealing and long-lasting outdoor spaces, from retaining walls and pathways to decorative rock gardens and water features.
2. Where Can You Find Igneous Rocks in the USA?
You can find igneous rocks in regions with a history of volcanic activity, such as the Western United States and areas along the East Coast. Identifying specific locations requires understanding regional geology and consulting geological maps. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), certain areas are particularly rich in igneous rock formations.
2.1. What are the Best Regions in the USA for Finding Igneous Rocks?
Regions with a history of volcanic activity are prime locations for finding igneous rocks:
- The Western United States: States like California, Oregon, Washington, Idaho, and Arizona are known for their volcanic landscapes.
- Hawaii: The Hawaiian Islands are entirely composed of volcanic rocks, offering numerous opportunities for discovery.
- The East Coast: Areas within the Appalachian region, such as Maryland’s Piedmont Plateau, also contain igneous formations.
2.2. How Can Geological Maps Help in Locating Igneous Rocks?
Geological maps provide detailed information about the types and distribution of rocks in a given area. These maps can help you identify regions with igneous rock formations and plan your rockhounding expeditions more effectively. The USGS offers a variety of geological maps and resources that can be invaluable for rock enthusiasts.
2.3. Are There Any Specific Igneous Rock Hotspots in the USA?
Yes, several locations are renowned for their abundance and variety of igneous rocks:
- Crater Lake National Park, Oregon: Known for its stunning volcanic caldera and diverse array of volcanic rocks.
- Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming: Features extensive geothermal activity and a wide range of volcanic formations.
- Devil’s Tower National Monument, Wyoming: Showcases a unique igneous intrusion that stands as a prominent geological landmark.
- Columbia River Basalt Group: This area covers parts of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho and is known for its extensive basalt flows.
3. What Tools and Equipment Do You Need for Igneous Rock Hunting?
To effectively and safely hunt for igneous rocks, you’ll need a few essential tools and equipment: a rock hammer, safety glasses, a geological pick, a magnifying glass, and a field notebook. High-quality tools enhance your chances of finding and identifying valuable specimens while ensuring your safety in the field.
3.1. What are the Essential Tools for Rockhounding?
- Rock Hammer: Used for breaking rocks and extracting specimens.
- Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from flying debris.
- Geological Pick: Helps in digging and prying rocks from the ground.
- Magnifying Glass: Aids in examining mineral compositions and textures.
- Field Notebook: For recording observations, locations, and descriptions of your finds.
- Gloves: Protect your hands from sharp edges and rough surfaces.
3.2. How Does Safety Gear Protect You During Rock Hunting?
Safety gear is crucial for minimizing risks associated with rockhounding. Safety glasses prevent eye injuries from flying rock fragments, while gloves protect your hands from cuts and abrasions. Sturdy footwear provides stability and prevents slips and falls on uneven terrain.
3.3. Why is a Field Notebook Important for Documenting Your Finds?
A field notebook serves as a comprehensive record of your rockhounding expeditions. It allows you to document the location, date, and specific characteristics of each find, which is essential for future reference and research. Detailed notes can also help you identify patterns in rock distribution and improve your understanding of the local geology.
4. How to Identify Different Types of Igneous Rocks?
You can identify different types of igneous rocks by examining their texture, color, and mineral composition. Understanding the basics of igneous rock classification is essential for accurate identification. According to “Igneous Rocks: A Classification and Glossary of Terms” by R.W. Le Maitre, distinguishing between intrusive and extrusive rocks is the first step in the identification process.
4.1. What are the Key Characteristics Used to Identify Igneous Rocks?
- Texture: Refers to the size, shape, and arrangement of mineral grains in the rock.
- Color: Indicates the overall chemical composition and mineral content.
- Mineral Composition: Identifies the specific minerals present, which can vary depending on the rock’s origin.
4.2. How Do Intrusive and Extrusive Rocks Differ?
- Intrusive Rocks: Form when magma cools slowly beneath the Earth’s surface, resulting in large, visible crystals. Examples include granite and diorite.
- Extrusive Rocks: Form when lava cools quickly on the Earth’s surface, resulting in small or no visible crystals. Examples include basalt and obsidian.
4.3. Can You Provide Examples of Common Igneous Rocks and Their Identifying Features?
| Igneous Rock | Texture | Color | Mineral Composition | Identifying Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Granite | Coarse-grained | Light-colored | Quartz, feldspar, mica | Large, visible crystals; often used for countertops and monuments. |
| Basalt | Fine-grained | Dark-colored | Plagioclase feldspar, pyroxene | Small or no visible crystals; commonly found in lava flows. |
| Obsidian | Glassy | Black or dark | Primarily silica | Smooth, glassy texture; forms when lava cools rapidly. |
| Pumice | Vesicular | Light-colored | Highly porous, various minerals | Lightweight and full of gas bubbles; often used in exfoliating products. |
| Diorite | Coarse-grained | Medium-colored | Plagioclase feldspar, hornblende, pyroxene | Similar to granite but with less quartz; often used for construction. |
| Rhyolite | Fine-grained | Light-colored | Quartz, feldspar, mica | Similar to granite in composition but with smaller crystals; often found in volcanic domes and flows. |
| Andesite | Fine-grained | Medium-colored | Plagioclase feldspar, pyroxene, hornblende | Intermediate composition between basalt and rhyolite; often found in volcanic arcs. |
| Gabbro | Coarse-grained | Dark-colored | Plagioclase feldspar, pyroxene, olivine | Dark-colored equivalent of diorite; often found in oceanic crust. |
| Peridotite | Coarse-grained | Greenish | Olivine, pyroxene | Rich in magnesium and iron; often found in Earth’s mantle. |
| Tuff | Fragmental | Variable | Volcanic ash, rock fragments | Formed from consolidated volcanic ash and debris; can contain a variety of rock fragments and minerals. |
| Pegmatite | Very Coarse-grained | Variable | Variable, often containing large crystals of quartz, feldspar, mica, and rare minerals | Characterized by extremely large crystals, sometimes several feet in length; forms during the late stages of magma cooling. |
5. What are the Best Practices for Responsible Rock Collecting?
Responsible rock collecting involves respecting private property, obtaining necessary permits, and minimizing environmental impact. Following ethical guidelines ensures that rockhounding remains a sustainable and enjoyable activity for everyone. The Geological Society of America emphasizes the importance of preserving geological resources for future generations.
5.1. How Can You Respect Private Property and Obtain Necessary Permits?
- Private Property: Always obtain permission from landowners before collecting rocks on their property.
- Public Lands: Research and adhere to the regulations of the managing agency, such as the National Park Service or Bureau of Land Management.
- Permits: Obtain any required permits for collecting rocks in specific areas.
5.2. What Steps Can You Take to Minimize Environmental Impact?
- Leave No Trace: Pack out everything you pack in and avoid disturbing vegetation and wildlife.
- Collect Sparingly: Take only what you need and avoid over-collecting in any one area.
- Stay on Trails: Minimize soil erosion by staying on established trails.
5.3. What are the Ethical Considerations for Rock Collecting?
- Preserve Geological Resources: Avoid collecting rare or scientifically significant specimens.
- Educate Others: Share your knowledge and promote responsible rock collecting practices among fellow enthusiasts.
- Support Conservation Efforts: Contribute to organizations that work to protect geological sites and resources.
6. How Can You Incorporate Igneous Rocks into Landscaping?
Igneous rocks can be used to create stunning landscape features, such as rock gardens, pathways, and water features. Their durability and aesthetic appeal make them ideal for adding natural beauty and geological interest to outdoor spaces. Rockscapes.net offers a variety of igneous rocks for landscaping projects, providing both aesthetic and functional benefits.
6.1. What are Some Creative Ways to Use Igneous Rocks in Your Garden?
- Rock Gardens: Create a visually appealing display of various igneous rocks, complemented by drought-resistant plants.
- Pathways: Use flat igneous rocks to create natural-looking pathways through your garden.
- Water Features: Incorporate igneous rocks into waterfalls, ponds, and streams to add a touch of geological charm.
6.2. How Do Igneous Rocks Enhance the Aesthetic Appeal of Outdoor Spaces?
Igneous rocks offer a range of colors, textures, and shapes that can enhance the visual appeal of any outdoor space. Their natural beauty complements plants, water features, and other landscaping elements, creating a harmonious and inviting environment.
6.3. What are the Functional Benefits of Using Igneous Rocks in Landscaping?
- Durability: Igneous rocks are highly resistant to weathering and erosion, making them ideal for long-lasting landscape features.
- Drainage: Rocks can improve soil drainage and prevent waterlogging in certain areas of your garden.
- Erosion Control: Larger rocks can be used to stabilize slopes and prevent soil erosion.
 Granite rock landscaping
Granite rock landscaping
7. Where Can You Learn More About Igneous Rocks and Geology?
There are numerous resources available for expanding your knowledge of igneous rocks and geology, including books, online courses, and local geological societies. Engaging with these resources can deepen your understanding and enhance your rockhounding skills. Universities with strong geology programs, such as Arizona State University, often provide valuable research and educational materials.
7.1. What are Some Recommended Books and Websites for Learning About Igneous Rocks?
- “Igneous Rocks: A Classification and Glossary of Terms” by R.W. Le Maitre: A comprehensive guide to igneous rock classification.
- “Volcanoes” by Peter Francis: An informative book about volcanic processes and the formation of igneous rocks.
- United States Geological Survey (USGS): Offers a wealth of information on geology, including maps, articles, and educational resources.
- Geological Society of America (GSA): Provides access to research publications, conferences, and educational materials.
- Minerals Education Coalition: A valuable source of information about minerals and their properties.
7.2. How Can Local Geological Societies Enhance Your Knowledge?
Local geological societies offer opportunities to connect with fellow enthusiasts, participate in field trips, and attend lectures and workshops. These societies can provide valuable insights into the geology of your region and enhance your rockhounding skills.
7.3. Are There Any Online Courses or Educational Programs Focused on Geology?
- Coursera: Offers a variety of online courses on geology and earth sciences from top universities around the world.
- edX: Provides access to courses on geology and related topics, taught by experts in the field.
- Khan Academy: Offers free educational resources on geology, including videos and interactive exercises.
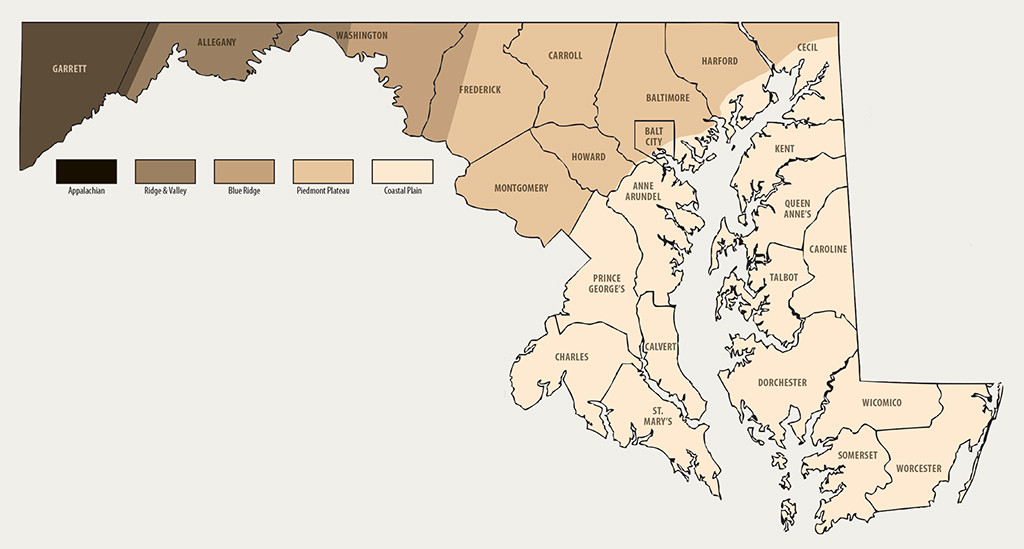
8. How Does Maryland’s Geology Influence Igneous Rock Finds?
Maryland’s diverse geology, divided into five physiographic provinces, offers unique opportunities for finding igneous rocks, particularly in the Piedmont Plateau. Understanding the state’s geological history and rock formations is crucial for successful rockhounding. According to the Maryland Geological Survey, the Piedmont Plateau contains some of the state’s oldest igneous rocks, dating back between 500 million and 1.1 billion years.
8.1. What are the Key Geological Provinces in Maryland and Their Significance?
- Coastal Plain Province: Consists of young sediments and is less likely to contain significant igneous rock formations.
- Piedmont Plateau Province: Contains ancient igneous and metamorphic rocks, offering the best opportunities for finding igneous specimens.
- Blue Ridge Province: Features volcanic and sedimentary rocks overlying granite-gneiss formations.
- Ridge and Valley Province: Primarily composed of sedimentary rocks, with limited igneous formations.
- Appalachian Plateaus Province: Similar to the Ridge and Valley, with mostly sedimentary rocks.
8.2. Where are the Best Locations in Maryland to Find Igneous Rocks?
The Piedmont Plateau is the most promising region for finding igneous rocks in Maryland. Specific locations include:
- Baltimore County: Known for its Baltimore Gneiss, an ancient metamorphic rock with igneous origins.
- Montgomery County: Features igneous pegmatite rocks that may contain rare minerals.
- Harford County: Contains various igneous and metamorphic formations.
8.3. What Types of Igneous Rocks Can Be Found in Maryland?
- Gneiss: A metamorphic rock with igneous origins, characterized by its banded appearance.
- Pegmatite: A coarse-grained igneous rock that may contain valuable minerals.
- Granite: An intrusive igneous rock found in certain areas of the Piedmont Plateau.
9. How Can You Turn Your Rockhounding Hobby into a Business?
If you have a passion for rockhounding and a keen eye for unique specimens, you can turn your hobby into a business by selling your finds online or at local markets. Building a brand, understanding market trends, and complying with legal regulations are essential steps for success. Rockscapes.net serves as an excellent platform for inspiration and learning about the business side of rock collecting and landscaping.
9.1. What are the Steps to Start a Rock and Mineral Business?
- Develop a Business Plan: Outline your goals, target market, and financial projections.
- Source Inventory: Collect rocks and minerals ethically and sustainably.
- Create a Brand: Develop a unique identity and marketing strategy.
- Set Up an Online Store: Use platforms like Etsy or Shopify to sell your products online.
- Comply with Legal Regulations: Obtain any necessary permits and licenses.
9.2. How Can You Market Your Rock and Mineral Products Effectively?
- Use Social Media: Promote your products on platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Pinterest.
- Attend Local Markets: Participate in craft fairs and gem and mineral shows.
- Network with Other Enthusiasts: Connect with fellow rockhounds and industry professionals.
- Create High-Quality Photos: Showcase the beauty and uniqueness of your products.
- SEO Optimization: Ensure your website or online store is easily discoverable through search engines.
9.3. What are the Legal and Ethical Considerations for Selling Rocks and Minerals?
- Obtain Necessary Permits: Ensure you have the required permits for collecting and selling rocks and minerals.
- Disclose Information: Provide accurate information about the origin and properties of your products.
- Practice Sustainable Collecting: Avoid over-collecting and minimize environmental impact.
- Respect Private Property: Obtain permission before collecting on private land.
10. What are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid When Searching for Igneous Rocks?
Avoiding common mistakes, such as neglecting safety precautions and misidentifying rocks, can enhance your rockhounding experience. Learning from the errors of others and following expert advice can lead to more successful and enjoyable expeditions. Experts at rockscapes.net emphasize the importance of thorough research and careful planning to avoid these pitfalls.
10.1. What are the Most Common Safety Mistakes Made by Rockhounds?
- Neglecting Eye Protection: Failing to wear safety glasses can lead to eye injuries from flying rock fragments.
- Ignoring Weather Conditions: Rockhounding during severe weather can be dangerous.
- Trespassing on Private Property: Always obtain permission before entering private land.
- Not Informing Others: Always let someone know your rockhounding plans.
10.2. How Can You Avoid Misidentifying Igneous Rocks?
- Study Rock Identification Guides: Familiarize yourself with the key characteristics of different igneous rocks.
- Use a Magnifying Glass: Examine the texture and mineral composition closely.
- Compare Your Finds: Compare your specimens to known examples and consult with experienced rockhounds.
- Take Detailed Notes: Record the location, date, and characteristics of each find.
- Consult with Experts: Reach out to geologists or rock and mineral experts for identification assistance.
10.3. Why is it Important to Plan Your Rockhounding Trips Carefully?
- Research Locations: Identify promising areas with a history of igneous rock formations.
- Check Regulations: Ensure you have any required permits and adhere to local rules.
- Prepare for the Terrain: Wear appropriate clothing and footwear for the environment.
- Bring Necessary Supplies: Pack essential tools, safety gear, and navigation equipment.
- Consider Weather Conditions: Check the forecast and plan accordingly to avoid hazardous weather.
Ready to embark on your igneous rock hunting adventure? Explore rockscapes.net for more inspiration, detailed information on various rock types, and expert tips to make your search successful. Discover the beauty and wonder of igneous rocks and transform your landscape into a geological masterpiece! Contact us at Address: 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States or call us at Phone: +1 (480) 965-9011. Visit our Website: rockscapes.net to learn more.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What exactly are igneous rocks?
Igneous rocks are rocks formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. They are one of the three main types of rocks, along with sedimentary and metamorphic rocks, and provide valuable insights into Earth’s geological history.
2. Where is the best place to find igneous rocks?
Regions with a history of volcanic activity are prime locations for finding igneous rocks. In the USA, the Western United States, Hawaii, and areas along the East Coast are known for their volcanic landscapes.
3. What tools do I need for rockhounding?
Essential tools for rockhounding include a rock hammer, safety glasses, a geological pick, a magnifying glass, and a field notebook. These tools help you safely and effectively collect and identify rock specimens.
4. How can I identify different types of igneous rocks?
You can identify different types of igneous rocks by examining their texture, color, and mineral composition. Understanding the basics of igneous rock classification is essential for accurate identification.
5. Is it legal to collect rocks on public lands?
Regulations regarding rock collecting on public lands vary depending on the managing agency. It’s important to research and adhere to the rules of the specific area you plan to visit.
6. How can I use igneous rocks in my landscaping?
Igneous rocks can be used to create stunning landscape features, such as rock gardens, pathways, and water features. Their durability and aesthetic appeal make them ideal for adding natural beauty and geological interest to outdoor spaces.
7. What is the difference between intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks?
Intrusive rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the Earth’s surface, resulting in large, visible crystals. Extrusive rocks form when lava cools quickly on the Earth’s surface, resulting in small or no visible crystals.
8. How can I minimize my environmental impact while rockhounding?
To minimize environmental impact, practice responsible rock collecting by leaving no trace, collecting sparingly, and staying on established trails.
9. What are some common mistakes to avoid when searching for igneous rocks?
Common mistakes to avoid include neglecting safety precautions, misidentifying rocks, and trespassing on private property. Careful planning and thorough research can help you avoid these pitfalls.
10. Where can I learn more about igneous rocks and geology?
There are numerous resources available for expanding your knowledge of igneous rocks and geology, including books, online courses, and local geological societies. Engaging with these resources can deepen your understanding and enhance your rockhounding skills.
