Rock snot, or Didymosphenia geminata, might sound like something you’d find in a child’s nose, but it’s actually a freshwater diatom that can create nuisance blooms. At rockscapes.net, we’re dedicated to helping you understand and manage the challenges that nature presents, so you can create beautiful and sustainable landscapes. Let’s dive into understanding this algae, its impact, and how to mitigate its spread. Rock snot is relevant to environmental stewardship and landscape preservation.
1. What Exactly Is Rock Snot (Didymo)?
Rock snot, scientifically known as Didymosphenia geminata, is a type of freshwater diatom or single-celled alga that can form extensive blooms in rivers and streams. Unlike other algae, didymo creates a thick, cotton-like or woolly mat that attaches to rocks and substrates in the water. Its appearance can be quite unappealing, resembling clumps of tissue paper or, as the name suggests, snot. These blooms can be a nuisance, impacting aquatic ecosystems and recreational activities. According to research from Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, didymo thrives in cold, nutrient-poor waters, often outcompeting other algae species.
1.1 What Does Rock Snot Look Like?
Rock snot appears as slimy, white or grayish-brown mats clinging to rocks and streambeds. The texture is often described as woolly or cotton-like, and it can feel slippery to the touch.
1.2 Why Is It Called Rock Snot?
The unflattering name “rock snot” comes from its unpleasant appearance and slimy texture. When didymo blooms proliferate, they form thick mats that look like clumps of nasal mucus clinging to rocks in rivers and streams. The name may be unappealing, but it’s certainly memorable and helps people quickly understand what this invasive alga looks like.
2. Where Is Rock Snot Found?
Historically, didymo was primarily found in the cool, running freshwaters of the northern hemisphere, including North America, Europe, and Asia. However, in recent decades, it has spread to other parts of the world, including New Zealand and South America. The map below shows the density of Rock Snot distribution:
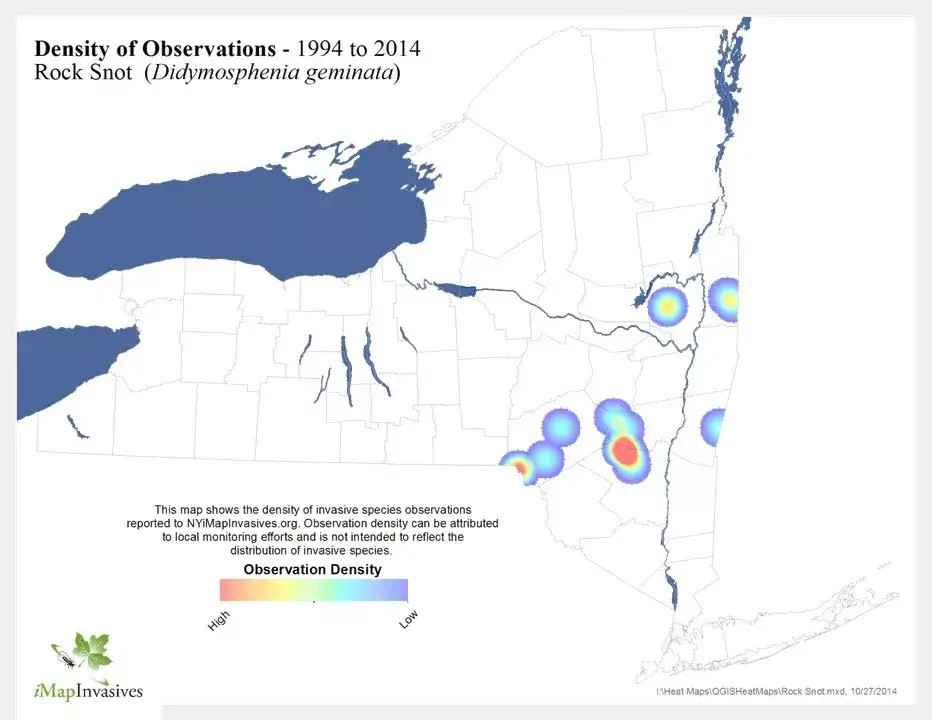 Map showing the density of where Rock Snot has been found
Map showing the density of where Rock Snot has been found
2.1 How Has Rock Snot Spread Globally?
The spread of didymo across the globe is largely attributed to human activities. The microscopic diatoms can easily attach to fishing gear, waders, boats, and other equipment. Because they can survive for extended periods outside of water, even in damp conditions, they are easily transported from one waterway to another. This makes recreational activities like fishing and boating potential vectors for the spread of didymo.
2.2 Where Is Rock Snot Found in the United States?
In the United States, didymo has been reported in numerous states, particularly in the Northeast, the Pacific Northwest, and the Rocky Mountain region. States like Montana, Colorado, New York, and Vermont have all experienced didymo blooms. The diatom can be found in rivers, streams, and even some lakes.
2.3 Is Rock Snot in Arizona?
While not as widely reported as in some other states, didymo has been found in Arizona. The Arizona Department of Environmental Quality monitors waterways for invasive species like didymo to protect the state’s aquatic ecosystems. If you’re in Arizona and enjoying its beautiful waterways, it’s always a good idea to be aware and take precautions to prevent the spread of rock snot. You can contact rockscapes.net, Address: 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States or call Phone: +1 (480) 965-9011 for consultancy.
3. What Causes Rock Snot Blooms?
While didymo is a naturally occurring alga, certain environmental conditions can trigger excessive blooms. These blooms can be unsightly and harmful to aquatic ecosystems.
3.1 What Environmental Conditions Favor Rock Snot?
Didymo tends to thrive in cold, clear, and nutrient-poor waters. It prefers stable flow conditions and can tolerate a wide range of pH levels. These conditions are often found in rivers and streams that are fed by snowmelt or groundwater.
3.2 How Do Nutrient Levels Affect Rock Snot Growth?
Paradoxically, didymo blooms often occur in waters with very low phosphorus levels. While most algae thrive in nutrient-rich environments, didymo is adapted to survive and even flourish in nutrient-poor conditions. The exact reasons for this are still being studied, but it’s believed that didymo may have unique mechanisms for nutrient uptake and storage that give it a competitive advantage over other algae in these environments.
3.3 What Role Do Human Activities Play in Rock Snot Blooms?
Human activities can indirectly contribute to didymo blooms. For example, changes in land use, such as deforestation or urbanization, can alter nutrient runoff patterns and water flow regimes, creating conditions that favor didymo growth. Additionally, the introduction of didymo to new areas via human vectors, such as contaminated fishing gear, can lead to the establishment of new blooms.
4. Why Is Rock Snot a Problem?
While rock snot may seem like just an unsightly nuisance, it can have significant ecological and economic impacts. Understanding these impacts is crucial for managing and mitigating its spread.
4.1 How Does Rock Snot Affect Aquatic Ecosystems?
Didymo blooms can alter the structure and function of aquatic ecosystems. The thick mats of algae can smother bottom-dwelling organisms, such as insects and snails, reducing their habitat and food sources. This, in turn, can affect fish populations that rely on these organisms for food. Additionally, didymo blooms can alter nutrient cycling and oxygen levels in the water, further disrupting the balance of the ecosystem.
4.2 Can Rock Snot Affect Fish Populations?
Yes, rock snot can indirectly affect fish populations. By reducing the abundance of aquatic insects and other invertebrates, it can decrease the food supply available to fish. This can lead to reduced growth rates, lower reproductive success, and even population declines in some fish species. However, note that didymo doesn’t directly harm fish.
4.3 What Are the Economic Impacts of Rock Snot?
The economic impacts of rock snot can be significant, particularly in areas that rely on recreational fishing and tourism. Didymo blooms can make rivers and streams less appealing for anglers, leading to reduced fishing activity and revenue for local businesses. The cost of managing and mitigating didymo blooms can also be substantial, requiring resources for monitoring, research, and public education campaigns.
5. How Can Rock Snot Be Prevented?
Preventing the spread of rock snot is crucial for protecting aquatic ecosystems and recreational resources. A multi-pronged approach that includes education, preventative measures, and best practices is essential.
5.1 What Is “Check, Clean, Dry”?
“Check, Clean, Dry” is a simple yet effective protocol for preventing the spread of aquatic invasive species, including didymo. The protocol involves:
- Check: Inspecting and removing any visible plants, animals, and mud from equipment and clothing.
- Clean: Cleaning equipment and clothing thoroughly with hot water (ideally above 140°F or 60°C) or a disinfectant solution.
- Dry: Drying equipment and clothing completely for at least 48 hours in a dry environment.
Following these steps can significantly reduce the risk of spreading didymo and other invasive species.
5.2 Why Is It Important to Clean Fishing Gear?
Fishing gear, such as waders, boots, nets, and lines, can easily pick up didymo cells and transport them to new locations. Felt-soled wading boots are particularly problematic, as the porous material can harbor didymo cells for extended periods. Cleaning fishing gear thoroughly after each use is essential for preventing the spread of didymo. Many anglers are switching to rubber or synthetic-soled boots to reduce this risk.
5.3 What Disinfectants Are Effective Against Rock Snot?
Several disinfectants can be effective against didymo, including bleach, quaternary ammonium compounds, and vinegar. A solution of 2% bleach (1/4 cup of bleach per gallon of water) is commonly recommended for disinfecting equipment. However, it’s important to use disinfectants carefully and follow all safety precautions. Always rinse equipment thoroughly after disinfection to remove any residual chemicals.
6. How Can Rock Snot Be Removed?
While preventing the spread of rock snot is the best approach, there may be situations where removal is necessary. However, removing didymo can be challenging, and the effectiveness of different methods can vary.
6.1 Is It Possible to Manually Remove Rock Snot?
In some cases, it may be possible to manually remove didymo from small areas, such as individual rocks or streambeds. This can be done using brushes, scrapers, or high-pressure hoses. However, manual removal is labor-intensive and may not be feasible for large-scale blooms. Additionally, it’s important to dispose of the removed didymo properly to prevent it from spreading to other areas.
6.2 Are There Chemical Treatments for Rock Snot?
Chemical treatments for rock snot are generally not recommended due to potential impacts on non-target organisms and water quality. While some chemicals, such as copper sulfate, have been used to control algae blooms in other situations, their use in didymo management is controversial and may not be effective.
6.3 Can Natural Processes Control Rock Snot?
In some cases, natural processes may help control rock snot blooms. For example, high flows or floods can physically remove didymo mats from streambeds. Additionally, changes in nutrient levels or water temperature can sometimes lead to the decline of didymo blooms. However, relying on natural processes alone may not be sufficient to manage didymo in all situations.
7. What Research Is Being Done on Rock Snot?
Researchers are actively studying didymo to better understand its ecology, spread, and management. This research is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent and control didymo blooms.
7.1 What Are Scientists Learning About Rock Snot Ecology?
Scientists are investigating various aspects of didymo ecology, including its nutrient requirements, reproductive strategies, and responses to environmental stressors. They are also studying the genetic diversity of didymo populations to understand how it is spreading and adapting to new environments.
7.2 How Is DNA Technology Being Used to Track Rock Snot?
DNA technology is being used to track the spread of didymo and identify its origins. By analyzing the DNA of didymo samples from different locations, researchers can determine whether they are from the same source population or represent new introductions. This information can help inform management strategies and prevent further spread.
7.3 What Are the Latest Findings on Rock Snot Management?
Recent research has focused on developing and evaluating different management strategies for didymo. This includes studies on the effectiveness of different disinfectants, the impacts of flow manipulation, and the potential for biological control. While there is no silver bullet for managing didymo, ongoing research is providing valuable insights that can help inform management decisions.
8. Rock Snot and Landscaping: Is There a Connection?
While rock snot is primarily an issue in aquatic environments, there are indirect connections to landscaping. Understanding these connections can help landscapers and homeowners make informed decisions that protect water quality and prevent the spread of invasive species.
8.1 How Can Landscaping Practices Affect Water Quality?
Landscaping practices can have a significant impact on water quality. For example, excessive use of fertilizers can lead to nutrient runoff, which can contribute to algae blooms in nearby waterways. Similarly, improper erosion control can lead to sediment pollution, which can harm aquatic habitats.
8.2 What Role Can Rockscapes.net Play in Sustainable Landscaping?
At rockscapes.net, we promote sustainable landscaping practices that protect water quality and minimize the risk of spreading invasive species. This includes using native plants that require less water and fertilizer, implementing effective erosion control measures, and avoiding the use of felt materials in landscaping projects.
8.3 How Can Homeowners Help Prevent the Spread of Rock Snot?
Homeowners can play an important role in preventing the spread of rock snot. This includes:
- Avoiding the use of felt-soled boots or waders when working near waterways.
- Cleaning and disinfecting any equipment that comes into contact with water.
- Properly disposing of any aquatic plants or debris.
- Educating themselves and others about the risks of rock snot and other invasive species.
9. Case Studies: Rock Snot in Different Regions
Examining how rock snot has impacted different regions can provide valuable insights into its management and prevention.
9.1 Rock Snot in New Zealand: A Cautionary Tale
New Zealand has experienced severe didymo blooms, particularly on the South Island. These blooms have had significant ecological and economic impacts, leading to widespread efforts to control its spread. New Zealand’s experience highlights the importance of early detection, rapid response, and public education in managing didymo.
 Man holding a pile of Didymo in stream on New Zealand’s South Island
Man holding a pile of Didymo in stream on New Zealand’s South Island
9.2 Rock Snot in the Delaware River Basin: A Collaborative Effort
The Delaware River Basin, which includes parts of New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware, has also experienced didymo blooms. A collaborative effort involving state and federal agencies, local organizations, and the public is underway to monitor and manage didymo in the basin. This effort includes research, monitoring, education, and outreach.
9.3 Rock Snot in the Western United States: Adapting to a Changing Environment
The Western United States, with its many cold, clear rivers and streams, is particularly susceptible to didymo blooms. States like Montana, Colorado, and Idaho have implemented various management strategies, including public education campaigns and restrictions on felt-soled waders. These states are also working to understand how climate change and other environmental factors may be affecting didymo blooms.
10. Frequently Asked Questions About Rock Snot
Here are some frequently asked questions about rock snot, along with answers to help you better understand this aquatic nuisance.
10.1 Is Rock Snot Harmful to Humans?
Rock snot is not directly harmful to humans. It does not produce toxins or pose a health risk if you come into contact with it. However, it can be a nuisance in recreational areas, making rivers and streams less appealing for swimming, fishing, and boating.
10.2 Can Pets Get Sick From Rock Snot?
No, rock snot is not known to be harmful to pets. However, it’s always a good idea to prevent your pets from drinking water from streams or rivers that may be contaminated with algae or other pollutants.
10.3 How Can I Tell if a Stream Has Rock Snot?
Rock snot is usually easy to identify by its distinctive appearance. It forms thick, cotton-like or woolly mats that cling to rocks and streambeds. The mats are typically white or grayish-brown in color and can feel slimy to the touch. If you suspect that a stream has rock snot, you can report it to your local environmental agency.
10.4 What Should I Do if I Find Rock Snot on My Gear?
If you find rock snot on your gear, it’s important to clean and disinfect it thoroughly to prevent the spread of the alga to other waterways. Follow the “Check, Clean, Dry” protocol: check your gear for any visible signs of algae, clean it with hot water or a disinfectant solution, and dry it completely before using it again.
10.5 Is There Any Way to Get Rid of Rock Snot Permanently?
Unfortunately, there is no guaranteed way to get rid of rock snot permanently. While various management strategies can help control blooms and prevent their spread, didymo is a resilient alga that can persist in waterways for long periods. Prevention is the key to managing rock snot.
10.6 Does Rock Snot Only Grow in Pristine Waters?
While rock snot is often associated with cold, clear, nutrient-poor waters, it can also grow in waters with moderate levels of nutrients. The exact conditions that favor didymo growth are complex and not fully understood.
10.7 Can Rock Snot Affect Drinking Water Supplies?
Rock snot is not typically a concern for drinking water supplies. It does not produce toxins that would contaminate the water, and water treatment processes can effectively remove any algae cells that may be present.
10.8 Are There Any Benefits to Rock Snot?
While rock snot is generally considered a nuisance, it may have some limited benefits. For example, it can provide habitat for some aquatic insects and other invertebrates. However, these benefits are typically outweighed by the negative impacts of didymo blooms on aquatic ecosystems.
10.9 How Can I Get Involved in Rock Snot Monitoring and Management?
You can get involved in rock snot monitoring and management by volunteering with local environmental organizations or participating in citizen science programs. These programs often involve monitoring waterways for invasive species, collecting data, and educating the public about the risks of rock snot and other aquatic nuisances.
10.10 Where Can I Find More Information About Rock Snot?
You can find more information about rock snot from your local environmental agency, state Department of Natural Resources, or organizations like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). At rockscapes.net, we also provide resources and information about sustainable landscaping practices that can help protect water quality and prevent the spread of invasive species.
Understanding rock snot is crucial for protecting the health of our aquatic ecosystems. By following the “Check, Clean, Dry” protocol, supporting sustainable landscaping practices, and staying informed about the latest research, we can all play a role in preventing the spread of this aquatic nuisance.
Ready to transform your landscape into a sustainable and beautiful oasis? Visit rockscapes.net today for inspiration, information, and expert advice on using natural stone in your landscape design. Discover the beauty and versatility of rockscapes and create a landscape that you’ll love for years to come. Explore design ideas, learn about different types of rocks, and get tips for installation and maintenance. Let rockscapes.net be your guide to creating a stunning and sustainable landscape. Contact us now to discuss your project!
