Are rocks useful to us? Absolutely! Rocks are essential to our daily lives, from building materials to technological components, and rockscapes.net is your go-to resource for understanding how these geological wonders enhance our world. This article explores the many ways rocks benefit us, highlighting their diverse applications and crucial role in our environment and economy. Delve into the world of geology and landscape design as we uncover the utility of various stone formations, uncovering how rock materials and landscape rocks impact our lives.
1. Rocks as Fundamental Building Blocks
How Are Rocks Useful To Us when it comes to construction? They are the foundation! Rocks provide essential raw materials for constructing our homes, buildings, and infrastructure.
- Construction Materials: Granite, limestone, and sandstone are commonly used as building stones. Their durability and aesthetic appeal make them ideal for facades, foundations, and decorative elements. For example, granite’s compressive strength makes it a popular choice for structural support, while limestone’s workability allows for intricate architectural details.
 Granite used in building facade
Granite used in building facade - Aggregates: Crushed rocks, such as gravel and crushed stone, are vital components of concrete and asphalt. These aggregates provide bulk and strength to these composite materials, ensuring the longevity and stability of roads, bridges, and buildings.
- Cement Production: Limestone is a primary ingredient in cement manufacturing. Cement is the binder that holds concrete together, making it an indispensable material in modern construction.
- Landscaping: Rocks are increasingly utilized in landscaping for both practical and aesthetic purposes. They can serve as retaining walls, pathways, decorative features, and erosion control measures. Rockscapes.net offers a wide array of design ideas and practical tips for incorporating rocks into your outdoor spaces.
2. Rocks in Energy Production
How are rocks useful to us in powering our world? They are sources for both traditional and renewable energy.
- Fossil Fuels: Sedimentary rocks like shale, sandstone, and limestone often contain fossil fuels such as oil, natural gas, and coal. These resources, formed from the remains of ancient organisms, are extracted and processed to generate electricity, fuel vehicles, and heat homes.
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy harnesses the heat stored within the Earth’s crust. Geothermal power plants tap into underground reservoirs of hot water and steam, which are heated by rocks deep beneath the surface. This renewable energy source provides a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels in certain regions.
- Nuclear Energy: Certain rocks contain uranium, a radioactive element used in nuclear power plants. Nuclear fission generates heat, which is used to produce steam and drive turbines to generate electricity.
- Hydropower: While not directly providing the energy, rocks are essential in the construction of dams and reservoirs that facilitate hydroelectric power generation. The stability and impermeability of rock formations are critical for creating these large-scale water storage systems.
3. Rocks in Agriculture
How are rocks useful to us in nourishing our crops? They contribute essential nutrients to the soil.
- Soil Enrichment: Rocks gradually weather and break down, releasing essential minerals into the soil. These minerals, such as potassium, phosphorus, and calcium, are vital for plant growth and overall soil health.
- Phosphate Fertilizers: Phosphate rock is a key ingredient in the production of phosphate fertilizers. Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for plant development, promoting root growth, flowering, and fruit production.
- Potash Fertilizers: Potash, derived from potassium-rich rocks, is another important fertilizer. Potassium helps plants regulate water uptake, resist diseases, and develop strong stems.
- Liming: Agricultural lime, made from crushed limestone or dolomite, is used to neutralize acidic soils. By raising the pH level of the soil, liming improves nutrient availability and creates a more favorable environment for plant growth.
4. Rocks in Manufacturing and Industry
How are rocks useful to us in creating the products we use daily? They are essential raw materials for numerous industrial processes.
- Metal Production: Ores, which are rocks containing valuable metals, are mined and processed to extract metals like iron, copper, aluminum, and gold. These metals are used in a wide range of applications, from construction and transportation to electronics and manufacturing.
- Glass Production: Sandstone, particularly quartz-rich sand, is a primary ingredient in glass manufacturing. Glass is used in windows, containers, optical fibers, and countless other products.
- Ceramics Production: Clay, a type of fine-grained sedimentary rock, is used to make ceramics. Ceramics are used in pottery, tiles, bricks, and advanced materials for various industries.
- Chemical Industry: Rocks provide raw materials for producing a variety of chemicals. For example, sulfur is extracted from sulfur-bearing rocks and used to manufacture sulfuric acid, a key ingredient in many industrial processes.
 Geologist sampling basaltic lava flow for geochronology
Geologist sampling basaltic lava flow for geochronology
5. Rocks in Environmental Management
How are rocks useful to us in protecting our environment? They play a critical role in various environmental applications.
- Water Filtration: Sand and gravel are used in water filtration systems to remove impurities and pollutants from water. These materials provide a porous medium that traps sediment, bacteria, and other contaminants.
- Wastewater Treatment: Rocks are also used in wastewater treatment processes. Limestone, for example, can be used to neutralize acidic wastewater, while other types of rocks can help remove heavy metals and other pollutants.
- Erosion Control: Rocks are frequently used to stabilize shorelines, riverbanks, and slopes. Rock riprap, which consists of large boulders and stones, protects against erosion caused by water and wind.
- Carbon Sequestration: Certain types of rocks, such as basalt, can react with carbon dioxide to form stable minerals, effectively removing CO2 from the atmosphere. This process, known as mineral carbonation, has the potential to play a significant role in mitigating climate change. According to research from Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, in July 2025, basalt rock formations in the US Southwest provide the most cost-effective places for Carbon Sequestration.
- Mine Reclamation: Rocks and minerals are used in mine reclamation projects to stabilize tailings piles, control acid mine drainage, and restore the landscape. These efforts help minimize the environmental impacts of mining activities.
6. Rocks in Technology
How are rocks useful to us in advancing our technology? They provide essential elements for modern devices.
- Electronics: Rare earth elements, which are found in certain rocks, are crucial components in smartphones, computers, and other electronic devices. These elements are used in magnets, displays, and other critical components.
- Batteries: Lithium, another element found in rocks, is a key ingredient in lithium-ion batteries. These batteries power electric vehicles, laptops, and mobile phones.
- Semiconductors: Silicon, derived from quartz-rich rocks, is the primary material used in semiconductors. Semiconductors are the building blocks of computer chips and other electronic components.
- Aerospace: Rocks provide materials for high-performance alloys used in aerospace applications. These alloys must withstand extreme temperatures and stresses, making them essential for aircraft and spacecraft.
7. Rocks in Art and Decoration
How are rocks useful to us in enhancing our aesthetic environment? They are valued for their beauty and artistic potential.
- Sculpture: Marble, granite, and other types of rocks are used by sculptors to create works of art. The durability and unique textures of these materials make them ideal for producing enduring and visually stunning sculptures.
- Jewelry: Gemstones, which are rare and beautiful minerals found in rocks, are used in jewelry. Diamonds, emeralds, rubies, and sapphires are among the most prized gemstones.
- Ornamental Stones: Decorative stones like agate, jasper, and petrified wood are used to create ornamental objects, such as paperweights, bookends, and decorative tiles.
- Aquariums: Rocks and gravel are used in aquariums to create a natural-looking environment for fish and other aquatic organisms. These materials provide substrate for plants and hiding places for animals.
8. Rocks in Scientific Research
How are rocks useful to us in understanding our planet? They provide invaluable information about Earth’s history and processes.
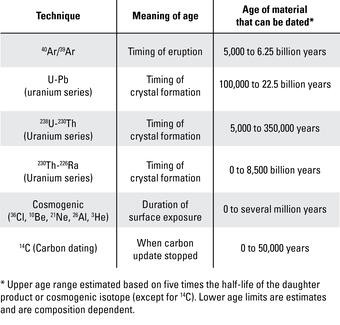
- Geochronology: Rocks are used to determine the age of the Earth, its geological formations, and past events. Radiometric dating techniques, which measure the decay of radioactive isotopes in rocks, provide precise age estimates.
- Paleontology: Rocks contain fossils, which are the preserved remains of ancient organisms. Fossils provide evidence of past life forms and help scientists understand the evolution of life on Earth.
- Geophysics: Rocks are studied to understand the physical properties of the Earth, such as its magnetic field, gravity, and seismic activity. These studies help scientists monitor and predict earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and other geological hazards.
- Mineralogy: The study of minerals, which are the building blocks of rocks, provides insights into the chemical composition and structure of the Earth. Mineralogical studies have led to the discovery of new materials with unique properties.
- Petrology: The study of rocks themselves, including their origin, composition, and alteration, helps us understand the formation and evolution of the Earth’s crust and mantle.
9. Rocks in Landscaping and Garden Design
How are rocks useful to us in creating beautiful outdoor spaces? They enhance the beauty and functionality of landscapes.
- Rock Gardens: Rock gardens are designed to showcase a variety of rocks and alpine plants. These gardens create a visually appealing and low-maintenance landscape.
- Water Features: Rocks are used to create waterfalls, streams, and ponds in gardens. These water features add a sense of tranquility and natural beauty to outdoor spaces.
- Pathways and Walkways: Rocks are used to create pathways and walkways in gardens. Flagstone, gravel, and stepping stones are popular choices for creating durable and attractive walkways.
- Retaining Walls: Rocks are used to build retaining walls, which help prevent soil erosion and create terraced gardens. These walls can be constructed from natural stone, concrete blocks, or gabions filled with rocks.
- Mulch: Crushed rock and gravel can be used as mulch in gardens. Rock mulch helps retain moisture in the soil, suppress weed growth, and regulate soil temperature.
- Decorative Features: Rocks are used to create decorative features in gardens, such as rock sculptures, cairns, and Zen gardens. These features add a unique and artistic touch to outdoor spaces. Rockscapes.net offers a plethora of creative ideas and practical advice for incorporating rocks into your landscape design.
10. Sustainable Use of Rocks
How can we ensure the sustainable use of rocks? Responsible practices are essential to minimize environmental impacts.
- Responsible Mining Practices: Implement mining practices that minimize environmental disturbance, such as reducing deforestation, controlling erosion, and preventing water pollution.
- Recycling and Reuse: Recycle and reuse rocks and minerals whenever possible. For example, crushed concrete can be used as aggregate in new construction projects.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Source rocks and minerals from suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. Look for certifications and labels that indicate responsible sourcing.
- Conservation: Conserve rocks and minerals by using them efficiently and minimizing waste. Design buildings and infrastructure that require fewer resources.
- Restoration: Restore mined areas to their natural state. Replant vegetation, stabilize slopes, and reclaim water resources.
FAQ: Your Questions About the Usefulness of Rocks Answered
1. Why are rocks important to humans?
Rocks are essential to humans because they provide raw materials for construction, energy production, agriculture, manufacturing, and technology. They are also used in environmental management, art, and scientific research.
2. How do rocks contribute to construction?
Rocks such as granite, limestone, and sandstone are used as building stones for foundations, facades, and decorative elements. Crushed rocks, like gravel and crushed stone, are vital components of concrete and asphalt.
3. What role do rocks play in energy production?
Sedimentary rocks contain fossil fuels like oil, natural gas, and coal. Geothermal energy harnesses heat from rocks deep beneath the surface, and certain rocks contain uranium for nuclear energy.
4. How are rocks used in agriculture?
Rocks release essential minerals into the soil, enriching it for plant growth. Phosphate and potash fertilizers are derived from rocks, and agricultural lime, made from crushed limestone, neutralizes acidic soils.
5. In what ways are rocks utilized in manufacturing and industry?
Rocks provide ores for metal production, sandstone for glass manufacturing, and clay for ceramics production. They also supply raw materials for various chemicals used in industrial processes.
6. How do rocks contribute to environmental management?
Rocks are used in water filtration and wastewater treatment, erosion control, carbon sequestration, and mine reclamation. They help remove pollutants, stabilize shorelines, and restore landscapes.
7. What is the significance of rocks in technology?
Rare earth elements found in rocks are crucial components in electronics. Lithium is used in batteries, and silicon, derived from quartz-rich rocks, is the primary material in semiconductors.
8. How are rocks used in art and decoration?
Marble, granite, and other rocks are used in sculpture. Gemstones, found in rocks, are used in jewelry, and decorative stones are used to create ornamental objects.
9. What can rocks tell us about our planet?
Rocks contain fossils, which provide evidence of past life forms and help scientists understand the evolution of life on Earth. They also help scientist learn about Geochronology. Radiometric dating techniques, which measure the decay of radioactive isotopes in rocks, provide precise age estimates.
10. How can we use rocks more sustainably?
By implementing responsible mining practices, recycling and reusing rocks and minerals, sourcing from sustainable suppliers, conserving resources, and restoring mined areas.
Discover the Beauty and Utility of Rocks with Rockscapes.net
From the foundations of our homes to the landscapes we cherish, rocks play a vital role in our lives. At Rockscapes.net, we’re passionate about showcasing the beauty and versatility of rocks in landscape design. Explore our website for a wealth of design ideas, detailed information on various rock types, and practical tips for incorporating rocks into your outdoor spaces. Let us help you transform your landscape with the enduring beauty and functionality of rocks!
Address: 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States
Phone: +1 (480) 965-9011
Website: rockscapes.net
Ready to enhance your landscape with stunning rock features? Visit rockscapes.net today to discover endless design possibilities and expert advice. Let’s create a breathtaking outdoor space together!