A Rock Is Lively, a vibrant testament to Earth’s dynamic processes, constantly evolving and shaping our landscapes. At rockscapes.net, we delve into the captivating world of rocks and their transformative power in creating stunning and sustainable landscapes.
1. What Makes A Rock Lively? Unveiling The Hidden Vitality
A rock is lively not in the biological sense, but in its dynamic nature, constantly changing through geological processes like weathering, erosion, and tectonic activity. This continuous transformation gives rocks a unique story to tell, reflecting millions of years of Earth’s history.
Think of it this way:
- Erosion: The relentless force of wind and water sculpts rocks, creating unique formations.
- Weathering: Chemical and physical processes break down rocks, releasing minerals that nourish the soil.
- Tectonic Activity: The Earth’s plates collide, creating mountains and volcanoes, forever altering the rock landscape.
These processes, though slow on a human timescale, are constantly at work, making every rock a dynamic and ever-changing entity. The concept of “lively” here refers to the fact that rocks are not static objects. They are products of immense energy and ongoing change.
2. How Does The Rock Cycle Demonstrate That A Rock Is Lively?
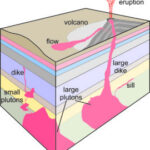
The rock cycle vividly illustrates that a rock is lively by showing the continuous transformation between igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rock types. This cycle highlights the dynamic processes of melting, cooling, weathering, erosion, compaction, cementation, heat, and pressure that reshape rocks over geological time.
The rock cycle is a fundamental concept in geology, demonstrating how rocks are continuously created, destroyed, and reformed. This cycle involves the following key processes:
- Melting: Rocks deep within the Earth melt to form magma.
- Cooling: Magma cools and solidifies, forming igneous rocks.
- Weathering and Erosion: Rocks on the Earth’s surface are broken down and transported.
- Compaction and Cementation: Sediments accumulate and are compressed into sedimentary rocks.
- Heat and Pressure: Existing rocks are transformed into metamorphic rocks.
According to research from Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, the rock cycle is a continuous loop, with each rock type potentially transforming into any other type. This dynamic process ensures that rocks are never truly static but are constantly evolving.
3. What Are The Three Main Types Of Rocks, And How Does Their Formation Show That A Rock Is Lively?
The three main types of rocks—igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic—demonstrate that a rock is lively through their distinct formation processes, each reflecting different dynamic geological activities. Igneous rocks form from cooled magma or lava, sedimentary rocks from compacted sediments, and metamorphic rocks from the transformation of existing rocks under heat and pressure.
Here’s a closer look at each type:
- Igneous Rocks: Formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Extrusive igneous rocks, like basalt, cool quickly on the surface, while intrusive igneous rocks, like granite, cool slowly beneath the surface.
- Sedimentary Rocks: Formed from the accumulation and cementation of sediments, such as sand, silt, and clay. Examples include sandstone, shale, and limestone.
- Metamorphic Rocks: Formed when existing rocks are transformed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions. Examples include marble (from limestone) and gneiss (from granite).
Each of these rock types undergoes continuous change through the rock cycle, demonstrating that rocks are not static entities but are constantly being reshaped by Earth’s dynamic processes.
4. How Do Rocks Contribute To Soil Formation, And Why Does This Show That A Rock Is Lively?
Rocks contribute to soil formation through weathering and erosion, processes that break down rocks into smaller particles, releasing minerals that enrich the soil. This gradual transformation illustrates that a rock is lively as it actively participates in creating the foundation for plant life and ecosystems.
The process of soil formation, known as pedogenesis, involves the following steps:
- Physical Weathering: Rocks are broken down by mechanical forces like freeze-thaw cycles and abrasion.
- Chemical Weathering: Rocks are decomposed by chemical reactions, such as oxidation and hydrolysis.
- Biological Weathering: Organisms like lichens and roots break down rocks.
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the minerals released from rocks during weathering provide essential nutrients for plants. This continuous breakdown and release of minerals demonstrate that rocks are dynamic contributors to soil fertility and ecosystem health.
5. What Role Do Rocks Play In Shaping Landscapes, And How Does This Underscore The Idea That A Rock Is Lively?
Rocks play a crucial role in shaping landscapes through erosion and weathering, creating formations like mountains, valleys, and canyons. These geological processes demonstrate that a rock is lively, as rocks are active agents in sculpting the Earth’s surface, constantly responding to environmental forces.
Consider these examples:
- Grand Canyon: Carved by the Colorado River over millions of years, exposing layers of sedimentary rock.
- Yosemite Valley: Shaped by glacial erosion, leaving behind granite cliffs and valleys.
- Arches National Park: Features over 2,000 natural sandstone arches, formed by wind and water erosion.
These landscapes are testaments to the dynamic interaction between rocks and the environment, proving that rocks are not static but actively involved in shaping the Earth’s surface.
 Sedimentary rocks along the Virgin River in Zion National Park
Sedimentary rocks along the Virgin River in Zion National Park
Caption: Eroded sedimentary rock formations beside the Virgin River in Zion National Park, exemplifying the ongoing geological processes that shape our landscapes.
6. What Are Some Practical Uses Of Rocks That Show That A Rock Is Lively In Human Applications?
Rocks have numerous practical uses that demonstrate their lively role in human applications, from construction and art to technology and medicine. Their diverse properties make them essential materials in various industries, showcasing their dynamic utility.
Here are some examples:
- Construction: Granite, limestone, and sandstone are used for building materials due to their durability and aesthetic appeal.
- Art: Marble, soapstone, and alabaster are used for sculptures and carvings.
- Technology: Quartz is used in electronics for its piezoelectric properties.
- Medicine: Calcium carbonate, derived from limestone, is used in antacids and dietary supplements.
- Landscaping: Rocks are used to create rock gardens, retaining walls, and decorative features, adding natural beauty to outdoor spaces.
These applications highlight how rocks are not just inert materials but active components in human endeavors, contributing to various aspects of our lives.
7. How Can Rocks Be Used In Landscaping To Create Dynamic And Engaging Spaces?
Rocks can transform landscapes into dynamic and engaging spaces by providing natural beauty, structural support, and ecological benefits. Incorporating rocks into landscape design can create visually stunning and sustainable environments.
Here are some ways to use rocks in landscaping:
- Rock Gardens: Create a naturalistic setting with a variety of rocks and plants.
- Retaining Walls: Use large rocks to stabilize slopes and create terraced gardens.
- Water Features: Incorporate rocks into ponds, waterfalls, and streams to enhance their aesthetic appeal.
- Pathways: Use flagstone or gravel to create natural and durable pathways.
- Xeriscaping: Use drought-tolerant plants and rocks to create low-water landscapes.
At rockscapes.net, you can find a wealth of ideas and inspiration for incorporating rocks into your landscape design, creating dynamic and engaging outdoor spaces.
8. What Types Of Rocks Are Best Suited For Landscaping In Different Climates?
Different types of rocks are best suited for landscaping in different climates due to their varying resistance to weathering, porosity, and aesthetic qualities. Selecting the right rocks can ensure the longevity and beauty of your landscape design.
Here’s a guide to choosing rocks for different climates:
| Climate | Best Rock Types | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Arid | Granite, Quartzite, Sandstone | Durable, heat-resistant, and blend well with desert landscapes |
| Humid | Slate, Limestone, River Rock | Water-resistant, good drainage, and add a natural touch to gardens |
| Coastal | Basalt, Granite | Salt-tolerant, durable, and can withstand harsh coastal conditions |
| Cold | Granite, Fieldstone | Freeze-thaw resistant, durable, and add a rustic charm to winter landscapes |
| Temperate | Sandstone, Limestone, Flagstone | Versatile, aesthetically pleasing, and suitable for a variety of landscape styles |
Choosing the right rocks for your climate ensures that your landscape remains beautiful and functional for years to come.
9. How Do Rocks Help To Conserve Water In Landscaping, Demonstrating Their Lively Role In Sustainable Practices?
Rocks help conserve water in landscaping by reducing soil evaporation, providing shade, and improving drainage, thus demonstrating their lively role in sustainable practices. Using rocks in xeriscaping and other water-wise designs can significantly reduce water consumption.
Here’s how rocks contribute to water conservation:
- Reduced Evaporation: Rocks act as a mulch, reducing water loss from the soil surface.
- Shade: Rocks provide shade, which helps to cool the soil and reduce evaporation.
- Improved Drainage: Rocks can improve soil drainage, preventing waterlogging and promoting healthy root growth.
- Xeriscaping: Rocks are a key element in xeriscaping, a water-wise landscaping technique that uses drought-tolerant plants and materials.
By incorporating rocks into your landscape design, you can create a beautiful and sustainable environment that conserves water and supports local ecosystems.
10. How Can Rockscapes.Net Help Me Find The Right Rocks For My Landscaping Project And Bring The Concept That A Rock Is Lively To My Yard?
Rockscapes.net can help you find the right rocks for your landscaping project by providing a wide selection of rock types, expert advice, and inspiration for creating dynamic and engaging outdoor spaces, bringing the concept that a rock is lively to your yard. We offer detailed information on different rock types, their properties, and their suitability for various landscaping applications.
Here’s how rockscapes.net can assist you:
- Extensive Rock Selection: We offer a diverse range of rocks, including granite, limestone, sandstone, and more.
- Expert Advice: Our team of landscaping professionals can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific needs and climate.
- Inspiration and Ideas: We showcase stunning landscape designs that incorporate rocks, providing you with inspiration for your own project.
- Step-by-Step Guides: We offer detailed guides on how to install rocks in your landscape, from creating rock gardens to building retaining walls.
- Local Suppliers: We can connect you with reputable rock suppliers in your area, ensuring you get high-quality materials at competitive prices.
Visit rockscapes.net today to explore the endless possibilities of rock landscaping and bring the dynamic beauty of rocks to your outdoor spaces.
11. What Geological Factors Influence Rock Formation?
Several geological factors influence rock formation, including temperature, pressure, and chemical composition. These elements are pivotal in the creation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, highlighting how a rock is lively through dynamic processes.
- Temperature: High temperatures cause rocks to melt, forming magma, which cools to create igneous rocks.
- Pressure: Intense pressure deep within the Earth transforms existing rocks into metamorphic rocks.
- Chemical Composition: The presence of different minerals and elements influences the type of rock that forms.
- Weathering and Erosion: These processes break down rocks into sediments, which compact and cement to form sedimentary rocks.
- Tectonic Activity: Plate movements create mountains and volcanoes, influencing rock formation and distribution.
12. How Do Weathering And Erosion Contribute To The Ever-Changing Nature Of Rocks?
Weathering and erosion contribute to the ever-changing nature of rocks by breaking them down into smaller particles and transporting them to new locations. These processes demonstrate how a rock is lively by reshaping landscapes and creating new geological formations.
- Physical Weathering: Mechanical forces like freeze-thaw cycles and abrasion break rocks down into smaller pieces.
- Chemical Weathering: Chemical reactions like oxidation and hydrolysis decompose rocks.
- Erosion: Wind, water, and ice transport weathered materials to new locations.
- Sedimentation: Eroded materials accumulate and form sedimentary rocks.
- Landscape Evolution: Weathering and erosion sculpt landscapes, creating features like canyons, valleys, and mountains.
13. What Role Do Minerals Play In Determining The Characteristics Of A Rock?
Minerals play a crucial role in determining the characteristics of a rock, influencing its color, hardness, texture, and chemical composition. The specific combination of minerals in a rock reflects the conditions under which it formed.
- Color: Different minerals impart different colors to rocks. For example, quartz is often white or clear, while feldspar can be pink or gray.
- Hardness: The hardness of a rock depends on the hardness of its constituent minerals. The Mohs hardness scale is used to measure the resistance of minerals to scratching.
- Texture: The size, shape, and arrangement of minerals in a rock determine its texture.
- Chemical Composition: The chemical composition of a rock is determined by the chemical formulas of its minerals.
14. How Are Rocks Used In Sustainable Construction Practices?
Rocks are used in sustainable construction practices for their durability, thermal mass, and natural aesthetic, contributing to energy-efficient and environmentally friendly buildings. Their use underscores that a rock is lively through its incorporation into sustainable designs.
- Thermal Mass: Rocks store heat, helping to regulate indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption.
- Durability: Rocks are long-lasting and require minimal maintenance, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Natural Aesthetic: Rocks add a natural and aesthetically pleasing element to buildings.
- Local Sourcing: Using locally sourced rocks reduces transportation costs and carbon emissions.
- Green Building Certifications: The use of sustainable building materials like rocks can contribute to LEED certification.
15. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Rocks?
Some common misconceptions about rocks include thinking they are inert, unchanging objects and that all rocks are hard and solid. In reality, rocks are dynamic, constantly evolving, and come in various forms and compositions, illustrating that a rock is lively through its diversity.
- Misconception: Rocks are inert and unchanging.
- Reality: Rocks are constantly being transformed by geological processes.
- Misconception: All rocks are hard and solid.
- Reality: Rocks vary in hardness and composition, with some being soft and porous.
- Misconception: Rocks are only useful for construction.
- Reality: Rocks have diverse uses in art, technology, medicine, and landscaping.
- Misconception: All rocks are the same color.
- Reality: Rocks come in a wide range of colors, depending on their mineral composition.
- Misconception: Rocks are not important for the environment.
- Reality: Rocks play a crucial role in soil formation, water filtration, and carbon sequestration.
16. How Can You Identify Different Types Of Rocks?
You can identify different types of rocks by examining their color, texture, mineral composition, and formation processes. Using a rock identification key or consulting with a geologist can also help.
- Color: Observe the overall color of the rock.
- Texture: Examine the size, shape, and arrangement of mineral grains.
- Mineral Composition: Identify the minerals present in the rock.
- Formation Processes: Consider how the rock formed (e.g., from magma, sediments, or existing rocks).
- Rock Identification Key: Use a rock identification key to narrow down the possibilities.
- Geologist Consultation: Consult with a geologist for expert identification.
17. What Tools And Techniques Are Used To Study Rocks?
Various tools and techniques are used to study rocks, including microscopes, X-ray diffraction, and chemical analysis. These methods provide insights into the mineral composition, structure, and formation history of rocks.
- Microscopes: Used to examine the microscopic features of rocks.
- X-ray Diffraction: Used to identify the mineral composition of rocks.
- Chemical Analysis: Used to determine the chemical elements present in rocks.
- Petrographic Analysis: Used to study the texture and mineralogy of rocks.
- Geochronology: Used to determine the age of rocks.
18. How Do Rocks Store And Release Carbon Dioxide?
Rocks store carbon dioxide through weathering and release it through volcanic activity and metamorphism, playing a crucial role in the global carbon cycle. This dynamic process demonstrates how a rock is lively in regulating Earth’s climate.
- Weathering: Rocks absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during chemical weathering.
- Carbon Sequestration: Carbon dioxide is stored in carbonate minerals like limestone.
- Volcanic Activity: Volcanoes release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- Metamorphism: Heat and pressure transform carbonate rocks, releasing carbon dioxide.
- Carbon Cycle: Rocks play a key role in the long-term cycling of carbon on Earth.
19. What Are The Benefits Of Using Natural Stone In Landscape Design?
The benefits of using natural stone in landscape design include its durability, aesthetic appeal, low maintenance, and environmental sustainability. Incorporating natural stone adds value and beauty to outdoor spaces.
- Durability: Natural stone is long-lasting and can withstand harsh weather conditions.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Natural stone adds a timeless and elegant touch to landscapes.
- Low Maintenance: Natural stone requires minimal maintenance.
- Environmental Sustainability: Natural stone is a natural and sustainable material.
- Increased Property Value: Natural stone enhances the value of your property.
20. How Do Rocks Protect Coastlines From Erosion?
Rocks protect coastlines from erosion by acting as natural barriers, absorbing wave energy, and stabilizing the shoreline. Large rocks and boulders are often used to create breakwaters and seawalls.
- Wave Energy Absorption: Rocks absorb wave energy, reducing the impact on the shoreline.
- Shoreline Stabilization: Rocks stabilize the shoreline, preventing erosion.
- Breakwaters and Seawalls: Large rocks are used to create breakwaters and seawalls, protecting coastlines from storms and high tides.
- Habitat Creation: Rocks provide habitat for marine organisms, enhancing biodiversity.
- Coastal Resilience: Rocks enhance the resilience of coastlines to climate change impacts.
21. What Is The Role Of Rocks In Aquifer Systems?
Rocks play a vital role in aquifer systems by storing and filtering groundwater, providing a crucial source of freshwater for human consumption and ecosystems. Their porous nature allows water to permeate and be stored.
- Water Storage: Porous rocks like sandstone and limestone store groundwater.
- Water Filtration: Rocks filter groundwater, removing impurities.
- Aquifer Formation: Rocks form the geological structure of aquifers.
- Water Supply: Aquifers provide a crucial source of freshwater for human consumption and ecosystems.
- Groundwater Recharge: Rocks facilitate the recharge of aquifers through precipitation.
22. How Do Rocks Contribute To The Formation Of Mineral Deposits?
Rocks contribute to the formation of mineral deposits by acting as host rocks for valuable minerals and ores. Hydrothermal processes and magmatic activity concentrate minerals within rock formations.
- Host Rocks: Rocks act as host rocks for mineral deposits.
- Hydrothermal Processes: Hot, mineral-rich fluids deposit minerals in rock fractures.
- Magmatic Activity: Magma cools and crystallizes, forming mineral deposits.
- Ore Formation: Rocks contain valuable ores, such as gold, silver, and copper.
- Economic Resources: Mineral deposits provide valuable economic resources for human use.
23. What Are The Environmental Impacts Of Rock Quarrying?
The environmental impacts of rock quarrying include habitat destruction, air and water pollution, and landscape alteration. Sustainable quarrying practices can mitigate these impacts.
- Habitat Destruction: Quarrying destroys natural habitats.
- Air Pollution: Quarrying generates dust and air pollutants.
- Water Pollution: Quarrying can contaminate water sources.
- Landscape Alteration: Quarrying alters the natural landscape.
- Sustainable Practices: Sustainable quarrying practices can minimize environmental impacts.
24. How Can Rocks Be Used To Create Sustainable Drainage Systems?
Rocks can be used to create sustainable drainage systems by improving soil permeability, filtering stormwater runoff, and reducing erosion. These systems help manage water resources and protect water quality.
- Soil Permeability: Rocks improve soil permeability, allowing water to infiltrate the ground.
- Stormwater Filtration: Rocks filter stormwater runoff, removing pollutants.
- Erosion Control: Rocks prevent erosion, stabilizing slopes and shorelines.
- Rain Gardens: Rocks are used in rain gardens to capture and filter stormwater.
- Permeable Pavements: Rocks are used in permeable pavements to allow water to infiltrate the ground.
25. What Are Some Examples Of Famous Rock Formations Around The World?
Examples of famous rock formations around the world include the Grand Canyon, the White Cliffs of Dover, and the Giant’s Causeway. These formations showcase the dynamic processes that shape our planet.
- Grand Canyon (USA): A vast canyon carved by the Colorado River, exposing layers of sedimentary rock.
- White Cliffs of Dover (England): Towering cliffs of chalk, formed from the remains of marine organisms.
- Giant’s Causeway (Northern Ireland): Interlocking basalt columns, formed by volcanic activity.
- Uluru (Australia): A massive sandstone monolith, sacred to indigenous Australians.
- Zhangjiajie National Forest Park (China): Towering sandstone pillars, inspiration for the movie Avatar.
26. How Do Rocks Influence The Distribution Of Plant Life?
Rocks influence the distribution of plant life by affecting soil composition, water availability, and microclimate conditions. Different rock types support different plant communities.
- Soil Composition: Rocks influence the mineral content and texture of soils.
- Water Availability: Rocks affect water drainage and retention in soils.
- Microclimate Conditions: Rocks create microclimates that can be favorable or unfavorable for plant growth.
- Plant Communities: Different rock types support different plant communities.
- Habitat Diversity: Rocks create habitat diversity, supporting a variety of plant species.
27. What Are Some Cultural And Historical Uses Of Rocks?
Cultural and historical uses of rocks include building monuments, creating tools, and practicing spiritual rituals. Rocks have played a significant role in human civilization throughout history.
- Monuments: Rocks have been used to build monuments like Stonehenge and the pyramids of Egypt.
- Tools: Rocks have been used to create tools like axes, spears, and grinding stones.
- Spiritual Rituals: Rocks have been used in spiritual rituals and ceremonies.
- Art and Sculpture: Rocks have been used to create art and sculptures.
- Building Materials: Rocks have been used as building materials for homes, temples, and walls.
28. How Do Rocks Help Regulate River Systems?
Rocks help regulate river systems by controlling water flow, preventing erosion, and providing habitat for aquatic organisms. Rocks play a vital role in maintaining the health and stability of river ecosystems.
- Water Flow Control: Rocks control the flow of water in rivers, preventing floods and droughts.
- Erosion Prevention: Rocks prevent erosion of riverbanks, stabilizing the river channel.
- Habitat Provision: Rocks provide habitat for aquatic organisms, supporting biodiversity.
- Water Quality: Rocks filter water in rivers, improving water quality.
- River Ecosystem Health: Rocks contribute to the overall health and stability of river ecosystems.
29. What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken When Working With Rocks In Landscaping?
When working with rocks in landscaping, safety precautions should include wearing protective gear, using proper lifting techniques, and ensuring stable rock placement. Safety is paramount to avoid injuries.
- Protective Gear: Wear gloves, safety glasses, and sturdy shoes.
- Lifting Techniques: Use proper lifting techniques to avoid back injuries.
- Stable Rock Placement: Ensure rocks are placed on stable foundations to prevent them from rolling or falling.
- Heavy Equipment Operation: Operate heavy equipment safely, following all safety guidelines.
- First Aid: Keep a first aid kit on hand for minor injuries.
30. What Questions Should I Ask A Rock Supplier To Ensure I Am Getting Quality Materials?
To ensure you are getting quality materials from a rock supplier, ask about the rock’s source, durability, suitability for your climate, and any warranties offered. Transparency and quality assurance are essential.
- Source of the Rock: Where does the rock come from?
- Durability: How durable is the rock?
- Suitability for Your Climate: Is the rock suitable for your climate?
- Warranty: Does the supplier offer any warranties on the rock?
- References: Can the supplier provide references from previous customers?
Discover the enduring beauty and lively potential of rocks at rockscapes.net. Explore our extensive collection, gain expert insights, and let us help you create a landscape that truly rocks.
Ready to transform your outdoor space with the dynamic beauty of rocks? Visit rockscapes.net today for inspiration, expert advice, and the finest selection of landscape stones. Let’s create a landscape that truly comes alive! You can find us at 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States or call us at +1 (480) 965-9011.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Rocks
1. How does the rock cycle make a rock lively?
The rock cycle makes a rock lively by continuously transforming it between igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic states through melting, cooling, weathering, and pressure.
2. What are the three main types of rocks, and how do they demonstrate that a rock is lively?
The three main types of rocks are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic, and they demonstrate that a rock is lively through their unique formation processes that involve dynamic geological activities.
3. How do rocks contribute to soil formation, proving that a rock is lively?
Rocks contribute to soil formation through weathering and erosion, breaking down into smaller particles and releasing minerals that enrich the soil, which is a dynamic process.
4. How do rocks help conserve water in landscaping, showing their lively role in sustainable practices?
Rocks help conserve water by reducing soil evaporation, providing shade, and improving drainage, making them essential for sustainable landscaping.
5. What types of rocks are best for landscaping in different climates?
The best rocks for landscaping vary by climate: granite and quartzite for arid climates, slate and limestone for humid climates, and basalt for coastal climates.
6. What geological factors influence rock formation?
Geological factors influencing rock formation include temperature, pressure, and chemical composition, which are key in the creation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
7. How do weathering and erosion contribute to the ever-changing nature of rocks?
Weathering and erosion break down rocks into smaller particles and transport them to new locations, reshaping landscapes and creating new geological formations.
8. How can rocks be used to create sustainable drainage systems?
Rocks can be used to improve soil permeability, filter stormwater runoff, and reduce erosion in sustainable drainage systems.
9. What are some cultural and historical uses of rocks?
Cultural and historical uses of rocks include building monuments, creating tools, and practicing spiritual rituals, reflecting their significance in human civilization.
10. What safety precautions should be taken when working with rocks in landscaping?
When working with rocks, wear protective gear, use proper lifting techniques, and ensure stable rock placement to avoid injuries.