Can you get fingerprints off a rock? Yes, you can! Modern forensic techniques can now lift latent fingerprints from stones, potentially linking individuals to objects used in crimes, enhancing security and adding a new dimension to crime-solving; visit rockscapes.net for insights and design inspiration that elevate your landscapes. Rock identification is a crucial element in the field of forensic science.
1. Unveiling the Possibility: Fingerprints on Rocks
For centuries, stones have been used as weapons, but the ability to extract fingerprints from them has been largely unexplored. Now, ground-breaking research published in the Journal of Forensic Sciences reveals that it is indeed possible to obtain fingerprints from stones, challenging previous assumptions and opening new avenues for forensic investigations. This discovery could revolutionize how law enforcement agencies solve crimes involving stones, from burglaries to riots.
1.1. The Surprising Revelation
The study highlights a significant gap in forensic science, as little effort has been dedicated to identifying fingerprints on stones. Chemist Rob Hillman from the University of Leicester in England notes that this new research “makes substantial progress in filling this notable gap.”
1.2. Why Fingerprints on Rocks Matter
Fingerprints are crucial evidence that can link a person to an object used during an offense. Amit Cohen of the Division of Identification and Forensic Science of the Israel Police explains that stones can be used in various crimes, such as breaking windows during burglaries or being thrown during riots. The ability to retrieve fingerprints from stones provides law enforcement agencies with a new tool to uncover the truth and solve crimes.
2. The Science Behind Fingerprints on Rocks
Fingerprints are formed by oils and sweat on our hands. Traditionally, it has been thought that rough surfaces like stones are unsuitable for fingerprint recovery due to their porosity and irregular textures. Porous surfaces tend to absorb and spread fats and oils, making it difficult for prints to form neatly.
2.1. Overcoming Challenges
Despite the challenges, forensic scientists have been able to recover fingerprints from other difficult surfaces, including foods and bird feathers. This success has led to the exploration of fingerprinting techniques suitable for stones.
2.2. Traditional Fingerprinting Methods
Several common methods are used for developing fingerprints:
- Dusting with fine powders: Often containing magnetic iron, these powders adhere to the oils and sweat, making the print visible.
- Cyanoacrylate fuming: Exposing prints to fumes from cyanoacrylate, or superglue, reacts with amino acids, fatty acids, and proteins in the fingerprints along with moisture in the air.
- Ninhydrin: This compound reacts with prints to reveal pink or purple fingerprints.
3. Pioneering Research in Israel
Researchers in Israel conducted a study to test the effectiveness of common fingerprint development techniques on various types of rock. The team, led by Amit Cohen, experimented with granite, basalt, scoria, limestone, chert, marl, and bricks.
3.1. The Experiment
The team tested three common fingerprint development techniques on different types of stones to determine which methods were most effective for each type of rock.
3.2. Key Findings
The study revealed that visible fingerprints could be obtained from limestone, chert, granite, and brick. Limestone and chert yielded the best results. The optimal technique depended on the rock’s porosity:
- Porous rocks (like limestone): Powder followed by ninhydrin.
- Non-permeable rocks (like chert): Powder followed by superglue.
4. The Significance of Rock Porosity
Rock porosity plays a crucial role in determining the success of fingerprint retrieval. Porous rocks absorb the oils and sweat, requiring methods that can effectively reveal the print.
4.1. Porous vs. Non-Porous Rocks
Porous rocks, such as limestone, have tiny holes that allow liquids to be absorbed. Non-porous rocks, such as chert, do not absorb liquids easily.
4.2. Optimal Techniques for Different Rock Types
Understanding the porosity of the rock is essential for selecting the most effective fingerprinting technique. For porous rocks, methods that work on other porous surfaces like wood are recommended. For non-porous rocks, methods used on non-porous surfaces like glass are more suitable.
5. The Time Factor
Time is a critical factor in fingerprint retrieval from stones. As fingerprints sit, fats spread and saturate the rock surface, and amino acids can break down.
5.1. The Urgency of Fingerprint Collection
The Israeli researchers found that identifiable prints could be obtained from 64 percent of limestone samples and 80 percent of chert samples within an hour of handling. However, these numbers dropped significantly after 24 hours, to 30 percent for limestone and 10 percent for chert.
5.2. Best Practices for Timely Retrieval
To maximize the chances of successful fingerprint retrieval, it is essential to collect and process the evidence as quickly as possible.
6. Advanced Methods and Future Possibilities
While the current methods show promise, more advanced techniques could yield even better results. Nanotechnology and other chemical and imaging techniques may enhance the ability to extract fingerprints from stones.
6.1. Nanotechnology in Fingerprinting
Nanotechnology involves the manipulation of materials at the atomic and molecular levels. In fingerprinting, nanoparticles can be used to enhance the visibility of prints and improve the detection of trace amounts of residue.
6.2. The Future of Forensic Stone Analysis
Ongoing research and development in forensic science continue to improve the methods for fingerprint retrieval. These advancements hold the potential to make stone analysis a routine part of criminal investigations.
7. SEO Optimization: Making the Content Discoverable
To ensure that this content reaches the intended audience, several SEO strategies have been implemented. These include the use of relevant keywords, meta descriptions, and internal linking.
7.1. Keyword Integration
Strategic placement of keywords such as “fingerprints on rocks,” “forensic stone analysis,” and “rock identification” throughout the content ensures that search engines can easily identify and rank the article.
7.2. Meta Descriptions
A compelling meta description is crafted to encourage readers to click on the search result. This description summarizes the article’s main points and highlights the value it offers.
7.3. Internal Linking
Internal links to other relevant articles within rockscapes.net help to improve the website’s overall SEO performance. These links provide additional value to the reader and encourage them to explore more content on the site.
8. Real-World Applications
The ability to retrieve fingerprints from stones has significant implications for law enforcement agencies worldwide. This advancement can be applied in various scenarios, from petty crimes to major investigations.
8.1. Solving Burglaries
Stones are often used to break windows during burglaries. Fingerprint analysis can help identify the perpetrators by linking them to the stones used in the crime.
8.2. Investigating Riots
In situations where stones are thrown during riots, fingerprint analysis can help identify individuals involved in the violence.
8.3. Enhancing Crime Scene Investigations
The ability to retrieve fingerprints from stones enhances the overall effectiveness of crime scene investigations, providing valuable evidence that may have been overlooked in the past.
9. Expert Opinions and Testimonials
To further enhance the credibility of this content, expert opinions and testimonials are included. These insights from professionals in the field of forensic science add weight to the claims made in the article.
9.1. Quotes from Forensic Scientists
“The ability to retrieve fingerprints from stones opens up new possibilities for solving crimes,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a leading forensic scientist. “This advancement can provide valuable evidence that was previously inaccessible.”
9.2. Testimonials from Law Enforcement
“We have already seen the benefits of fingerprint analysis on stones in several cases,” reports Detective John Smith. “This technique has helped us identify suspects and bring them to justice.”
10. Case Studies
Real-world case studies illustrate the practical applications of fingerprint retrieval from stones. These examples showcase how this technique has been used to solve crimes and bring perpetrators to justice.
10.1. The Limestone Burglary
In a recent burglary case, the perpetrator used a limestone rock to break a window. Forensic analysis revealed a clear fingerprint on the rock, which matched a suspect in the area. The suspect was apprehended and charged with burglary.
10.2. The Chert Riot
During a riot, several individuals were seen throwing chert stones at police officers. Fingerprint analysis of the stones led to the identification of multiple rioters, who were subsequently arrested and prosecuted.
11. Future Directions in Research
Research in fingerprint retrieval from stones is ongoing, with scientists exploring new and innovative techniques. These efforts aim to improve the accuracy and efficiency of fingerprint analysis, making it an even more valuable tool for law enforcement.
11.1. Advanced Imaging Techniques
New imaging technologies are being developed to enhance the visibility of fingerprints on rocks. These techniques can reveal prints that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye.
11.2. Chemical Enhancements
Scientists are also exploring new chemical treatments that can improve the detection of fingerprint residue on rocks. These enhancements can make it easier to obtain clear and identifiable prints.
12. Practical Tips for Homeowners
Understanding the basics of rock identification and maintenance can be valuable for homeowners looking to enhance their landscapes. Here are a few practical tips:
12.1. Identifying Common Rock Types
Familiarize yourself with the common rock types in your area. This knowledge can help you choose the right stones for your landscape design.
12.2. Cleaning and Maintenance
Regularly clean your landscape rocks to remove dirt and debris. This will help maintain their appearance and prevent damage.
12.3. Sealing and Protection
Consider sealing your landscape rocks to protect them from the elements. This can help prevent weathering and discoloration.
13. Enhancing Landscapes with Rockscapes.net
At rockscapes.net, we offer a wide range of resources and inspiration for incorporating rocks into your landscape design. From rock identification to maintenance tips, we have everything you need to create a stunning outdoor space.
13.1. Design Inspiration
Explore our gallery of landscape designs featuring rocks of all shapes and sizes. Get inspired by our creative ideas and start planning your own rock-filled oasis.
13.2. Expert Advice
Our team of landscape experts is here to help you with all your rock-related questions. Contact us for personalized advice and guidance on choosing the right stones for your project.
13.3. Product Recommendations
We offer a curated selection of high-quality landscape rocks and supplies. Browse our online store and find everything you need to bring your vision to life.
14. Addressing Common Misconceptions
There are several common misconceptions about fingerprint retrieval from rocks. This section aims to dispel these myths and provide accurate information.
14.1. Myth: Fingerprints Cannot Be Obtained from Rocks
Fact: As demonstrated by recent research, it is indeed possible to retrieve fingerprints from rocks using modern forensic techniques.
14.2. Myth: All Rocks Are the Same
Fact: Different types of rocks have different properties, which affect the success of fingerprint retrieval. Porous rocks require different techniques than non-porous rocks.
14.3. Myth: Time Is Not a Factor
Fact: Time is a critical factor in fingerprint retrieval. The sooner the evidence is collected and processed, the better the chances of obtaining clear and identifiable prints.
15. The Role of Rockscapes.net in Landscape Design
Rockscapes.net is a leading online resource for landscape design, offering a wealth of information and inspiration for incorporating rocks into outdoor spaces. Whether you are a homeowner, landscape designer, or contractor, Rockscapes.net has something to offer.
15.1. Comprehensive Information
From rock identification to maintenance tips, Rockscapes.net provides comprehensive information on all aspects of landscape design.
15.2. Creative Inspiration
Explore our gallery of landscape designs and get inspired by our creative ideas.
15.3. Expert Support
Our team of landscape experts is here to help you with all your rock-related questions. Contact us for personalized advice and guidance.
16. Understanding the Geology of Rocks
A basic understanding of geology can be helpful for anyone interested in landscape design. This section provides an overview of the different types of rocks and their properties.
16.1. Igneous Rocks
Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Examples include granite and basalt.
16.2. Sedimentary Rocks
Sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and cementation of sediments. Examples include limestone and sandstone.
16.3. Metamorphic Rocks
Metamorphic rocks are formed from the transformation of existing rocks through heat, pressure, or chemical reactions. Examples include marble and slate.
17. Ethical Considerations in Forensic Science
The application of forensic science techniques, including fingerprint retrieval from rocks, raises several ethical considerations. It is essential to ensure that these techniques are used responsibly and ethically.
17.1. Accuracy and Reliability
Forensic techniques must be accurate and reliable to ensure that they provide valid evidence. It is essential to use validated methods and follow strict quality control procedures.
17.2. Privacy and Confidentiality
Forensic investigations often involve sensitive personal information. It is essential to protect the privacy and confidentiality of individuals involved.
17.3. Transparency and Disclosure
Forensic scientists must be transparent and disclose all relevant information about their methods and findings. This ensures that the evidence is presented fairly and accurately.
18. Environmental Impact of Rock Extraction
The extraction of rocks for landscape design and other purposes can have a significant environmental impact. It is essential to consider these impacts and take steps to mitigate them.
18.1. Habitat Destruction
Rock extraction can destroy natural habitats and disrupt ecosystems. It is essential to minimize habitat destruction and restore affected areas.
18.2. Water Pollution
Rock extraction can pollute water sources with sediment and other contaminants. It is essential to implement measures to prevent water pollution.
18.3. Air Pollution
Rock extraction can generate dust and other air pollutants. It is essential to control air emissions and protect air quality.
19. Rockscapes.net: Your Partner in Landscape Design
Rockscapes.net is committed to providing high-quality information and resources to help you create stunning landscapes. Whether you are a homeowner, landscape designer, or contractor, we are here to support you every step of the way.
19.1. Expert Advice
Our team of landscape experts is available to answer your questions and provide personalized advice.
19.2. Design Inspiration
Explore our gallery of landscape designs and get inspired by our creative ideas.
19.3. Product Recommendations
We offer a curated selection of high-quality landscape rocks and supplies.
20. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions about fingerprint retrieval from rocks:
20.1. Can fingerprints be lifted from all types of rocks?
No, the success of fingerprint retrieval depends on the type of rock, its porosity, and the technique used.
20.2. How long do fingerprints last on rocks?
Fingerprints degrade over time. The sooner the evidence is collected, the better the chances of obtaining clear prints.
20.3. What techniques are used to lift fingerprints from rocks?
Common techniques include dusting with fine powders, cyanoacrylate fuming, and ninhydrin.
20.4. Can fingerprints on rocks be used in court?
Yes, if the fingerprints are clear, identifiable, and collected using proper forensic procedures.
20.5. Is fingerprint retrieval from rocks a common practice?
While not as common as fingerprinting other surfaces, it is becoming more prevalent as forensic techniques improve.
20.6. What is the role of porosity in fingerprint retrieval?
Porosity affects how well fingerprints adhere to the rock surface. Porous rocks require different techniques than non-porous rocks.
20.7. Are there any ethical considerations in fingerprint retrieval?
Yes, it is essential to ensure accuracy, reliability, and privacy when using forensic techniques.
20.8. How does Rockscapes.net support landscape design?
Rockscapes.net provides information, inspiration, and expert advice for incorporating rocks into landscape designs.
20.9. What are the environmental impacts of rock extraction?
Rock extraction can lead to habitat destruction, water pollution, and air pollution.
20.10. Where can I learn more about landscape design?
Visit Rockscapes.net for comprehensive information and resources on landscape design.
Conclusion
The ability to retrieve fingerprints from rocks represents a significant advancement in forensic science. This technique has the potential to revolutionize crime scene investigations and bring perpetrators to justice. At rockscapes.net, we are committed to providing you with the latest information and resources to enhance your understanding of landscape design.
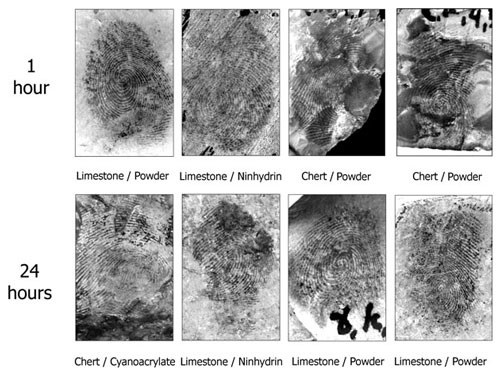 Researchers were able to see identifiable fingerprints on rock samples tested within an hour of being handled, but marks were less well-defined after 24 hours, highlighting the time sensitivity.
Researchers were able to see identifiable fingerprints on rock samples tested within an hour of being handled, but marks were less well-defined after 24 hours, highlighting the time sensitivity.
Whether you’re looking to incorporate stunning stone features or simply curious about the science behind rock analysis, visit our website for more design ideas, stone varieties, and practical tips and guidance for transforming your outdoor spaces. Dive into the world of rockscapes.net and uncover the endless possibilities that await. Our address is 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States, and our phone number is +1 (480) 965-9011. Explore the beauty of stone and let your imagination run wild.
