Dating rocks involves utilizing geochronology, a field of science that employs various techniques to determine the age of geological materials. At rockscapes.net, we provide insights into these methods, helping homeowners, landscape designers, and enthusiasts understand the age and origin of the stones they use in their projects, offering solutions to enhance the aesthetic and historical value of landscapes. Exploring the timeline of Earth’s formations through radiometric dating and cosmogenic nuclide dating allows us to unlock the secrets held within these ancient formations.
1. What is Geochronology and Why is it Important?
Geochronology is the science of determining the age of rocks, fossils, and sediments. Knowing the age of geological materials is crucial for understanding Earth’s history, including the timing of volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and other geological events. It is particularly relevant for landscape designers and homeowners who wish to incorporate rocks with significant historical context into their outdoor spaces.
Why is Geochronology Important for Understanding Earth’s History?
Geochronology provides a chronological framework for understanding the sequence of geological events that have shaped our planet. This is vital for:
- Understanding Evolutionary Processes: By dating fossils and the rocks they are found in, scientists can construct a timeline of life’s evolution on Earth.
- Assessing Natural Hazards: Dating past volcanic eruptions and earthquakes helps in predicting future events, enhancing preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Resource Exploration: Determining the age of rock formations aids in the exploration for valuable resources like oil, gas, and minerals.
- Climate Change Studies: By dating ice cores and sediments, scientists can reconstruct past climate conditions and understand long-term climate trends.
How Does Geochronology Apply to Landscape Design?
For landscape designers and homeowners, geochronology adds a layer of depth and appreciation to the rocks used in landscaping. Understanding the age and origin of stones can transform a simple garden into a landscape that tells a story of geological time. Rockscapes.net offers a curated selection of stones with documented geological histories, allowing you to create landscapes that are both beautiful and scientifically significant.
2. What are the Main Geochronological Techniques Used by Geologists?
Geologists use several key techniques to date rocks, each based on different scientific principles. The most common methods include radiometric dating, cosmogenic surface exposure dating, and paleomagnetism.
Radiometric Dating: Measuring Radioactive Decay
Radiometric dating is one of the most reliable methods for determining the age of rocks and minerals. This technique relies on the decay of radioactive isotopes, which transform into stable isotopes at a known rate. By measuring the ratio of parent isotopes (the original radioactive atoms) to daughter isotopes (the stable atoms they decay into), scientists can calculate the age of the sample.
How Does Radiometric Dating Work?
The process involves:
- Selecting a Suitable Isotope System: Different radioactive isotopes have different half-lives, making them suitable for dating materials of different ages. For example, carbon-14 dating is used for organic materials up to about 50,000 years old, while uranium-lead dating is used for much older rocks.
- Sample Collection and Preparation: Geologists collect rock or mineral samples from the site of interest. The samples are then carefully prepared to isolate the minerals that contain the radioactive isotopes.
- Mass Spectrometry: The prepared samples are analyzed using a mass spectrometer, which measures the precise amounts of parent and daughter isotopes.
- Age Calculation: Using the known decay rate of the isotope, scientists calculate the age of the sample.
What are Some Common Radiometric Dating Techniques?
-
Argon Dating (40Ar/39Ar):
- Based on the decay of potassium-40 to argon-40.
- Suitable for dating volcanic rocks and minerals.
- Effective for materials ranging from 10,000 years to billions of years old.
- According to research from the U.S. Geological Survey, Argon Dating can inform how long magmas sit in the crust before erupting.
-
Uranium-Series Dating:
- Based on the decay of uranium-238.
- Used to date crystal formations and calcium carbonate materials.
- Useful for materials ranging from hundreds of years to billions of years old.
- According to research from the Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, in July 2025, combining eruption age information from 40Ar/39Ar geochronology with the timing of crystal formation from U-series dating can inform how long magmas sit in the crust before erupting.
-
Carbon Dating (14C):
- Based on the decay of carbon-14.
- Used for dating organic materials like wood, charcoal, and bones.
- Effective for materials up to about 50,000 years old.
- In volcanic environments, this might include charcoal found under lava flows representing plants that were burned by the lava.
Cosmogenic Surface Exposure Dating: Measuring Cosmic Ray Exposure
Cosmogenic surface exposure dating is used to determine how long a rock surface has been exposed to cosmic rays. These high-energy particles from space interact with the atoms in rocks, producing rare isotopes. By measuring the concentration of these cosmogenic isotopes, scientists can estimate the time since the rock surface was exposed.
How Does Cosmogenic Surface Exposure Dating Work?
The process involves:
- Cosmic Ray Interaction: When cosmic rays strike a rock surface, they cause nuclear reactions that produce cosmogenic isotopes like beryllium-10, aluminum-26, and chlorine-36.
- Sample Collection: Geologists collect samples from the exposed surface of the rock.
- Isotope Measurement: The samples are analyzed to measure the concentration of cosmogenic isotopes.
- Age Calculation: Using the known production rate of the isotopes, scientists calculate the exposure age of the rock surface.
What are the Applications of Cosmogenic Dating?
- Dating Lava Flows: Determining when a lava flow was deposited.
- Glacial Geology: Estimating the age of glacial deposits, which helps in understanding past climate changes.
- Landslide Studies: Dating the timing of landslides and other geomorphic events.
- Rockscapes: It can also determine when glacial deposits formed, which helps constrain the timing of glaciations.
Paleomagnetism: Reading the Earth’s Magnetic History
Paleomagnetism is a technique that uses the magnetic properties of rocks to determine their age and the position of the Earth’s magnetic poles in the past. When a rock forms, magnetic minerals within it align with the Earth’s magnetic field. This alignment is “locked in” as the rock cools, providing a record of the magnetic field at the time of formation.
How Does Paleomagnetism Work?
The process involves:
- Magnetic Mineral Alignment: When a rock forms, magnetic minerals align with the Earth’s magnetic field.
- Sample Collection: Geologists collect oriented rock samples, carefully noting their position and orientation.
- Magnetometry: The samples are analyzed using a magnetometer, which measures the direction and intensity of the magnetic field recorded in the rock.
- Age Determination: By comparing the measured magnetic direction with the known history of the Earth’s magnetic field, scientists can estimate the age of the rock.
What are the Applications of Paleomagnetism?
- Determining Relative Age: Comparing the magnetic directions of different rock layers to determine their relative ages.
- Reconstructing Plate Tectonics: Tracking the movement of continents over time by studying the magnetic alignment in rocks from different locations.
- Understanding Magnetic Field Changes: Studying the history of the Earth’s magnetic field, including reversals in polarity.
 Basaltic lava flow along the Madison River yielding samples for 40Ar/39Ar geochronology
Basaltic lava flow along the Madison River yielding samples for 40Ar/39Ar geochronology
3. How Do Geologists Choose the Right Dating Technique?
Selecting the appropriate dating technique depends on several factors, including the age of the sample, the type of material, and the geological context. Geologists often use multiple techniques to cross-validate their results and ensure accuracy.
Factors Influencing the Choice of Dating Technique
- Age Range: Different dating methods are suitable for different age ranges. For example, carbon dating is used for relatively young materials, while uranium-lead dating is used for very old rocks.
- Material Type: Some dating methods are specific to certain types of materials. For example, carbon dating is used for organic materials, while argon dating is used for volcanic rocks.
- Geological Context: The geological setting of the sample can influence the choice of dating method. For example, cosmogenic dating is best suited for surfaces that have been exposed to cosmic rays.
- Accuracy and Precision: The desired level of accuracy and precision can also influence the choice of dating method. Some methods are more precise than others.
Combining Multiple Techniques for Accurate Results
Geologists often use a combination of dating techniques to improve the accuracy and reliability of their results. For example, they might use radiometric dating to determine the absolute age of a rock and paleomagnetism to determine its relative age compared to other rocks in the area.
Examples of Geochronological Studies in Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park, with its rich volcanic history, is a prime location for geochronological studies. Scientists have used various dating techniques to understand the timing of volcanic eruptions, glacial events, and other geological processes in the park.
Dating Volcanic Eruptions
Argon dating (40Ar/39Ar) has been used extensively to date volcanic rocks in Yellowstone. This method has helped scientists to determine the timing of major eruptions, including the formation of the Yellowstone Caldera.
Studying Glacial History
Cosmogenic surface exposure dating has been used to study the timing of glaciations in Yellowstone. By dating glacial deposits, scientists have been able to reconstruct the history of ice ages in the region.
Understanding Magma Dynamics
Uranium-series dating, paired with argon dating, has provided insights into the dynamics of magma beneath Yellowstone. This research has helped scientists understand how long magmas reside in the crust before erupting.
4. How Does Geochronology Impact Landscape Architecture and Design?
Geochronology offers landscape architects and designers a unique opportunity to incorporate elements of geological history into their projects. By understanding the age and origin of rocks, designers can create landscapes that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also educational and historically significant.
Incorporating Geologically Significant Rocks into Landscapes
Using rocks with known geological histories can add a layer of depth and meaning to landscape designs. For example, incorporating rocks from a specific geological formation or time period can create a landscape that tells a story about the Earth’s past.
Creating Educational Landscapes
Landscapes can be designed to educate visitors about geological history. By incorporating rocks of different ages and origins, designers can create a timeline of geological events that have shaped the region.
Enhancing Aesthetic Value with Geological Context
Understanding the geological context of rocks can enhance their aesthetic value. For example, knowing that a particular rock was formed during a volcanic eruption or a glacial event can add to its visual appeal.
Sourcing Rocks from Responsible Quarries
When incorporating rocks into landscape designs, it is important to source them from responsible quarries that adhere to sustainable practices. This ensures that the extraction of rocks does not have a negative impact on the environment. Rockscapes.net is committed to sourcing rocks from quarries that follow ethical and environmentally responsible practices.
5. What Types of Rocks are Best Suited for Landscaping and How Do Their Ages Matter?
The choice of rocks for landscaping depends on various factors, including their aesthetic appeal, durability, and geological significance. Different types of rocks offer unique characteristics that can enhance the beauty and functionality of landscapes.
Popular Types of Rocks for Landscaping
-
Granite:
- Characteristics: A hard, durable igneous rock with a speckled appearance.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Offers a classic, timeless look that complements various design styles.
- Geological Significance: Granite is often billions of years old, providing a sense of ancient history.
-
Slate:
- Characteristics: A fine-grained metamorphic rock that splits into thin layers.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Provides a natural, rustic look that is ideal for pathways and patios.
- Geological Significance: Slate is formed from ancient sedimentary rocks, offering a glimpse into past environments.
-
Limestone:
- Characteristics: A sedimentary rock composed mainly of calcium carbonate.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Offers a light, natural look that is suitable for gardens and water features.
- Geological Significance: Limestone often contains fossils, providing insights into ancient marine life.
-
Sandstone:
- Characteristics: A sedimentary rock composed of sand-sized grains.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Offers a warm, earthy look that is ideal for walls and pathways.
- Geological Significance: Sandstone is formed from ancient sand dunes or riverbeds, reflecting past landscapes.
-
River Rock:
- Characteristics: Smooth, rounded rocks that have been shaped by flowing water.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Provides a natural, organic look that is ideal for water features and garden beds.
- Geological Significance: River rocks have been shaped by geological processes over long periods, showcasing the power of erosion.
How the Age of Rocks Influences Landscape Design
The age of rocks can influence landscape design in several ways:
- Historical Context: Using rocks from a specific geological period can add historical depth to a landscape.
- Aesthetic Considerations: The age of a rock can influence its color, texture, and overall appearance.
- Educational Opportunities: Incorporating rocks of different ages can create educational landscapes that teach visitors about geological history.
6. What Tools and Technologies Are Used in Geochronology?
Geochronology relies on a range of sophisticated tools and technologies to measure the age of rocks and minerals. These tools allow scientists to analyze the isotopic composition of samples with high precision and accuracy.
Mass Spectrometers: Measuring Isotope Ratios
Mass spectrometers are the primary tools used in radiometric dating. These instruments measure the precise amounts of parent and daughter isotopes in a sample, allowing scientists to calculate its age.
How Do Mass Spectrometers Work?
- Ionization: The sample is ionized, creating charged particles.
- Acceleration: The ions are accelerated through a magnetic field.
- Separation: The magnetic field separates the ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio.
- Detection: Detectors measure the abundance of each ion, providing data on the isotopic composition of the sample.
Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS)
LA-ICP-MS is a technique that combines laser ablation with mass spectrometry. It is used to measure the elemental and isotopic composition of solid samples with high spatial resolution.
How Does LA-ICP-MS Work?
- Laser Ablation: A laser beam is focused on the sample, vaporizing a small amount of material.
- Plasma Generation: The vaporized material is introduced into an inductively coupled plasma (ICP), which ionizes the atoms.
- Mass Spectrometry: The ions are analyzed using a mass spectrometer, providing data on the elemental and isotopic composition of the sample.
Magnetometers: Measuring Magnetic Properties
Magnetometers are used in paleomagnetism to measure the magnetic properties of rocks. These instruments can detect the direction and intensity of the magnetic field recorded in a rock sample.
How Do Magnetometers Work?
- Sample Preparation: The rock sample is carefully prepared and oriented.
- Magnetic Measurement: The magnetometer measures the magnetic field recorded in the sample.
- Data Analysis: The data is analyzed to determine the direction and intensity of the magnetic field, which can be used to estimate the age and origin of the rock.
7. What are Some Challenges and Limitations of Geochronology?
While geochronology is a powerful tool for understanding Earth’s history, it also has some challenges and limitations. These include the availability of suitable materials, the complexity of geological systems, and the potential for contamination.
Availability of Suitable Materials
Not all rocks and minerals are suitable for dating. Some rocks may not contain enough of the radioactive isotopes needed for radiometric dating, or they may have been altered by geological processes, making it difficult to obtain accurate results.
Complexity of Geological Systems
Geological systems can be complex, with multiple events affecting the age and composition of rocks. This can make it challenging to interpret the results of dating analyses and to determine the true age of a sample.
Potential for Contamination
Contamination can occur during sample collection, preparation, or analysis, leading to inaccurate dating results. It is important to follow strict protocols to minimize the risk of contamination and to validate the results using multiple dating techniques.
8. How Can Homeowners and Landscapers Use Geochronological Information to Enhance Their Projects?
Homeowners and landscapers can use geochronological information to add depth, meaning, and educational value to their projects. By understanding the age and origin of rocks, they can create landscapes that are not only beautiful but also historically and scientifically significant.
Selecting Rocks with Known Geological Histories
Choosing rocks with known geological histories can add a layer of depth and meaning to landscape designs. For example, incorporating rocks from a specific geological formation or time period can create a landscape that tells a story about the Earth’s past.
Creating Educational Landscapes
Landscapes can be designed to educate visitors about geological history. By incorporating rocks of different ages and origins, designers can create a timeline of geological events that have shaped the region.
Enhancing Aesthetic Value with Geological Context
Understanding the geological context of rocks can enhance their aesthetic value. For example, knowing that a particular rock was formed during a volcanic eruption or a glacial event can add to its visual appeal.
Examples of Creative Applications
- Fossil Gardens: Incorporating rocks that contain fossils to create a garden that showcases ancient life forms.
- Geological Timelines: Arranging rocks of different ages to create a timeline of geological events.
- Volcanic Landscapes: Using volcanic rocks to create a landscape that resembles a volcanic environment.
- Glacial Landscapes: Using glacial rocks to create a landscape that reflects the history of ice ages.
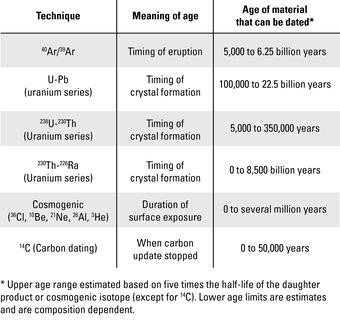 Table of geochronology techniques detailing age range and material type
Table of geochronology techniques detailing age range and material type
9. What are Some Recent Advances in Geochronology?
Geochronology is a constantly evolving field, with new techniques and technologies being developed all the time. Recent advances have improved the accuracy, precision, and applicability of dating methods.
Improved Mass Spectrometry Techniques
Advances in mass spectrometry have allowed scientists to measure isotope ratios with greater precision and accuracy. This has led to more reliable dating results and a better understanding of Earth’s history.
Development of New Dating Methods
Scientists are constantly developing new dating methods to address the limitations of existing techniques. These new methods are expanding the range of materials that can be dated and improving the accuracy of age estimates.
Application of Geochronology to New Fields
Geochronology is being applied to new fields, such as archaeology and environmental science. This is providing new insights into human history and the impact of climate change on the environment.
Examples of Cutting-Edge Research
- Dating Ancient Artifacts: Using geochronology to date ancient artifacts and understand human migration patterns.
- Studying Climate Change: Using geochronology to reconstruct past climate conditions and understand the impact of climate change on the environment.
- Exploring the Solar System: Using geochronology to date rocks from other planets and moons, providing insights into the formation and evolution of the solar system.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Dating Rocks
1. How Do You Date Rocks?
Rocks are dated using various geochronological techniques, primarily radiometric dating, which measures the decay of radioactive isotopes within the rock’s minerals.
2. What is radiometric dating?
Radiometric dating is a method that uses the decay rates of radioactive isotopes to determine the age of rocks and minerals by measuring the ratio of parent to daughter isotopes.
3. What is argon dating used for?
Argon dating (40Ar/39Ar) is used to date volcanic rocks and minerals, effective for materials ranging from 10,000 years to billions of years old, providing eruption age information.
4. How does cosmogenic surface exposure dating work?
Cosmogenic surface exposure dating measures the concentration of isotopes produced by cosmic rays interacting with rock surfaces, determining how long the surface has been exposed.
5. What is paleomagnetism?
Paleomagnetism uses the magnetic properties of rocks to determine their age and the position of Earth’s magnetic poles at the time of the rock’s formation.
6. What factors influence the choice of dating technique?
The choice depends on the age of the sample, the type of material, the geological context, and the desired level of accuracy and precision.
7. What types of rocks are best suited for landscaping?
Granite, slate, limestone, sandstone, and river rock are popular choices, each offering unique aesthetic and geological characteristics.
8. How can homeowners use geochronological information?
Homeowners can use this information to select rocks with known geological histories, create educational landscapes, and enhance the aesthetic value of their projects.
9. What are the limitations of geochronology?
Limitations include the availability of suitable materials, the complexity of geological systems, and the potential for contamination, which can affect accuracy.
10. What recent advances have been made in geochronology?
Recent advances include improved mass spectrometry techniques, the development of new dating methods, and the application of geochronology to new fields like archaeology and environmental science.
Understanding how to date rocks opens up a world of possibilities for landscape design and appreciation of Earth’s history. At rockscapes.net, we provide the resources and expertise to help you select the perfect stones for your projects, ensuring they are both beautiful and historically significant.
Ready to start your geologically inspired landscape project? Visit rockscapes.net today to explore our wide selection of rocks and discover expert tips and design ideas. Contact us at Address: 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States or Phone: +1 (480) 965-9011 to speak with our specialists and bring your vision to life. Let rockscapes.net help you create a landscape that tells a story millions of years in the making!