Is the rock cooking a safe and effective way to prepare food outdoors? It certainly is! Rock cooking offers a unique, flavorful twist to campfire cuisine, expanding your culinary horizons beyond basic grilling. This guide from rockscapes.net explores which rocks are ideal, safety considerations, and tips for delicious meals cooked directly on stone. Discover how to select the right rocks and transform your outdoor cooking experience with stone-fired flavors.
1. Understanding the Basics of Cooking on Rocks
What Is The Rock Cooking? Rock cooking, also known as stone cooking, is an age-old method where food is cooked directly on heated rocks. This technique imparts a unique, earthy flavor and texture to the food.
To delve deeper, let’s explore various facets of this cooking method:
-
Historical Context: Humans have been cooking on rocks for millennia. Early civilizations utilized hot stones to cook food before the advent of metal cookware.
-
Flavor Enhancement: The porous nature of some rocks can absorb and radiate flavors, adding a distinct taste profile to the food.
-
Heat Distribution: Rocks provide even heat distribution, ensuring that food is cooked uniformly.
-
Versatility: Rock cooking is suitable for a wide range of foods, from meats and vegetables to breads and pizzas.
-
Health Benefits: Cooking on rocks can be healthier as it often requires less oil compared to traditional cooking methods.
2. Identifying the Best Types of Rocks for Cooking
Which types of rocks are best suited for cooking, ensuring both safety and optimal flavor? The best rocks for cooking are dense, non-porous, and free from toxic minerals, such as granite, lava rock, and Himalayan pink salt.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
-
Granite: Granite is an excellent choice due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and distribute heat evenly. It’s suitable for cooking various foods, including meats, seafood, and vegetables. According to research from Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, granite’s thermal properties make it ideal for retaining heat.
-
Lava Rock: Lava rocks are highly effective at retaining heat, making them perfect for pit cooking. However, their porous nature means they can absorb juices and sauces, which may affect hygiene.
-
Himalayan Pink Salt: Himalayan pink salt blocks can withstand temperatures up to 230°C and add a unique flavor to the food. They also possess antibacterial properties, enhancing food safety.
-
Soapstone: Soapstone is another good option because of its density and heat-retention capabilities. It’s often used for cooking surfaces because it heats evenly and doesn’t react with foods.
Table 1: Comparison of Rocks for Cooking
| Rock Type | Heat Resistance | Porosity | Flavor Impact | Durability | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Granite | High | Low | Neutral | High | Meats, Vegetables, Seafood |
| Lava Rock | High | High | Earthy | Medium | Pit Cooking |
| Himalayan Pink Salt | Medium | Low | Salty, Mineral-Rich | Low | Grilling, Serving |
| Soapstone | High | Low | Neutral | High | Searing, Grilling |
3. Rocks to Avoid: Safety First
What types of rocks should you avoid when cooking to prevent potential health risks? Avoid porous, sedimentary rocks like sandstone and limestone, as well as any rocks from unknown sources, as they may contain harmful toxins or explode when heated.
Here’s a list of rocks to steer clear of and why:
-
Sandstone and Limestone: These rocks are highly porous and can absorb harmful bacteria and toxins. They are also prone to cracking and exploding under high heat.
-
Shale: Shale is a fine-grained, sedimentary rock that can contain high levels of organic matter. When heated, it can release unpleasant odors and potentially harmful substances.
-
Rocks from Unknown Sources: It’s crucial to avoid using rocks from unknown sources as they may contain toxic minerals or have been exposed to pollutants.
-
Rocks Near Water: Rocks collected near water sources are often saturated and more likely to explode when heated.
According to the National Park Service, using the wrong type of rock for cooking can lead to serious health hazards due to the release of toxic minerals.
4. Preparing Your Rock for Cooking
How do you properly prepare a rock for cooking to ensure it is clean and safe to use? Preparing your rock involves thorough cleaning with a stiff brush and hot water, followed by a slow, gradual heating process to remove any residual moisture and prevent cracking.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
-
Cleaning: Scrub the rock with a stiff brush and hot water to remove any dirt, debris, or loose particles. Avoid using soap, as it can be absorbed into the rock.
-
Inspection: Examine the rock for any cracks, fissures, or signs of weakness. Discard the rock if any flaws are detected.
-
Preheating: Place the rock near the fire or heat source, gradually increasing the temperature over several hours. This process helps to eliminate any remaining moisture and reduces the risk of cracking.
-
Seasoning (for Granite): Lightly coat the granite with cooking oil and heat it to create a non-stick surface.
-
Cooling: Allow the rock to cool naturally after each use. Avoid quenching it with water, as this can cause it to crack.
5. Essential Safety Tips for Rock Cooking
What are the most important safety precautions to take when cooking on rocks to prevent accidents and ensure food safety? Essential safety tips include using appropriate rocks, preheating slowly, avoiding wet rocks, and monitoring the rock for signs of cracking or instability.
Here are detailed safety guidelines:
-
Rock Selection: Always use rocks that are known to be safe for cooking, such as granite, lava rock, or Himalayan pink salt.
-
Gradual Heating: Heat the rock slowly to prevent thermal shock and cracking.
-
Dry Rocks: Ensure the rock is completely dry before heating it, as moisture can cause it to explode.
-
Protective Gear: Wear heat-resistant gloves and eye protection to prevent burns and injuries from flying debris.
-
Stable Base: Place the rock on a stable, non-flammable surface, away from flammable materials.
-
Monitoring: Continuously monitor the rock for signs of cracking or instability. If any issues are detected, carefully remove the rock from the heat source and allow it to cool.
6. Cooking Techniques: Maximizing Flavor and Safety
How can you maximize flavor and safety when cooking on rocks, ensuring delicious and well-cooked meals? Maximize flavor and safety by using proper heating techniques, seasoning the rock, controlling cooking time, and monitoring internal food temperatures.
Consider the following techniques:
-
Even Heating: Ensure the rock is heated evenly by rotating it periodically.
-
Seasoning: Season the rock with oil or herbs to enhance flavor and prevent sticking.
-
Temperature Control: Regulate the fire or heat source to maintain a consistent cooking temperature.
-
Food Placement: Place food directly on the heated rock, ensuring it is evenly distributed.
-
Cooking Time: Monitor cooking times closely to prevent overcooking or burning.
-
Internal Temperature: Use a food thermometer to ensure meats and seafood reach a safe internal temperature.
7. Recipes for Rock Cooking: Delicious Ideas to Try
What are some delicious and easy recipes to try when cooking on rocks, showcasing the versatility of this method? Some delicious and easy recipes include grilled steak, roasted vegetables, seafood skewers, and flatbreads, all cooked directly on the heated rock.
Here are a few inspiring recipes:
7.1. Granite-Grilled Steak
- Ingredients:
- 1 lb steak (ribeye, New York strip)
- 2 tbsp olive oil
- 1 tsp salt
- 1/2 tsp black pepper
- 1 clove garlic, minced
- Fresh rosemary sprigs
- Instructions:
- Preheat a granite slab slowly over a campfire or grill.
- Rub the steak with olive oil, salt, pepper, and garlic.
- Place rosemary sprigs on the heated granite.
- Place the steak on top of the rosemary and cook for 3-5 minutes per side, or until desired doneness.
- Let rest for 5 minutes before slicing and serving.
7.2. Lava Rock-Roasted Vegetables
- Ingredients:
- 1 zucchini, sliced
- 1 bell pepper, sliced
- 1 onion, sliced
- 1 cup cherry tomatoes
- 2 tbsp olive oil
- Salt and pepper to taste
- Instructions:
- Preheat lava rocks in a pit or on a grill.
- Toss the vegetables with olive oil, salt, and pepper.
- Place the vegetables in a grill basket or directly on the lava rocks.
- Roast for 10-15 minutes, or until tender and slightly charred.
7.3. Himalayan Pink Salt Seafood Skewers
- Ingredients:
- 1 lb shrimp or scallops
- 1 red bell pepper, cubed
- 1 yellow bell pepper, cubed
- 1 red onion, cubed
- 2 tbsp olive oil
- Salt and pepper to taste
- Instructions:
- Preheat a Himalayan pink salt block on a grill.
- Thread the shrimp, bell peppers, and onion onto skewers.
- Brush the skewers with olive oil and season with salt and pepper.
- Place the skewers on the heated salt block and cook for 2-3 minutes per side, or until the seafood is cooked through.
8. Maintaining Your Cooking Rocks
How should you properly maintain your cooking rocks to prolong their lifespan and ensure they remain safe for cooking? To maintain your cooking rocks, clean them gently, avoid thermal shock, and store them properly.
Follow these maintenance tips:
-
Gentle Cleaning: Clean the rocks with a soft brush and warm water. Avoid using soap or harsh chemicals.
-
Avoid Thermal Shock: Allow the rocks to cool naturally after each use. Avoid quenching them with water, as this can cause them to crack.
-
Proper Storage: Store the rocks in a dry, well-ventilated place to prevent moisture buildup and bacterial growth.
-
Regular Inspection: Inspect the rocks regularly for any signs of cracking, chipping, or damage. Discard any rocks that are no longer safe to use.
9. Exploring Rockscapes.net for Stone Cooking Inspiration and Resources
Are you looking for more inspiration and resources for stone cooking? Rockscapes.net is your go-to source! Discover a wide range of stone types suitable for cooking, innovative design ideas, and expert tips to elevate your outdoor culinary experiences.
At Rockscapes.net, you’ll find:
-
Extensive Stone Selection: Browse a diverse collection of natural stones perfect for cooking, each offering unique thermal properties and aesthetic appeal.
-
Design Inspiration: Explore stunning project galleries featuring stone-cooked meals in various outdoor settings, from rustic campfires to elegant backyard kitchens.
-
Expert Advice: Access in-depth articles and tutorials on stone selection, preparation, cooking techniques, and safety, ensuring you have the knowledge to cook with confidence.
-
Local Stone Suppliers: Find reputable stone suppliers near you, making it easy to source the perfect materials for your next cooking adventure.
-
Community Forum: Connect with fellow outdoor cooking enthusiasts to share recipes, tips, and inspiration, fostering a collaborative and supportive community.
10. Addressing Common Concerns About Rock Cooking
What are some common concerns about cooking on rocks, and how can they be addressed? Common concerns include rock safety, hygiene, and flavor contamination, which can be addressed through proper rock selection, cleaning, and cooking techniques.
Here are some frequently asked questions and their answers:
-
Q: Is it safe to cook on any type of rock?
- A: No, it is not safe to cook on any type of rock. You should only use dense, non-porous rocks like granite, lava rock, or Himalayan pink salt.
-
Q: How do I clean a cooking rock?
- A: Clean a cooking rock with a stiff brush and hot water. Avoid using soap or harsh chemicals.
-
Q: Can cooking rocks explode?
- A: Yes, cooking rocks can explode if they are porous or contain moisture. To prevent this, use the right type of rock and heat it slowly.
-
Q: How hot should the rock be before I start cooking?
- A: The rock should be hot enough to sizzle when a drop of water is placed on it. This indicates that it has reached a suitable cooking temperature.
-
Q: Can I use oil on my cooking rock?
- A: Yes, you can use oil on granite and soapstone to prevent sticking. Avoid using oil on Himalayan pink salt, as it can degrade the block.
-
Q: How do I store my cooking rock?
- A: Store your cooking rock in a dry, well-ventilated place to prevent moisture buildup and bacterial growth.
-
Q: What if my rock cracks while cooking?
- A: If your rock cracks while cooking, carefully remove it from the heat source and allow it to cool. Discard the rock, as it is no longer safe to use.
-
Q: Can I cook acidic foods on my rock?
- A: Yes, you can cook acidic foods on granite and lava rock. Avoid cooking acidic foods on Himalayan pink salt, as it can erode the block.
-
Q: How do I know if my food is cooked properly on a rock?
- A: Use a food thermometer to ensure meats and seafood reach a safe internal temperature.
-
Q: Can I reuse cooking rocks?
- A: Yes, you can reuse cooking rocks as long as they are properly maintained and show no signs of damage.
Cooking on rocks offers a unique and flavorful way to prepare food outdoors. By selecting the right type of rock, following safety precautions, and mastering cooking techniques, you can enjoy delicious meals with a distinctive earthy taste.
Ready to elevate your outdoor cooking? Visit rockscapes.net for inspiration, expert advice, and the finest selection of natural stones to transform your next culinary adventure. Contact us at 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States, or call +1 (480) 965-9011 to explore the possibilities.
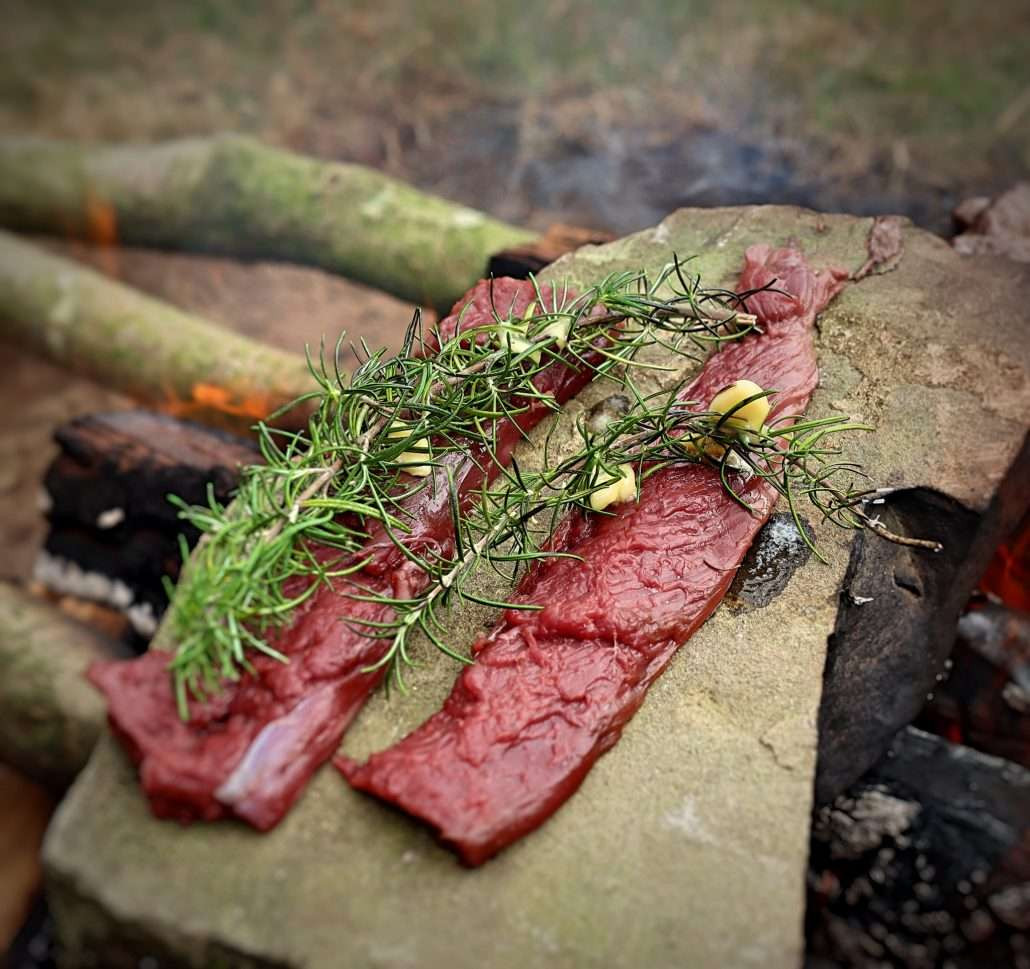 Granite cooking rock with steak and rosemary
Granite cooking rock with steak and rosemary
11. The Environmental Impact of Rock Cooking
How does cooking on rocks affect the environment, and what steps can be taken to minimize any negative impacts? The environmental impact of rock cooking is minimal if sustainable practices are followed, such as sourcing rocks responsibly and minimizing fire usage.
Here’s a breakdown of the environmental considerations:
-
Rock Sourcing: Obtain rocks from sustainable sources to minimize environmental disruption. Avoid collecting rocks from protected areas or sensitive ecosystems.
-
Fire Usage: Use firewood sparingly and responsibly. Consider using alternative heat sources, such as propane stoves, to reduce emissions.
-
Waste Disposal: Dispose of food waste and ash properly to prevent pollution.
-
Leave No Trace: Practice the principles of Leave No Trace by minimizing your impact on the environment.
12. The Future of Rock Cooking
What does the future hold for rock cooking, and how can it continue to evolve as a culinary trend? The future of rock cooking involves innovation in techniques, sustainable practices, and broader adoption in both home and professional kitchens.
Here are some potential developments:
-
Innovative Techniques: Experimentation with new types of rocks and cooking methods to enhance flavor and efficiency.
-
Sustainable Practices: Adoption of eco-friendly practices, such as sourcing rocks from recycled materials and using renewable energy sources.
-
Broader Adoption: Increased use of rock cooking in restaurants and home kitchens, driven by its unique flavor and health benefits.
-
Technological Integration: Development of specialized equipment, such as rock ovens and grills, to streamline the cooking process.
Cooking on rocks is a timeless method that combines the simplicity of nature with the art of culinary innovation. As it continues to evolve, it promises to offer even more exciting and sustainable ways to enjoy delicious, stone-fired meals.
Whether you’re a seasoned outdoor enthusiast or a curious home cook, rock cooking offers a unique and rewarding experience. Embrace the adventure, explore the possibilities, and savor the flavors of the earth.
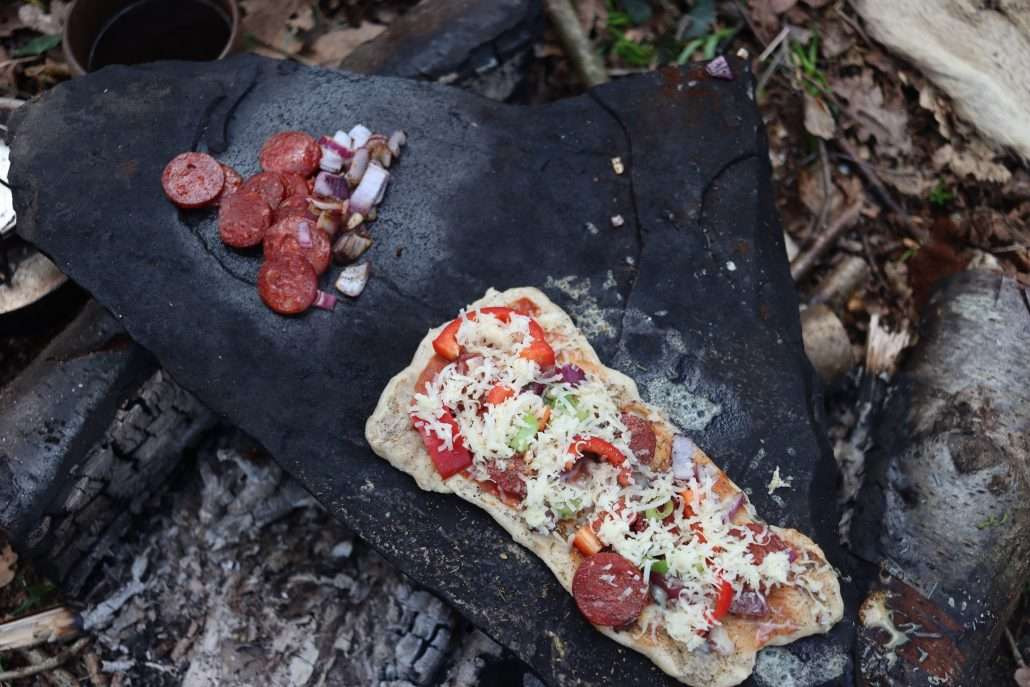 Pizza on granite cooking rock
Pizza on granite cooking rock
13. Adding a Touch of Stone to Your Landscape with Rockscapes.net
How can you incorporate the beauty and functionality of natural stone into your landscape design with Rockscapes.net? Rockscapes.net offers a wide array of decorative stones, expert advice, and innovative design ideas to enhance your outdoor spaces with natural elegance.
Here are some ways to integrate stone into your landscape:
-
Stone Pathways: Create inviting pathways with flagstone, pavers, or gravel.
-
Rock Gardens: Design stunning rock gardens with a variety of stones, succulents, and alpine plants.
-
Water Features: Incorporate natural stone into waterfalls, ponds, and fountains.
-
Retaining Walls: Build durable and attractive retaining walls with natural stone.
-
Fire Pits: Construct cozy fire pits with stone borders for outdoor gatherings.
At Rockscapes.net, you’ll find:
-
Stone Selection: Discover a wide range of natural stones, including granite, limestone, sandstone, and more.
-
Design Inspiration: Explore stunning project galleries featuring stone landscapes in various styles.
-
Expert Advice: Access in-depth articles and tutorials on stone selection, installation, and maintenance.
-
Local Stone Suppliers: Find reputable stone suppliers near you.
-
Community Forum: Connect with fellow landscape enthusiasts to share ideas, tips, and inspiration.
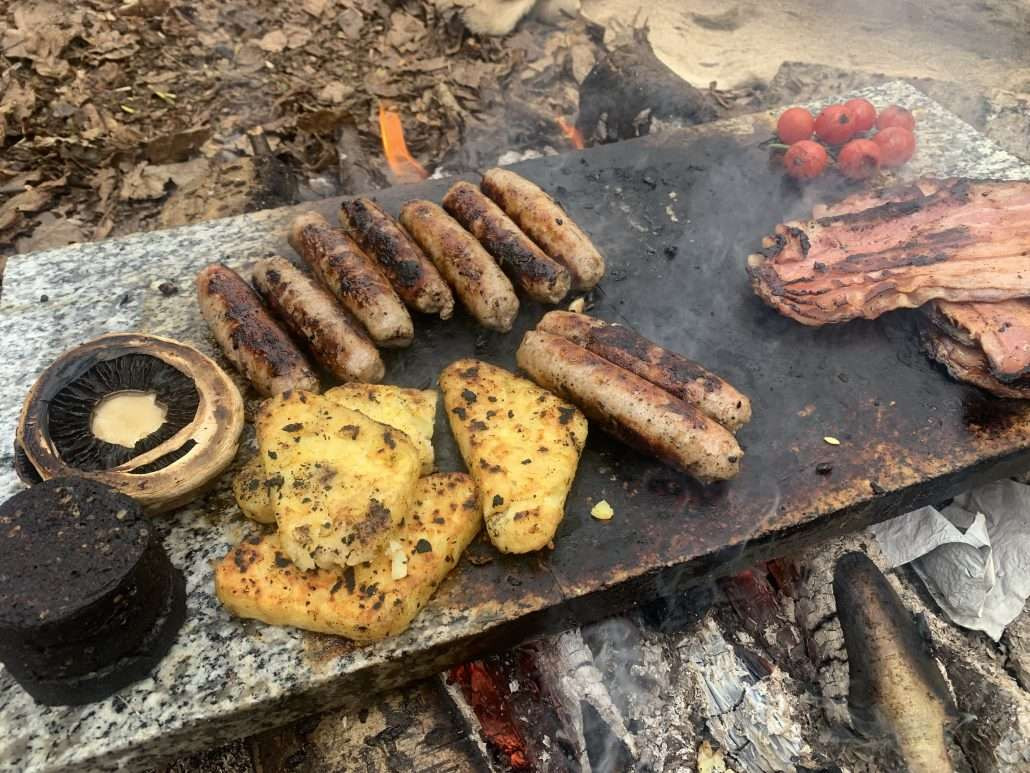 Breakfast on marble cooking stone
Breakfast on marble cooking stone
14. Understanding Geological Formations for Rock Cooking
Why is understanding geological formations important for rock cooking, and how does it influence rock selection? Understanding geological formations helps in selecting rocks that are safe, durable, and suitable for high-temperature cooking, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
Here’s how geological knowledge impacts rock selection:
-
Formation Process: Rocks formed under high pressure and temperature, like metamorphic rocks (e.g., slate), are generally more heat-resistant.
-
Mineral Composition: Rocks with high quartz and feldspar content, like granite, can withstand thermal stress due to their strong crystalline structure.
-
Porosity: Understanding porosity helps avoid rocks that trap moisture and could explode when heated.
-
Bedding Planes: Knowledge of bedding planes helps identify rocks that may split along these planes under heat stress.
15. Enhancing Food Safety and Hygiene in Rock Cooking
How can you ensure optimal food safety and hygiene when cooking on rocks to prevent contamination and health risks? Enhance food safety by thoroughly cleaning rocks, using high heat to kill bacteria, and avoiding porous rocks that can harbor pathogens.
Follow these guidelines:
-
Thorough Cleaning: Always clean rocks with a stiff brush and hot water before each use.
-
High Heat: Heat rocks to high temperatures to kill any surface bacteria.
-
Non-Porous Rocks: Use non-porous rocks like granite, which are less likely to harbor bacteria.
-
Avoid Contamination: Do not use rocks that have been exposed to chemicals or pollutants.
-
Separate Cooking Surfaces: Use different rocks for meats, seafood, and vegetables to prevent cross-contamination.
16. The Art of Seasoning and Flavor Infusion in Rock Cooking
How can you effectively season and infuse flavors into food during rock cooking to enhance the taste experience? Season and infuse flavors by using herbs, oils, and spices directly on the rock, allowing the heat to release their aromas and impart them to the food.
Try these techniques:
-
Herb Infusion: Place fresh herbs like rosemary, thyme, or sage directly on the heated rock before adding food.
-
Oil Seasoning: Brush the rock with flavored oils, such as garlic-infused or chili-infused oil.
-
Spice Rubs: Rub meats and vegetables with spice blends before placing them on the rock.
-
Salt Blocks: Use Himalayan pink salt blocks to add a salty, mineral-rich flavor.
 Himalayan Pink Salt Block ready for cooking
Himalayan Pink Salt Block ready for cooking
17. Adapting Rock Cooking to Different Climates and Environments
How can you adapt rock cooking techniques to suit various climates and outdoor environments for a successful cooking experience? Adapt techniques by considering the local climate, sourcing appropriate rocks, and adjusting heating methods to suit different weather conditions.
Here’s how to adapt:
-
Arid Climates: In dry climates, use denser rocks that retain heat longer.
-
Humid Climates: In humid climates, ensure rocks are thoroughly dried before heating to prevent cracking.
-
Cold Climates: In cold environments, use larger rocks and higher heat to compensate for heat loss.
-
Coastal Environments: Avoid using rocks from coastal areas, as they may contain salt that can affect flavor.
18. Troubleshooting Common Rock Cooking Issues
What are some common issues encountered during rock cooking, and how can you troubleshoot them for a smoother cooking process? Common issues include uneven heating, sticking, and cracking, which can be resolved with proper preparation, temperature control, and rock selection.
Here are some solutions:
-
Uneven Heating: Rotate the rock periodically to ensure even heat distribution.
-
Sticking: Season the rock with oil or use a higher heat setting.
-
Cracking: Heat the rock slowly and avoid sudden temperature changes.
-
Smoke: Use dry wood and avoid overheating the rock to reduce smoke.
-
Flavor Contamination: Use separate rocks for different types of food.
19. Innovative Tools and Equipment for Rock Cooking
What specialized tools and equipment can enhance your rock cooking experience and make it more efficient? Specialized tools include rock cooking stands, heat-resistant gloves, and temperature probes, which enhance safety and efficiency.
Here are some useful tools:
-
Rock Cooking Stands: Provide a stable base for heating rocks over a campfire or grill.
-
Heat-Resistant Gloves: Protect hands from burns when handling hot rocks.
-
Temperature Probes: Monitor the internal temperature of food to ensure it is cooked properly.
-
Grill Baskets: Prevent food from falling between rocks and make it easier to handle.
-
Rock Cleaning Brushes: Simplify the process of cleaning rocks after use.
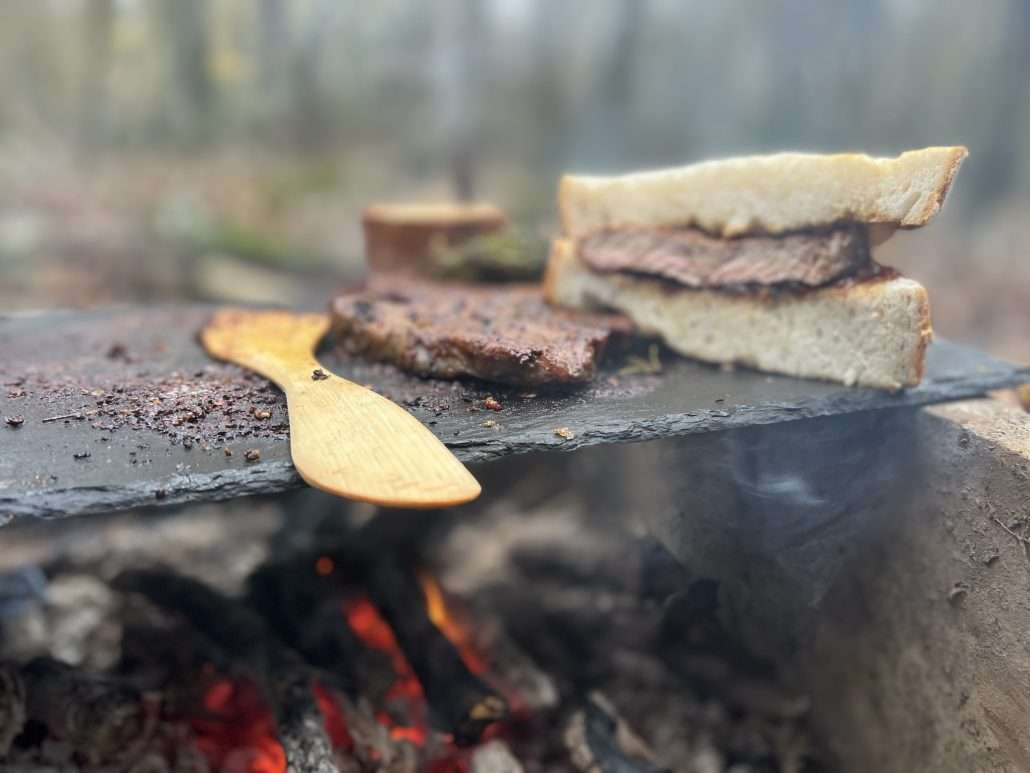 Steak sandwich cooked on slate
Steak sandwich cooked on slate
20. Creating a Stone-Cooking Community with Rockscapes.net
How does Rockscapes.net foster a community of stone-cooking enthusiasts, and what benefits does it offer to members? Rockscapes.net fosters a community by providing a platform for sharing recipes, tips, and experiences, creating a collaborative environment for learning and inspiration.
Here are some community benefits:
-
Recipe Sharing: Exchange favorite rock-cooking recipes with fellow enthusiasts.
-
Tip Exchange: Share tips and tricks for selecting, preparing, and cooking on rocks.
-
Experience Sharing: Discuss successes, challenges, and lessons learned in rock cooking.
-
Inspiration: Find new ideas and inspiration for rock cooking projects.
-
Support: Receive support and encouragement from fellow community members.
By providing a platform for connection and collaboration, rockscapes.net helps to foster a vibrant community of stone-cooking enthusiasts. Join today and start sharing your passion for rock cooking with the world.
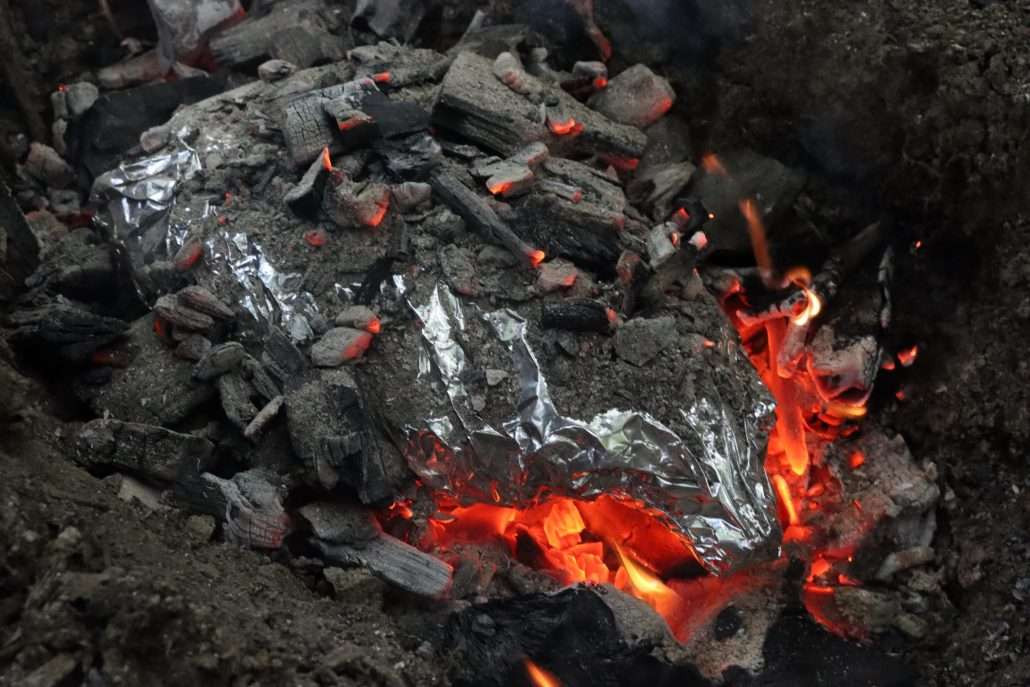 Lamb cooked in a pit with lava rocks
Lamb cooked in a pit with lava rocks
21. Maximizing Heat Retention for Rock Cooking
What are the best strategies for maximizing heat retention when cooking on rocks, ensuring consistent and efficient cooking temperatures? Maximize heat retention by using dense, thick rocks, preheating them slowly, and insulating the cooking area.
-
Dense, Thick Rocks: Choose rocks that are dense and thick, as they retain heat more effectively. Granite and soapstone are excellent choices.
-
Slow Preheating: Preheat the rocks slowly and gradually to allow them to absorb and retain heat evenly.
-
Insulation: Insulate the cooking area by surrounding the rocks with soil, sand, or other insulating materials. This helps to minimize heat loss and maintain consistent temperatures.
-
Wind Protection: Protect the cooking area from wind, which can quickly dissipate heat. Use windbreaks or shelters to create a more stable cooking environment.
-
Heat Reflectors: Use heat reflectors, such as aluminum foil or metal sheets, to direct heat back onto the rocks.
22. Exploring Culinary Traditions and Rock Cooking
How does rock cooking connect to various culinary traditions around the world, and what unique dishes can be created using this method? Rock cooking is rooted in numerous culinary traditions worldwide, inspiring dishes like Asado, Kalua, and Pierrade.
-
Asado (South America): This traditional barbecue method involves cooking meats over an open fire on a grill, often using heated stones to enhance flavor.
-
Kalua (Hawaii): This cooking technique involves wrapping food (typically pork) in banana leaves and burying it in an underground oven with heated rocks.
-
Pierrade (Switzerland): This involves cooking thin slices of meat on a heated stone at the table, allowing diners to customize their cooking preferences.
-
Lovo (Fiji): Similar to Kalua, Lovo involves cooking food in an underground oven lined with heated rocks.
-
Barbecue (Various Cultures): Many barbecue traditions use heated stones to provide consistent heat and enhance the smoky flavor of the food.
23. Creative Presentations and Plating Techniques for Stone-Cooked Dishes
How can you creatively present and plate stone-cooked dishes to enhance their visual appeal and create a memorable dining experience? Creative presentation involves using natural elements, contrasting textures, and innovative plating techniques to highlight the unique qualities of stone-cooked dishes.
-
Natural Elements: Serve stone-cooked dishes on wooden boards, slate platters, or stone slabs to enhance their rustic appeal.
-
Contrasting Textures: Pair crispy, stone-cooked meats with creamy sauces, crunchy vegetables, or soft breads to create a balance of textures.
-
Garnishes: Use fresh herbs, edible flowers, or colorful sauces to add visual interest and enhance the flavors of the dish.
-
Innovative Plating: Experiment with different plating techniques, such as stacking, layering, or arranging elements in a circular pattern.
-
Storytelling: Share the story behind the dish, highlighting the unique cooking method and the connection to culinary traditions.
24. Health Benefits of Mineral Absorption in Rock Cooking
Are there potential health benefits associated with mineral absorption when cooking on certain types of rocks? Cooking on rocks like Himalayan pink salt may provide trace minerals, but the impact is minimal compared to a balanced diet.
Some points to consider:
-
Mineral Transfer: Cooking on Himalayan pink salt blocks may transfer trace amounts of minerals like iron, potassium, and magnesium to the food.
-
Minimal Impact: The mineral content absorbed from the rock is likely to be minimal compared to the nutrients obtained from a balanced diet.
-
Balanced Diet: Focus on consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods for optimal health.
-
Consultation: Consult a healthcare professional or nutritionist for personalized dietary advice.
Rock cooking can be a fun and flavorful way to prepare food, but it’s important to prioritize a balanced diet and consult with experts for personalized advice.