Determining the age of rocks involves various sophisticated techniques, offering valuable insights into Earth’s history, and at rockscapes.net, we’re here to guide you through this fascinating field. By exploring methods like radiometric dating, cosmogenic surface exposure dating, and paleomagnetism, geologists can unlock the secrets held within these ancient formations. These methods help us understand geological events and how to apply this knowledge to the landscapes we design and appreciate. Delve into the world of geological timelines, absolute dating methods, and isotope analysis.
1. What is Geochronology and How Does it Help Determine the Age of Rocks?
Geochronology is the science of determining the age of rocks, fossils, and sediments. It helps us understand the timeline of Earth’s history and geological events. This field employs various techniques to date geological materials, giving us insights into the processes that shaped our planet. Geochronology is essential for understanding the sequence and timing of events like volcanic eruptions, mountain formation, and the evolution of life. Dating techniques also help to correlate rock formations across different regions and create a comprehensive geological history.
1.1 What Techniques are Used in Geochronology?
Geochronology employs several techniques, including radiometric dating, cosmogenic surface exposure dating, and paleomagnetism. Radiometric dating measures the decay of radioactive isotopes in rocks and minerals. Cosmogenic surface exposure dating calculates how long a rock surface has been exposed to cosmic rays. Paleomagnetism studies the magnetic properties of rocks to determine their age and the Earth’s past magnetic field. Each method offers a unique way to date geological materials, depending on the age range and type of sample.
1.2 What Role Does Geochronology Play in Landscape Design?
Geochronology provides a deeper understanding of the geological context in which landscapes evolve. Understanding the age and formation of rocks used in landscape design enhances the appreciation and authenticity of the design. For instance, knowing the origin and age of stone materials can inform their use in creating natural-looking and sustainable landscapes. At rockscapes.net, we use geochronological data to select and place rocks in ways that reflect the natural history of the region, enhancing the aesthetic and educational value of our designs.
2. How Does Radiometric Dating Work?
Radiometric dating determines the age of rocks and minerals by measuring the decay of radioactive isotopes. Radioactive isotopes decay at a known rate, transforming into stable isotopes. By measuring the ratio of parent (radioactive) to daughter (stable) isotopes, scientists can calculate how long ago the rock or mineral formed. This method is highly accurate and applicable to a wide range of geological materials.
2.1 What are the Different Types of Radiometric Dating Techniques?
Several radiometric dating techniques exist, including 40Ar/39Ar (argon) dating, U-series (uranium) dating, and carbon dating. Argon dating is used for volcanic rocks, uranium dating for crystal formation, and carbon dating for organic materials. Each technique is suited to different materials and age ranges, allowing geochronologists to select the most appropriate method for a given sample.
2.1.1 How Does 40Ar/39Ar Geochronology Work?
40Ar/39Ar geochronology is based on the decay of potassium-40 (40K) to argon-40 (40Ar) and is used to date volcanic rocks. This technique involves irradiating a sample with neutrons to convert potassium-39 to argon-39, then measuring the ratio of 40Ar to 39Ar to determine the age. 40Ar/39Ar dating is versatile and can date rocks and minerals ranging from 10,000 years to billions of years old.
2.1.2 What is U-Series Geochronology?
U-series geochronology is based on the decay of uranium isotopes, such as uranium-238 (238U), and is used to date crystal formation. This method is useful for dating materials over a wide age range, from hundreds to billions of years. By measuring the concentrations of different isotopes in the uranium decay chain, scientists can determine the age of the sample and gain insights into Earth processes.
2.1.3 When is Carbon Dating Used?
Carbon dating is used to date organic materials, such as charcoal, that are rich in carbon. This technique relies on the decay of carbon-14 (14C), a radioactive isotope of carbon. Because 14C has a relatively short half-life, carbon dating is most effective for materials up to about 50,000 years old. In volcanic environments, carbon dating can be used to date charcoal found under lava flows.
2.2 What Equipment is Used in Radiometric Dating?
Radiometric dating requires sophisticated equipment, including mass spectrometers, which measure the proportions of parent and daughter isotopes. Mass spectrometers separate ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio, allowing for precise measurement of isotope concentrations. Sample preparation labs are also essential for cleaning and preparing samples for analysis, ensuring accurate and reliable results.
3. What is Cosmogenic Surface Exposure Dating?
Cosmogenic surface exposure dating determines how long a rock surface has been exposed to cosmic rays. Cosmic rays interact with rocks and minerals, producing cosmogenic isotopes like chlorine-36, helium-3, beryllium-10, neon-21, and aluminum-26. By measuring the concentration of these isotopes, scientists can determine the exposure age of the surface.
3.1 How Does Exposure Time Affect Isotope Concentration?
The longer a rock surface is exposed to cosmic rays, the higher the concentration of cosmogenic isotopes. The production rate of these isotopes is known, so measuring their concentration allows scientists to calculate the exposure time. This technique is useful for dating geological features like lava flows, glacial deposits, and rock surfaces.
3.2 What Can Cosmogenic Dating Tell Us About Glacial History?
Cosmogenic dating can help determine when glacial deposits formed, providing insights into the timing of glaciations. By dating the surfaces of glacial moraines and other glacial features, scientists can reconstruct the history of ice sheet advance and retreat. This information is crucial for understanding past climate changes and their impact on landscapes. According to research from Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, in July 2025, cosmogenic dating will provide more precise timelines for glacial events, helping us understand climate patterns.
4. How Does Paleomagnetism Determine the Age of Rocks?
Paleomagnetism uses the magnetic properties of rocks to determine their age. When magma cools and solidifies, magnetic minerals align with the Earth’s magnetic field. This alignment is “locked in” as the rock cools, providing a record of the magnetic field’s direction at the time of formation. By measuring the magnetic direction, scientists can determine the rock’s age.
4.1 How Does Earth’s Magnetic Field Relate to Rock Dating?
The Earth’s magnetic field changes over time, with the magnetic north pole wandering around the geographic north pole. These changes are well-documented, allowing scientists to compare the magnetic direction recorded in a rock to the known magnetic field direction at different times. If the rock’s magnetic direction matches a known period, its age can be determined. In some cases, the relative age of two rocks can be determined by comparing their magnetic directions.
4.2 What Equipment is Used in Paleomagnetism?
Paleomagnetism uses magnetometers to measure the magnetic direction and intensity of rocks. Magnetometers are sensitive instruments that can detect even weak magnetic signals. Sample preparation is also crucial, ensuring that the rock samples are oriented correctly and free from contamination. Paleomagnetic laboratories are equipped with specialized equipment for measuring and analyzing rock magnetism.
5. Combining Geochronological Methods for Accurate Rock Dating
Combining different geochronological methods enhances the accuracy and reliability of rock dating. No single method is perfect for all situations, so geologists often use multiple techniques to cross-validate their results. Integrating radiometric dating, cosmogenic surface exposure dating, and paleomagnetism provides a more comprehensive understanding of a rock’s age and history.
5.1 How Does Combining Methods Improve Accuracy?
Combining methods improves accuracy by reducing uncertainties and potential errors associated with individual techniques. For example, radiometric dating can provide absolute ages, while paleomagnetism can detect age differences of hundreds of years. By integrating these methods, geologists can refine their age estimates and gain a more detailed understanding of geological events.
5.2 Can You Provide Examples of Combined Geochronological Studies?
Combined geochronological studies are common in volcanic regions, where scientists use both radiometric dating and paleomagnetism to understand eruption history. Radiometric dating can determine the age of volcanic rocks, while paleomagnetism can reveal the sequence of eruptions and identify subtle age differences. Cosmogenic dating can also be used to date lava flows and other volcanic features, providing additional constraints on eruption timing.
6. Real-World Applications of Rock Dating
Rock dating has numerous real-world applications, including understanding volcanic activity, reconstructing glacial history, and informing landscape design. By accurately dating rocks and geological events, scientists can better understand Earth’s dynamic processes and their impact on our environment.
6.1 How Does Rock Dating Help in Understanding Volcanic Activity?
Rock dating is essential for understanding volcanic activity, allowing scientists to determine the timing and frequency of eruptions. Radiometric dating, particularly 40Ar/39Ar geochronology, is used to date volcanic rocks and minerals, providing a timeline of volcanic events. This information is crucial for assessing volcanic hazards and predicting future eruptions. In places like Yellowstone National Park, detailed rock dating has revealed the intricate history of volcanic activity.
6.2 How Does Rock Dating Help in Understanding Glacial History?
Rock dating plays a crucial role in understanding glacial history by determining when glacial deposits formed. Cosmogenic surface exposure dating is used to date glacial moraines and other glacial features, providing insights into the timing of ice sheet advances and retreats. This information helps scientists reconstruct past climate changes and understand the dynamics of ice ages.
6.3 Can Rock Dating Help in Landscape Design?
Rock dating informs landscape design by providing a deeper understanding of the geological context. Knowing the age and origin of rocks used in landscape features enhances the authenticity and aesthetic appeal of the design. At rockscapes.net, we use geochronological data to select and place rocks in ways that reflect the natural history of the region, creating landscapes that are both beautiful and educational.
7. What Are the Limitations of Rock Dating Techniques?
Rock dating techniques have limitations, including uncertainties in measurements, sample contamination, and the availability of suitable materials. Radiometric dating requires the presence of radioactive isotopes, while cosmogenic dating is limited to surface exposures. Paleomagnetism requires rocks with stable magnetic properties. Understanding these limitations is crucial for interpreting dating results and selecting the most appropriate techniques.
7.1 What Factors Can Affect the Accuracy of Rock Dating?
Several factors can affect the accuracy of rock dating, including uncertainties in isotope measurements, contamination of samples, and alteration of rocks over time. Careful sample preparation and analysis are essential for minimizing these errors. Scientists also use multiple dating techniques to cross-validate their results and ensure accuracy.
7.2 How Do Scientists Account for These Limitations?
Scientists account for the limitations of rock dating by using rigorous quality control procedures, cross-validating results with multiple techniques, and carefully interpreting the data in the context of geological evidence. Statistical methods are used to quantify uncertainties and assess the reliability of age estimates. By understanding and addressing these limitations, scientists can obtain accurate and reliable age determinations.
8. Recent Advances in Rock Dating Technology
Recent advances in rock dating technology have improved the precision, accuracy, and efficiency of dating methods. These advances include the development of more sensitive mass spectrometers, improved sample preparation techniques, and new methods for analyzing isotope data. These technological advancements have expanded the range of materials that can be dated and increased the resolution of geological timelines.
8.1 What Are Some Recent Breakthroughs in Radiometric Dating?
Recent breakthroughs in radiometric dating include the development of multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometers (MC-ICP-MS), which allow for more precise measurement of isotope ratios. Improved laser ablation techniques have also enhanced the ability to date small samples and specific mineral grains. These advances have significantly improved the accuracy and resolution of radiometric dating.
8.2 How Have These Advances Impacted Our Understanding of Earth’s History?
These advances have significantly impacted our understanding of Earth’s history by providing more accurate and detailed timelines of geological events. Higher precision dating has allowed scientists to refine the timing of volcanic eruptions, glacial cycles, and other important events. These improved timelines have led to new insights into the processes that have shaped our planet.
9. Understanding the Age of Arizona’s Rocks
Arizona’s diverse geology offers a unique opportunity to study Earth’s history through rock dating. The state’s rocks range from ancient Precambrian formations to more recent volcanic deposits, each telling a different part of Arizona’s geological story. By dating these rocks, scientists can reconstruct the state’s tectonic history, volcanic activity, and climate changes.
9.1 Which Geological Formations in Arizona Have Been Dated?
Several geological formations in Arizona have been extensively dated, including the Grand Canyon’s layered rocks, the volcanic fields of the San Francisco Peaks, and the metamorphic rocks of the Basin and Range Province. These formations provide a comprehensive record of Arizona’s geological evolution, from its ancient origins to its more recent volcanic and tectonic activity.
9.2 What Do These Dates Tell Us About Arizona’s Geological Past?
The dates obtained from Arizona’s rocks reveal a complex geological past, including periods of mountain building, volcanic eruptions, and sedimentary deposition. The Grand Canyon’s rocks document hundreds of millions of years of sedimentary history, while the volcanic rocks of the San Francisco Peaks record more recent volcanic activity. These dates provide insights into the processes that have shaped Arizona’s landscapes.
10. Rockscapes.net: Your Resource for Understanding and Utilizing Rocks in Landscaping
Rockscapes.net is your premier resource for understanding and utilizing rocks in landscaping. We provide comprehensive information on various rock types, their geological origins, and their applications in landscape design. Our goal is to inspire and educate homeowners, landscape designers, and anyone interested in creating beautiful and sustainable landscapes with natural stone.
10.1 How Can Rockscapes.net Help You Choose the Right Rocks for Your Landscape?
Rockscapes.net offers detailed information on different rock types, including their appearance, properties, and suitability for various landscaping applications. We provide guidance on selecting rocks that complement your design aesthetic, climate, and environmental conditions. Our expert team can help you choose the perfect rocks to create stunning and sustainable landscapes.
10.2 What Design Ideas and Resources Does Rockscapes.net Offer?
Rockscapes.net features a wide range of design ideas and resources to inspire your landscaping projects. We showcase stunning examples of rock gardens, stone pathways, water features, and other landscape elements. Our website also offers practical tips and step-by-step guides for installing and maintaining rock features in your landscape.
Ready to transform your outdoor space with the timeless beauty of natural stone? Visit rockscapes.net today to explore our extensive collection of rocks, discover inspiring design ideas, and connect with our team of landscaping experts. Let us help you create a landscape that is both stunning and sustainable.
Address: 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States
Phone: +1 (480) 965-9011
Website: rockscapes.net
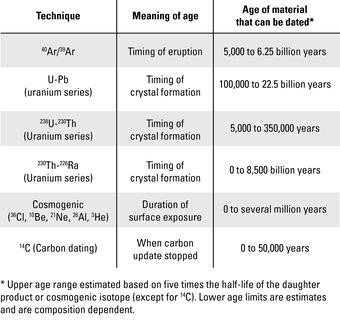 Geochronology Techniques Table
Geochronology Techniques Table
FAQ: Determining the Age of Rocks
Q1: How do scientists determine the age of rocks?
Scientists use various techniques such as radiometric dating, cosmogenic surface exposure dating, and paleomagnetism to determine the age of rocks, measuring the decay of radioactive isotopes or the alignment of magnetic minerals.
Q2: What is radiometric dating?
Radiometric dating is a method that measures the decay of radioactive isotopes in rocks and minerals to determine their age by comparing the ratio of parent to daughter isotopes.
Q3: How does carbon dating work?
Carbon dating measures the decay of carbon-14 in organic materials to determine their age, effective for materials up to 50,000 years old.
Q4: What is cosmogenic surface exposure dating?
Cosmogenic surface exposure dating determines how long a rock surface has been exposed to cosmic rays by measuring the concentration of cosmogenic isotopes produced by cosmic ray interactions.
Q5: What is paleomagnetism?
Paleomagnetism uses the magnetic properties of rocks to determine their age by measuring the alignment of magnetic minerals with the Earth’s magnetic field at the time of the rock’s formation.
Q6: Why is it important to date rocks?
Dating rocks helps us understand Earth’s history, including volcanic activity, glacial history, and the evolution of landscapes and ecosystems.
Q7: What are some limitations of rock dating techniques?
Limitations include uncertainties in measurements, sample contamination, the need for specific materials, and alteration of rocks over time.
Q8: How do scientists ensure the accuracy of rock dating?
Scientists use rigorous quality control, cross-validate results with multiple techniques, and interpret data in the context of geological evidence to ensure accuracy.
Q9: What is 40Ar/39Ar geochronology?
40Ar/39Ar geochronology is based on the decay of potassium-40 to argon-40 and is used to date volcanic rocks and minerals ranging from 10,000 years to billions of years old.
Q10: How can I learn more about using rocks in landscaping?
Visit rockscapes.net for comprehensive information on rock types, design ideas, and resources for creating beautiful and sustainable landscapes with natural stone.
