Are Rocks Flammable? Rocks, the foundation of our landscapes, possess a diverse range of characteristics, but whether they can burn is a common question. At rockscapes.net, we delve into the fascinating world of rock composition to clarify which types are combustible and why, offering solutions for understanding and utilizing these materials in your projects. Explore the science behind rock formation and discover how different elements contribute to their flammability, enhancing your landscaping and design choices with informed decisions.
1. What Determines if Rocks Are Flammable?
The flammability of a rock depends on its composition, specifically the presence of elements that react with oxygen to produce heat and light. Rocks containing sulfur, carbon, or hydrogen are combustible, while those primarily composed of silicate minerals are not.
Some rocks burn, while others do not, because of their chemical composition. According to research from Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, the ability of a rock to burn hinges on its constituent elements and their reactivity with oxygen. Rocks that contain elements such as sulfur, carbon, and hydrogen can ignite and combust when exposed to sufficient heat. This is because these elements readily react with oxygen in the air, producing heat and light in the form of flames. Conversely, rocks composed mainly of silicate minerals, which are common in igneous formations, are generally non-combustible. These minerals have high melting points and do not easily react with oxygen, making them resistant to burning. Therefore, whether a rock is flammable depends directly on its chemical makeup and its capacity to undergo exothermic reactions with oxygen.
2. How Are the Three Main Types of Rocks Formed?
The three main types of rocks—igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic—are formed through different geological processes, each influencing their flammability.
Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rocks typically contain silicate minerals and lack combustible elements. Because they crystallize at very high temperatures, they are resistant to burning.
Sedimentary rocks are created from compressed layers of broken bits of rocks, minerals, and organic material. The presence of sulfur, carbon, and hydrogen from organic matter makes sedimentary rocks potentially combustible.
Metamorphic rocks form when existing rocks are transformed by heat and pressure. Metamorphic rocks can be combustible if they are derived from sedimentary rocks containing organic material.
Understanding the formation of these rock types helps determine their potential for burning, which is critical for landscape design and material selection at rockscapes.net.
3. What Role Do Igneous Rocks Play in Flammability?
Igneous rocks generally do not burn due to their formation process and composition, which primarily consists of silicate minerals.
Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava, processes that result in a crystalline structure composed mainly of silicate minerals. These minerals have very high melting points and do not readily react with oxygen, which is necessary for combustion. According to a study by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), igneous rocks contain few to no combustible elements such as carbon, sulfur, or hydrogen, which are essential for a material to burn. The intense heat required to melt or alter igneous rocks makes them inherently resistant to burning under normal conditions. For example, granite, a common type of igneous rock, is used in construction and landscaping precisely because of its durability and non-combustible nature. Therefore, igneous rocks play a minimal role in flammability due to their high stability and lack of reactive elements.
4. How Does Organic Matter Affect the Flammability of Sedimentary Rocks?
Organic matter significantly increases the flammability of sedimentary rocks because it introduces combustible elements like carbon, hydrogen, and sulfur.
Sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and compression of sediments, which can include fragments of other rocks, minerals, and organic material. When organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, is present in these sediments, it introduces elements like carbon, hydrogen, and sulfur. These elements are highly reactive with oxygen and can ignite when exposed to sufficient heat. For example, coal, a type of sedimentary rock, is formed from the accumulation and compression of plant matter over millions of years and is highly combustible due to its high carbon content. According to research from the University of California, Berkeley, the presence of organic carbon in sedimentary rocks directly correlates with their ability to burn. This organic material provides the fuel necessary for combustion, making sedimentary rocks with high organic content significantly more flammable than those without.
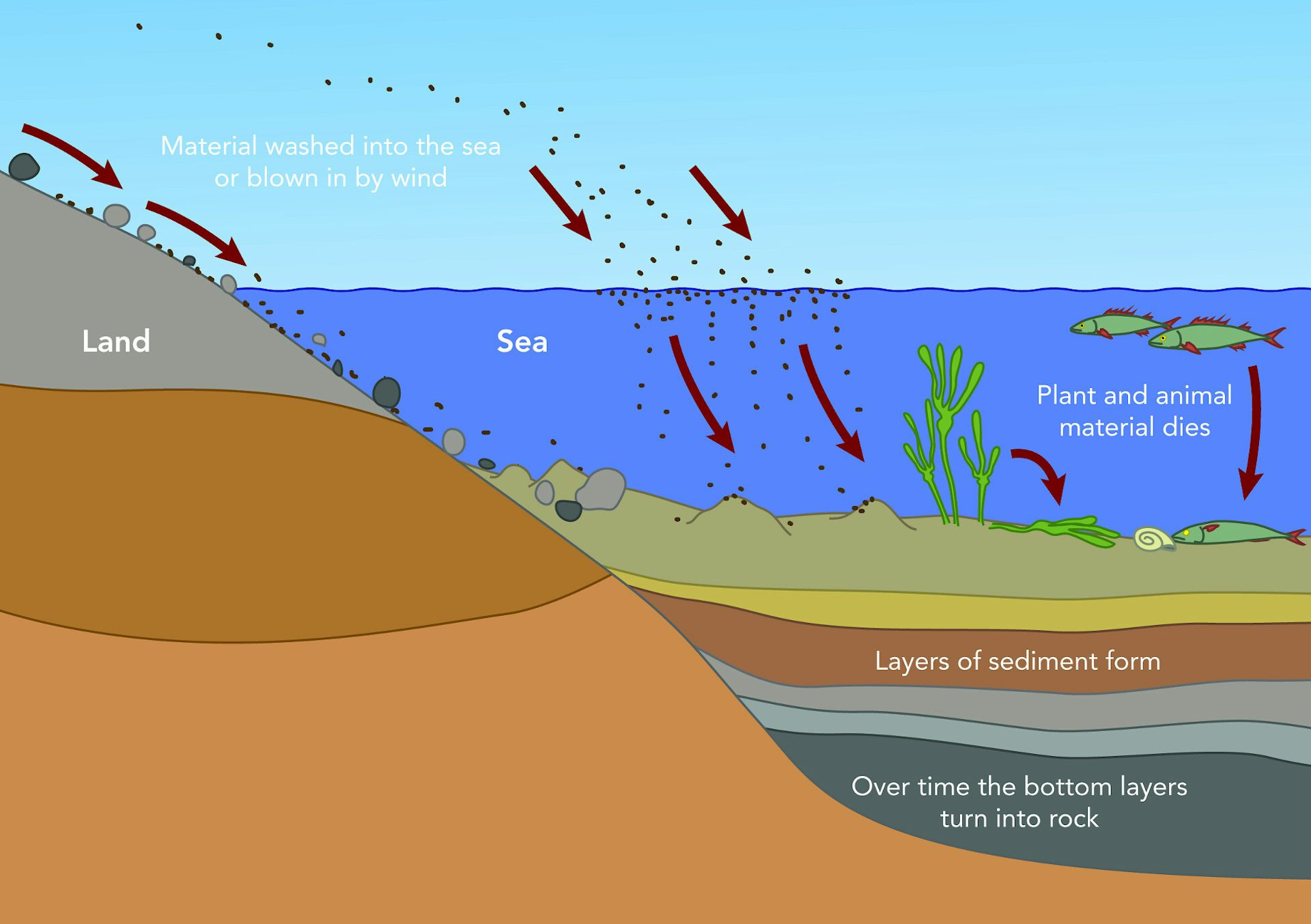 Sedimentary rock forms when layers of material are compressed over time, either on land or under water
Sedimentary rock forms when layers of material are compressed over time, either on land or under water
5. Can Metamorphic Rocks Be Flammable, and How?
Metamorphic rocks can be flammable if they are formed from sedimentary rocks that contain organic material.
Metamorphic rocks are created when existing rocks are transformed by heat and pressure. If a sedimentary rock containing organic material undergoes metamorphism, the resulting metamorphic rock may retain combustible elements. For example, anthracite coal, a metamorphic rock, is formed from sedimentary coal that has been subjected to intense pressure and heat. This process increases the carbon content, making anthracite coal highly flammable. A study by Pennsylvania State University indicates that the flammability of metamorphic rocks depends on the composition of their parent rocks. Metamorphic rocks derived from igneous rocks, which lack combustible elements, will not be flammable. However, if the parent rock is a sedimentary rock rich in organic matter, the resulting metamorphic rock can indeed be flammable. This explains why some metamorphic rocks, like anthracite, are used as fuel sources.
6. What Is Coal, and Why Is It Flammable?
Coal is a sedimentary rock primarily composed of carbon, formed from the remains of ancient plant matter, making it highly flammable.
Coal forms over millions of years from accumulated plant material that is compressed and heated deep within the Earth. This process transforms the plant matter into a carbon-rich substance, which is the main component of coal. Due to its high carbon content, coal is extremely reactive with oxygen and readily ignites when exposed to heat. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), coal is classified into different types, such as lignite, bituminous, and anthracite, based on its carbon content and energy density. Anthracite coal, the most metamorphosed type, has the highest carbon content and burns with a clean, hot flame. The flammability of coal makes it a valuable energy source, but also poses risks such as underground coal fires, as seen in places like Centralia, Pennsylvania.
7. What Are Some Real-World Examples of Burning Rocks?
Examples of burning rocks include coal seam fires in Centralia, Pennsylvania, and instances of diamonds combusting under intense heat.
In Centralia, Pennsylvania, an underground coal seam has been burning for over 50 years, a stark example of a rock—coal—combusting in the real world. This fire started in the 1960s and continues to burn due to the high carbon content of the coal. Additionally, diamonds, which are pure carbon, can combust under intense heat. French chemist Antoine Lavoisier demonstrated this in 1772 by burning a diamond with a magnifying glass. These examples illustrate that rocks containing high amounts of carbon or other combustible elements can indeed burn under specific conditions. Research from the Smithsonian Magazine highlights the Centralia coal fire as a persistent environmental issue, while historical accounts document Lavoisier’s experiment as a scientific milestone.
8. How Do Coal Seam Fires Start and What Are Their Impacts?
Coal seam fires typically start from natural causes like lightning strikes or human activities such as mining, and they result in significant environmental and health impacts.
Coal seam fires often begin when a source of ignition, such as lightning or a surface fire, comes into contact with exposed coal seams. Human activities, like improper mining practices, can also ignite these fires by exposing coal to air and heat. Once ignited, these fires can burn for decades or even centuries, moving slowly through underground coal deposits. According to a report by the U.S. Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement, coal seam fires release large amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. They also emit toxic pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide and particulate matter, which degrade air quality and pose serious health risks to nearby communities. The fires can cause ground subsidence, destroy vegetation, and contaminate water sources, leading to long-term environmental damage.
9. Can Diamonds, the Hardest Mineral, Actually Burn?
Yes, diamonds, which are pure carbon, can burn under specific conditions, such as high temperatures and sufficient oxygen.
Despite being the hardest mineral, diamonds are composed entirely of carbon and can undergo combustion if the conditions are right. In 1772, Antoine Lavoisier demonstrated that diamonds could be burned by focusing sunlight on them with a magnifying glass, raising their temperature to the point of combustion. According to the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), diamonds require a temperature of around 1292 degrees Fahrenheit (700 degrees Celsius) in an oxygen-rich environment to ignite. When a diamond burns, it reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, similar to the combustion of other forms of carbon. While it is not easy to set a diamond on fire under normal conditions, this experiment proves that even the hardest mineral is not immune to burning if the necessary conditions are met.
10. Why Is It Important to Understand Which Rocks Are Flammable?
Understanding which rocks are flammable is crucial for safety, environmental protection, and making informed decisions in construction and landscaping.
Knowing the flammability of different types of rocks is essential for several reasons. For safety, it helps in preventing accidental fires and managing risks associated with combustible materials like coal. Environmentally, it aids in controlling and mitigating the impacts of coal seam fires, which release harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases. In construction and landscaping, understanding which rocks are flammable ensures the selection of appropriate materials for various applications, reducing fire hazards and promoting sustainable practices. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), using non-combustible materials in building construction can significantly reduce the risk of fire spread and structural damage. Therefore, understanding rock flammability is vital for ensuring safety, protecting the environment, and making informed choices in various industries.
11. How Can Rockscapes.net Help You Choose the Right Rocks for Your Landscape?
Rockscapes.net provides comprehensive information and expert guidance to help you select the best rocks for your landscape, ensuring both aesthetic appeal and safety.
At Rockscapes.net, we offer detailed profiles of various rock types, including their composition, flammability, and suitability for different landscaping applications. Our expert team can provide personalized consultations to help you choose rocks that meet your design preferences and safety requirements. We also offer resources on sustainable landscaping practices, ensuring that your project is both beautiful and environmentally responsible. Whether you are looking for non-combustible options for fire pits or decorative stones that enhance your garden, Rockscapes.net is your go-to source for informed rock selection. Contact us at 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States, or call +1 (480) 965-9011 to explore our extensive collection and receive expert advice.
12. What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken When Using Rocks in Fire Pits?
When using rocks in fire pits, it is essential to choose non-porous, non-combustible rocks and arrange them properly to prevent accidents and ensure safety.
Using the wrong type of rock in a fire pit can lead to dangerous situations. Porous rocks like sandstone and lava rock can trap moisture, which, when heated, can cause the rock to explode. It is crucial to select dense, non-porous rocks such as granite or slate, which do not absorb water and are less likely to crack or explode under high heat. Proper arrangement is also important; avoid tightly packing the rocks, as this can restrict airflow and increase the risk of overheating. Always allow adequate ventilation around the fire pit and keep a safe distance from flammable materials. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) recommends keeping a fire extinguisher or water hose nearby in case of emergencies.
13. What Are Some Non-Flammable Rock Options for Landscaping?
Non-flammable rock options for landscaping include granite, slate, and basalt, which are durable, aesthetically pleasing, and safe for various applications.
When selecting rocks for landscaping, it is important to choose materials that are not only visually appealing but also safe and durable. Granite is an excellent option due to its density and resistance to heat and weathering. Slate is another good choice, offering a unique texture and color that can enhance any landscape design. Basalt, an igneous rock, is also non-flammable and provides a dark, dramatic look. These rocks are suitable for pathways, retaining walls, decorative features, and fire pits, ensuring that your landscape remains both beautiful and safe. Rockscapes.net offers a wide variety of these non-flammable options, allowing you to create stunning landscapes with peace of mind.
14. How Do Different Climates Affect the Choice of Rocks for Landscaping?
Different climates significantly influence the choice of rocks for landscaping, requiring consideration of factors like freeze-thaw cycles, heat absorption, and weathering.
In regions with frequent freeze-thaw cycles, it is crucial to select rocks that are resistant to cracking and spalling. Porous rocks that absorb water can expand when frozen, leading to damage. Dense, non-porous rocks like granite and quartzite are better suited for these climates. In hot climates, rocks that reflect heat, such as light-colored limestone or sandstone, can help reduce the overall temperature of the landscape. Dark-colored rocks like basalt absorb more heat, which can be beneficial in cooler climates but may exacerbate heat issues in hotter regions. Additionally, consider the effects of weathering; some rocks are more resistant to erosion and chemical breakdown than others. The American Society of Landscape Architects (ASLA) recommends consulting with a local expert to choose rocks that are best suited for your specific climate and environmental conditions.
15. Where Can You Find Reliable Information About Rock Properties and Safety?
Reliable information about rock properties and safety can be found at geological surveys, universities, and specialized websites like Rockscapes.net.
Geological surveys, such as the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), provide comprehensive data on rock types, their properties, and their distribution. Universities with geology and environmental science departments often conduct research on rock properties and their behavior under different conditions. Specialized websites like Rockscapes.net offer curated information on rocks used in landscaping and construction, including their flammability and safety considerations. Additionally, professional organizations like the American Geosciences Institute (AGI) provide resources and publications on earth science topics. Consulting these sources ensures that you have access to accurate and reliable information for making informed decisions about rock selection and usage.
16. What Are the Environmental Benefits of Using Rocks in Landscaping?
Using rocks in landscaping offers numerous environmental benefits, including reduced water consumption, erosion control, and habitat creation.
Rocks can significantly reduce water consumption in landscaping by minimizing the need for irrigation. They act as a natural mulch, retaining soil moisture and reducing evaporation. Rocks also help control erosion by stabilizing soil on slopes and preventing runoff. Additionally, rock landscapes can create habitats for various species of insects, reptiles, and small mammals, enhancing biodiversity. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), implementing sustainable landscaping practices, such as using rocks and native plants, can significantly reduce water usage and promote ecological balance. Furthermore, rock landscapes require less maintenance than traditional lawns, reducing the need for fertilizers and pesticides, which can harm the environment.
17. How Can Rocks Be Used to Create Fire-Resistant Landscapes?
Rocks can be used to create fire-resistant landscapes by acting as a barrier against the spread of fire and reducing the amount of combustible vegetation.
Creating a fire-resistant landscape involves minimizing the amount of flammable material around your home. Rocks can play a crucial role in this by creating non-combustible zones that prevent the spread of fire. Using gravel or rock mulch instead of wood chips around plants can reduce the risk of ignition. Creating rock pathways and patios can also serve as firebreaks, preventing flames from spreading to other parts of the landscape. The Firewise USA program recommends maintaining a 30-foot defensible space around your home, using non-flammable materials like rocks and drought-resistant plants. These strategies can significantly reduce the risk of property damage in the event of a wildfire.
18. What Types of Rocks Are Best Suited for Building a Fire Pit?
The best types of rocks for building a fire pit are dense, non-porous options like granite, slate, and fire-resistant bricks, which can withstand high temperatures without cracking or exploding.
When constructing a fire pit, safety is paramount. It is essential to choose rocks that can withstand the intense heat without posing a risk of explosion. Granite is an excellent choice due to its density and low porosity. Slate is another good option, offering a natural, aesthetically pleasing look while being heat-resistant. Fire-resistant bricks, specifically designed for high-temperature applications, are also a reliable choice. Avoid using porous rocks like sandstone or river rocks, as they can trap moisture and explode when heated. Always consult with a professional or refer to local building codes to ensure that your fire pit is constructed safely and complies with all regulations.
19. How Do You Maintain a Rock Landscape to Ensure Safety and Longevity?
Maintaining a rock landscape involves regular inspections, removal of debris, and proper drainage to ensure safety, prevent erosion, and prolong its lifespan.
Regular inspections are essential to identify any signs of instability, such as shifting rocks or erosion. Remove any accumulated debris, such as leaves and twigs, which can become fire hazards. Ensure that drainage systems are functioning properly to prevent water from pooling and causing damage to the landscape. Periodically check for weeds and invasive plants, and remove them to prevent them from disrupting the rock arrangement. According to the International Society of Arboriculture (ISA), proper maintenance practices can significantly extend the life of a landscape and reduce the risk of accidents. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your rock landscape remains safe, attractive, and sustainable for years to come.
20. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Rocks and Fire?
Common misconceptions about rocks and fire include the belief that all rocks are non-combustible and that river rocks are safe for use in fire pits.
One common misconception is that all rocks are inherently non-combustible. While many rocks, such as granite and slate, are indeed fire-resistant, others, like coal, can burn under specific conditions. Another misconception is that river rocks are safe for use in fire pits. River rocks are often porous and can trap moisture, which can cause them to explode when heated. It is also a common misconception that lava rocks are safe for fire pits, though they are, it is important to note that they can explode, though they are very safe, if they are not pre-dried thoroughly. Understanding these misconceptions is crucial for ensuring safety and making informed decisions when using rocks in landscapes and fire features. Always consult with a professional or refer to reliable sources like Rockscapes.net for accurate information about rock properties and safety precautions.
FAQ: Are Rocks Flammable?
1. Are all rocks non-flammable?
No, not all rocks are non-flammable. Some rocks, like coal, contain combustible materials such as carbon and can burn under certain conditions.
2. What makes a rock flammable?
A rock is flammable if it contains elements that react with oxygen to produce heat and light. Common combustible elements found in rocks include carbon, sulfur, and hydrogen.
3. Can igneous rocks burn?
Generally, igneous rocks do not burn because they are formed from cooled magma and primarily contain silicate minerals, which are not combustible.
4. Are sedimentary rocks flammable?
Some sedimentary rocks can be flammable, especially those containing organic material. Coal, for example, is a sedimentary rock that is highly flammable due to its high carbon content.
5. Is it safe to use any type of rock in a fire pit?
No, it is not safe to use any type of rock in a fire pit. Porous rocks like sandstone and river rocks can trap moisture and explode when heated.
6. Which rocks are safe to use in a fire pit?
Safe rocks to use in a fire pit include dense, non-porous options like granite, slate, and fire-resistant bricks.
7. Can diamonds burn?
Yes, diamonds, which are pure carbon, can burn under specific conditions, such as high temperatures and sufficient oxygen.
8. What is a coal seam fire?
A coal seam fire is an underground fire that occurs in a coal deposit. These fires can start from natural causes or human activities and can burn for decades or even centuries.
9. How can I create a fire-resistant landscape?
To create a fire-resistant landscape, use non-combustible materials like rocks and gravel, maintain a defensible space around your home, and choose drought-resistant plants.
10. Where can I find more information about rock properties and safety?
You can find reliable information about rock properties and safety at geological surveys, universities, and specialized websites like Rockscapes.net.
By understanding the flammability of rocks and taking appropriate safety measures, you can create beautiful and safe landscapes that enhance your outdoor living space. Visit Rockscapes.net for more information and expert guidance on selecting the right rocks for your needs.
At Rockscapes.net, we are dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to create stunning and safe rock landscapes. Explore our website today to discover a wide range of rock options and expert advice, and let us help you bring your landscaping vision to life. Contact us at Address: 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States. Phone: +1 (480) 965-9011. Website: rockscapes.net.
