Sedimentary rock drawing involves capturing the unique textures and layered formations of these rocks, and understanding their aesthetic appeal is crucial for landscape design. At rockscapes.net, we will guide you through the process, providing you with the inspiration and knowledge you need to create stunning rock arrangements. Discover the secrets of sedimentary rock drawing and transform your outdoor spaces into breathtaking stone gardens. Learn about rock formations, geological history, and landscape architecture.
1. What is Sedimentary Rock and Why is it Important for Landscaping?
Sedimentary rock is formed through the accumulation and cementation of sediments, such as mineral or organic particles, on Earth’s surface, contributing to diverse geological formations. It’s important for landscaping because it adds natural beauty, stability, and unique textures to outdoor spaces. Sedimentary rocks are visually appealing because of their layered appearance and varied colors, which can enhance any landscape design.
1.1 How Does Sedimentary Rock Form?
Sedimentary rocks form through a fascinating process that begins with the weathering and erosion of existing rocks. According to research from Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration in July 2025, the creation of these rocks involves several key stages:
- Weathering and Erosion: Existing rocks are broken down into smaller pieces by wind, water, and ice.
- Transportation: These sediments are then transported by rivers, wind, and glaciers to new locations.
- Deposition: Sediments accumulate in layers, often in bodies of water.
- Compaction: Over time, the weight of upper layers compresses the lower layers.
- Cementation: Dissolved minerals precipitate out of water and bind the sediment particles together.
1.2 What are the Key Characteristics of Sedimentary Rocks?
Sedimentary rocks have several key characteristics:
- Layering (Stratification): Sedimentary rocks often exhibit distinct layers, providing visual interest and a sense of geological history.
- Fossils: Many sedimentary rocks contain fossils, offering a glimpse into past life forms.
- Varied Colors: The presence of different minerals results in a wide range of colors, from earthy browns and reds to vibrant yellows and greens.
- Textures: Sedimentary rocks can have fine-grained or coarse-grained textures, depending on the size of the sediment particles.
1.3 Why Choose Sedimentary Rock for Landscaping in the USA?
Choosing sedimentary rock for landscaping in the USA offers numerous benefits:
- Natural Appeal: Sedimentary rocks blend seamlessly with the environment, creating a natural and harmonious look.
- Durability: Many sedimentary rocks are durable and weather-resistant, making them ideal for outdoor use.
- Variety: The wide range of colors, textures, and shapes available in sedimentary rocks allows for creative and customized landscape designs.
- Erosion Control: Large sedimentary rocks can be used to stabilize slopes and prevent erosion.
- Water Management: Certain sedimentary rocks can improve drainage and reduce water runoff.
2. What are the Different Types of Sedimentary Rocks for Drawing and Landscaping?
There are many different types of sedimentary rocks, each with unique characteristics that make them suitable for various landscaping applications. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right materials for your project.
2.1 Clastic Sedimentary Rocks
Clastic sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation of broken pieces of other rocks and minerals.
| Rock Type | Description | Landscape Use |
|---|---|---|
| Sandstone | Composed of sand-sized grains, often quartz. Colors range from light tan to reddish-brown. | Paving stones, retaining walls, decorative boulders, garden pathways. |
| Shale | Made of fine-grained clay minerals. Typically gray, black, or reddish-brown. | Ground cover, erosion control, in areas where its fine texture and dark color can provide a contrast to other landscape elements. |
| Conglomerate | Consists of rounded gravel-sized rock fragments cemented together. Can have a variety of colors. | Decorative accents, water features, used to create a natural stream or pond bed due to its rounded and varied stone sizes. |
| Breccia | Similar to conglomerate but contains angular rock fragments. Often found in shades of gray and brown. | Used to highlight garden edges, add texture to rock gardens, or create small retaining walls due to its angular shapes. |
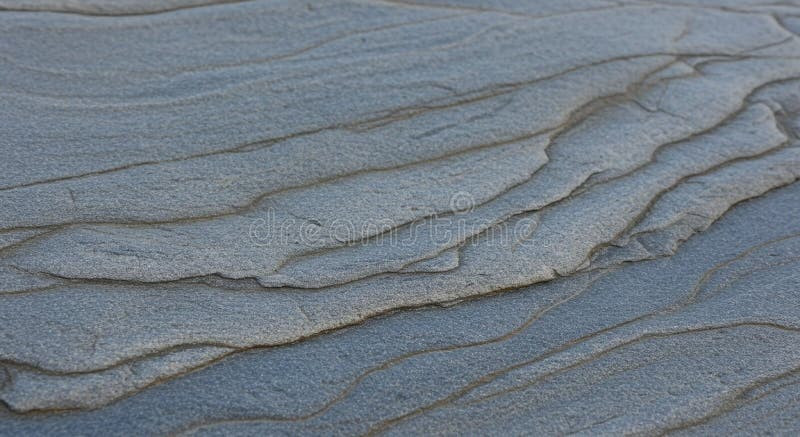 Sandstone rock surface showcasing sedimentary layers and grains
Sandstone rock surface showcasing sedimentary layers and grains
2.2 Chemical Sedimentary Rocks
Chemical sedimentary rocks form from the precipitation of minerals from water.
| Rock Type | Description | Landscape Use |
|---|---|---|
| Limestone | Composed primarily of calcium carbonate. Usually white or light gray. | Retaining walls, garden borders, decorative stones, can also be crushed for pathways and driveways. |
| Rock Salt | Made of sodium chloride. Typically clear or white. | Rarely used in landscaping due to its solubility, but can be used in controlled environments for specific artistic installations. |
| Chert | Composed of microcrystalline quartz. Can be various colors, including white, gray, and brown. | Rock gardens, edging, small decorative features. |
| Travertine | A form of limestone deposited by mineral springs. Often has a banded or layered appearance. | Paving stones, wall cladding, water features, known for its porous texture and ability to add a classic, elegant look. |
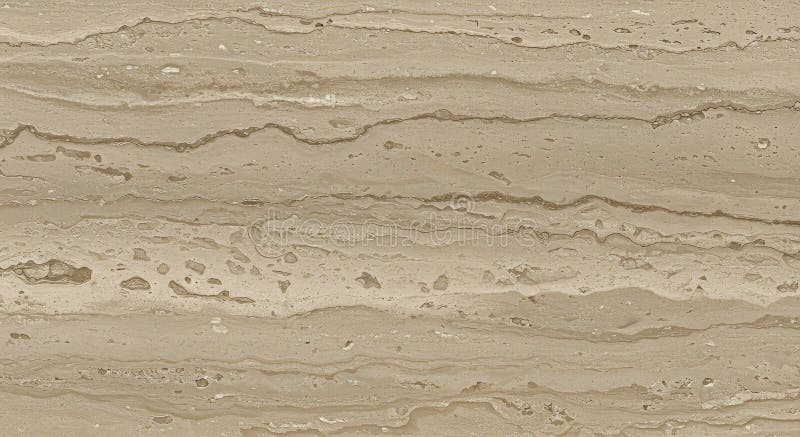 Limestone rock texture with fossil imprints and natural striations
Limestone rock texture with fossil imprints and natural striations
2.3 Organic Sedimentary Rocks
Organic sedimentary rocks form from the accumulation of organic matter.
| Rock Type | Description | Landscape Use |
|---|---|---|
| Coal | Formed from compressed plant matter. Black or dark brown. | While not typically used for decorative purposes, coal can be incorporated into soil mixtures to improve drainage and aeration. |
| Coquina | A limestone composed of cemented shells and coral fragments. Usually light in color. | Retaining walls, decorative features, and garden paths, adding a coastal or tropical theme with its distinctive shell-filled texture. |
| Diatomite | Composed of fossilized diatoms (microscopic algae). White or light gray. | Used as a soil amendment to improve drainage and aeration, as well as a natural insecticide. |
| Oil Shale | Contains organic matter that can be converted into oil. Typically dark brown or black. | Not commonly used in landscaping due to its potential environmental impact and odor when exposed to the elements. |
2.4 Unique Sedimentary Rock Formations in the USA
The USA is home to several unique sedimentary rock formations:
- The Wave, Arizona: Known for its undulating, colorful sandstone layers.
- Grand Canyon, Arizona: Displays layers of sedimentary rock spanning millions of years.
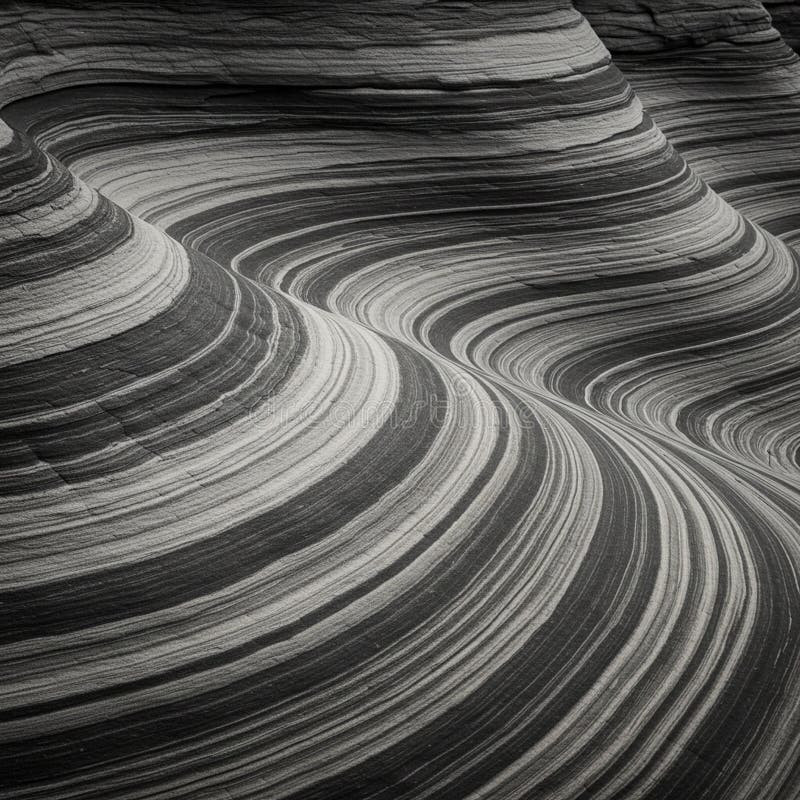 Undulating rock formations create rhythmic, flowing patterns resembling waves
Undulating rock formations create rhythmic, flowing patterns resembling waves
- Zion National Park, Utah: Features towering sandstone cliffs and narrow canyons.
- Bryce Canyon, Utah: Famous for its unique hoodoos, formed by erosion of sedimentary rock.
3. How Do You Draw Sedimentary Rock?
Drawing sedimentary rocks involves capturing their unique textures, layers, and colors. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you create realistic and captivating rock drawings.
3.1 Gathering Your Materials
Before you start drawing, gather the necessary materials:
- Pencils: A range of graphite pencils (HB, 2B, 4B, 6B) for different shades and values.
- Eraser: A kneaded eraser for lifting graphite and a regular eraser for corrections.
- Drawing Paper: Textured drawing paper to capture the roughness of the rock surface.
- Reference Images: Photographs of sedimentary rocks to guide your drawing.
- Blending Stumps: For smoothing out graphite and creating subtle tonal variations.
3.2 Understanding Sedimentary Rock Structure
Understanding the structure of sedimentary rocks is crucial for creating realistic drawings.
- Layers: Sedimentary rocks are characterized by distinct layers or strata.
- Textures: The surface of sedimentary rocks can be rough, smooth, or porous, depending on the type of rock and the effects of weathering.
- Colors: Sedimentary rocks come in a wide range of colors, influenced by the minerals present.
3.3 Step-by-Step Drawing Guide
Follow these steps to draw sedimentary rocks:
- Sketch the Outline: Begin by sketching the basic shape of the rock. Pay attention to the overall form and proportions.
- Define the Layers: Draw the layers or strata of the rock. Vary the thickness and direction of the lines to create a natural look.
- Add Texture: Use different pencil grades to add texture to the rock surface. Use short, broken lines for rough areas and smooth, blended tones for smoother surfaces.
- Create Shadows and Highlights: Add shadows to one side of the rock to create depth and dimension. Use highlights to emphasize the texture and form.
- Incorporate Details: Add details such as cracks, crevices, and small rock fragments to enhance realism.
- Blend and Refine: Use blending stumps to smooth out the graphite and create subtle tonal variations. Refine the drawing by adding more details and adjusting the values.
3.4 Tips for Capturing Realistic Textures and Patterns
Here are some tips for capturing realistic textures and patterns in your sedimentary rock drawings:
- Observe Carefully: Study your reference images closely to understand the textures and patterns of sedimentary rocks.
- Vary Your Strokes: Use a variety of pencil strokes to create different textures. Experiment with short, broken lines, smooth, blended tones, and stippling techniques.
- Use Light and Shadow: Pay attention to the way light and shadow interact with the rock surface. Use shadows to create depth and dimension, and highlights to emphasize texture and form.
- Incorporate Imperfections: Add imperfections such as cracks, crevices, and small rock fragments to enhance realism.
- Experiment with Techniques: Try different drawing techniques, such as dry brushing, scumbling, and cross-hatching, to create unique textures and patterns.
4. How to Incorporate Sedimentary Rock into Your Landscaping Design
Incorporating sedimentary rock into your landscaping design can add natural beauty, stability, and unique textures to your outdoor spaces.
4.1 Planning Your Landscape Design
Before you start, plan your landscape design:
- Assess Your Space: Evaluate the size, shape, and terrain of your yard. Consider the existing vegetation, soil type, and drainage.
- Determine Your Style: Choose a landscaping style that complements your home and personal taste. Consider styles such as naturalistic, rustic, or modern.
- Create a Layout: Sketch a layout of your yard, indicating the location of plants, rocks, and other features.
- Select Your Rocks: Choose sedimentary rocks that complement your landscape design. Consider factors such as color, texture, size, and shape.
4.2 Applications of Sedimentary Rock in Landscaping
Here are some popular ways to incorporate sedimentary rock into your landscape design:
- Rock Gardens: Create a rock garden featuring a variety of sedimentary rocks and drought-tolerant plants.
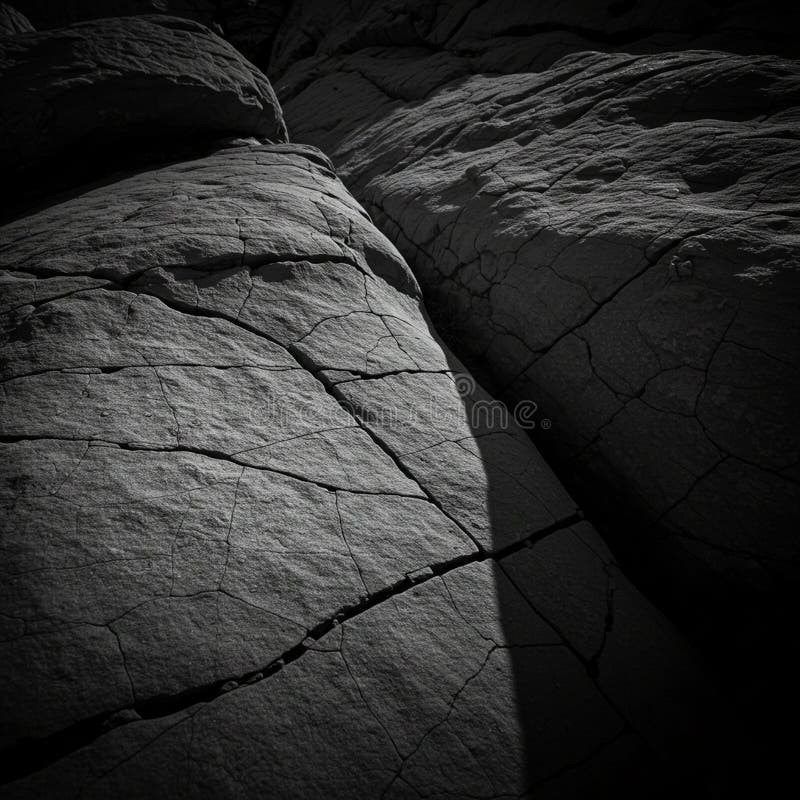 Rugged rock surface with visible cracks and crevices, likely sedimentary or metamorphic in nature
Rugged rock surface with visible cracks and crevices, likely sedimentary or metamorphic in nature
- Retaining Walls: Build a retaining wall using sedimentary rocks to create terraced gardens or stabilize slopes.
- Pathways: Use sedimentary rocks to create natural-looking pathways through your garden.
- Water Features: Incorporate sedimentary rocks into water features such as ponds, waterfalls, and streams.
- Decorative Boulders: Place large sedimentary boulders as focal points in your landscape design.
4.3 Practical Tips for Rock Placement and Arrangement
Follow these practical tips for rock placement and arrangement:
- Consider Scale: Choose rocks that are appropriately sized for your yard. Use larger rocks as focal points and smaller rocks as accents.
- Create Balance: Arrange rocks in a way that creates visual balance. Avoid placing too many rocks on one side of the yard.
- Mimic Nature: Observe natural rock formations and try to replicate them in your landscape design.
- Vary Textures and Colors: Use a variety of textures and colors to add visual interest.
- Secure Rocks: Ensure that rocks are securely placed and won’t shift or topple over time.
4.4 Choosing the Right Plants to Complement Sedimentary Rock
Choosing the right plants to complement sedimentary rock can enhance the beauty and harmony of your landscape design:
- Drought-Tolerant Plants: Select plants that thrive in dry conditions, such as succulents, cacti, and native grasses.
- Alpine Plants: Consider alpine plants, which are adapted to rocky environments, such as sedums, sempervivums, and dwarf conifers.
- Ground Cover: Use ground cover plants to soften the edges of rock formations and add a touch of greenery.
- Colorful Flowers: Incorporate colorful flowers to add visual interest and contrast to the rocks.
5. Where to Find Quality Sedimentary Rocks in the USA
Finding quality sedimentary rocks is essential for creating a beautiful and durable landscape. Here are some resources to help you locate the right materials for your project.
5.1 Local Quarries and Stone Yards
Local quarries and stone yards are excellent sources for sedimentary rocks. They offer a wide selection of rocks in various sizes, colors, and textures.
- Benefits:
- Wide selection of rocks
- Competitive prices
- Opportunity to inspect rocks in person
- Local expertise and advice
- How to Find:
- Search online for “stone yards near me” or “rock quarries near me”.
- Ask for recommendations from local landscapers or garden centers.
- Check online directories for stone suppliers in your area.
5.2 Online Retailers and Suppliers
Several online retailers and suppliers specialize in sedimentary rocks. They offer a convenient way to browse and purchase rocks from the comfort of your home.
- Benefits:
- Convenient shopping experience
- Wide selection of rocks from different regions
- Detailed product descriptions and images
- Customer reviews and ratings
- Things to Consider:
- Shipping costs
- Return policies
- Rock sizes and weights
- Reliability of the supplier
5.3 Tips for Selecting the Best Rocks for Your Project
Here are some tips for selecting the best sedimentary rocks for your landscaping project:
- Consider Your Design: Choose rocks that complement your overall landscape design.
- Check for Durability: Ensure that the rocks are durable and weather-resistant.
- Inspect for Flaws: Look for cracks, chips, or other flaws that could compromise the integrity of the rocks.
- Compare Prices: Compare prices from different suppliers to get the best deal.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask the supplier questions about the origin, composition, and properties of the rocks.
6. What are the Maintenance and Care Tips for Sedimentary Rock Landscapes?
Proper maintenance and care are essential for preserving the beauty and longevity of your sedimentary rock landscape.
6.1 Cleaning and Protecting Your Rocks
Here are some tips for cleaning and protecting your rocks:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean your rocks regularly to remove dirt, debris, and stains. Use a brush and water or a mild detergent solution.
- Pressure Washing: For tougher stains, consider using a pressure washer. Be careful not to damage the rocks with excessive pressure.
- Sealing: Apply a sealant to protect your rocks from weathering, staining, and fading.
- Weed Control: Keep your rock landscape free of weeds. Use herbicides or hand-pull weeds regularly.
6.2 Preventing Erosion and Damage
Preventing erosion and damage is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your rock landscape:
- Stabilize Slopes: Use large rocks or retaining walls to stabilize slopes and prevent erosion.
- Improve Drainage: Ensure that your landscape has adequate drainage to prevent water from pooling and eroding the soil.
- Protect from Traffic: Avoid placing rocks in areas where they are likely to be damaged by foot traffic or vehicles.
- Repair Damage: Repair any cracks, chips, or other damage to your rocks promptly.
6.3 Long-Term Care and Sustainability
Follow these tips for long-term care and sustainability:
- Monitor Your Landscape: Regularly monitor your landscape for signs of erosion, damage, or weed growth.
- Adjust Your Design: Adjust your landscape design as needed to accommodate changes in the environment.
- Use Sustainable Practices: Use sustainable landscaping practices, such as water conservation and organic gardening, to minimize your environmental impact.
- Consider Native Plants: Incorporate native plants into your landscape design to reduce water and maintenance requirements.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Drawing and Landscaping with Sedimentary Rocks
Here are some frequently asked questions about drawing and landscaping with sedimentary rocks.
7.1 What are the best pencils for drawing sedimentary rocks?
The best pencils for drawing sedimentary rocks are a range of graphite pencils (HB, 2B, 4B, 6B) for different shades and values.
7.2 How do I create realistic textures in my rock drawings?
To create realistic textures, vary your pencil strokes, use light and shadow, incorporate imperfections, and experiment with different drawing techniques.
7.3 What types of sedimentary rocks are best for retaining walls?
Sandstone and limestone are excellent choices for retaining walls due to their durability and aesthetic appeal.
7.4 How do I choose the right plants for my rock garden?
Choose drought-tolerant plants, alpine plants, ground cover, and colorful flowers that complement the rocks and your landscape design.
7.5 Where can I find quality sedimentary rocks in my area?
You can find quality sedimentary rocks at local quarries, stone yards, and online retailers and suppliers.
7.6 How do I clean sedimentary rocks in my landscape?
Clean sedimentary rocks with a brush and water or a mild detergent solution. For tougher stains, consider using a pressure washer.
7.7 What can I do to prevent erosion in my rock landscape?
To prevent erosion, stabilize slopes with large rocks or retaining walls and ensure that your landscape has adequate drainage.
7.8 How often should I seal my sedimentary rocks?
Seal your sedimentary rocks every 1-2 years, or as needed, to protect them from weathering, staining, and fading.
7.9 Can I use sedimentary rocks in a water feature?
Yes, sedimentary rocks can be incorporated into water features such as ponds, waterfalls, and streams.
7.10 What are some sustainable landscaping practices for rock gardens?
Sustainable practices include water conservation, organic gardening, using native plants, and minimizing your environmental impact.
8. Conclusion: Embracing the Beauty of Sedimentary Rock in Your Drawings and Landscapes
Sedimentary rock drawing and landscaping offer endless opportunities for creativity and self-expression. By understanding the formation, characteristics, and applications of sedimentary rocks, you can create stunning drawings and outdoor spaces that celebrate the beauty of nature. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to enhance your yard or a professional designer seeking inspiration, sedimentary rocks provide a unique and versatile medium for artistic and landscape design.
Ready to transform your outdoor space with the timeless beauty of sedimentary rock? Visit rockscapes.net today to explore our extensive collection of rocks, discover inspiring design ideas, and receive expert advice from our team of professionals. Let us help you create a landscape that reflects your personal style and enhances the value of your home. Contact us at 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States, call +1 (480) 965-9011, or visit rockscapes.net for more information.