Discovering gold feels like striking it rich, and at rockscapes.net, we’re passionate about all things rock and landscape. So, how much gold can you realistically expect to find in a ton of rock? On average, you might find about 1 gram of gold for every 3,000,000 metric tons of rock mined, highlighting the incredible effort involved in gold extraction. Unearth the realities of gold mining and its environmental implications, explore different ore grades, and learn how this knowledge impacts landscape design and material choices with rockscapes.net, including precious metal exploration and mineral extraction.
1. Understanding the Rock-to-Metal Ratio: What Does It Mean for Gold?
The rock-to-metal ratio is a key concept in understanding the world of mining and mineral extraction. For gold, this ratio can be astronomically high. What exactly does this mean for those interested in gold prospecting or the environmental impact of mining?
The rock-to-metal ratio represents the amount of ore and waste rock that needs to be processed to obtain a refined unit of a specific mineral. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) and Apple collaborated on a study published in Environmental Science & Technology, revealing that gold has an approximate rock-to-metal ratio of 3,000,000-to-1. This signifies that approximately three million metric tons of rock must be mined and processed to yield just one gram of gold. This substantial ratio underscores the intensive labor and resources required to extract even small quantities of gold, influencing everything from material sourcing to landscape design.
Why Is the Rock-to-Metal Ratio Important?
Understanding the rock-to-metal ratio is crucial for several reasons:
- Environmental Impact: A high ratio suggests a more significant environmental footprint due to the extensive mining and processing activities.
- Resource Management: It highlights the need for efficient mining techniques and waste management strategies.
- Economic Viability: Knowing the ratio helps in assessing the economic feasibility of mining operations.
- Sourcing Decisions: Manufacturing companies use this data to make informed decisions about where to source minerals.
- Recycling Benefits: The ratio quantifies the benefits of recycling by showing how much waste removal and ore mining could be avoided.
How Does the Rock-to-Metal Ratio Vary for Different Minerals?
The rock-to-metal ratio varies significantly among different mineral commodities. For instance, iron ore has a relatively low ratio of 9-to-1, meaning that for every nine metric tons of waste rock and ore processed, one metric ton of iron is produced. In contrast, gold’s extraordinarily high ratio of 3,000,000-to-1 illustrates the relative scarcity and difficulty in extracting this precious metal. The table below illustrates the differences:
| Mineral | Rock-to-Metal Ratio |
|---|---|
| Iron Ore | 9-to-1 |
| Gold | 3,000,000-to-1 |
| Copper | Varies Widely |
| Lithium | Varies |
| Rare Earth | Varies |
This disparity highlights the unique challenges and environmental considerations associated with mining each mineral.
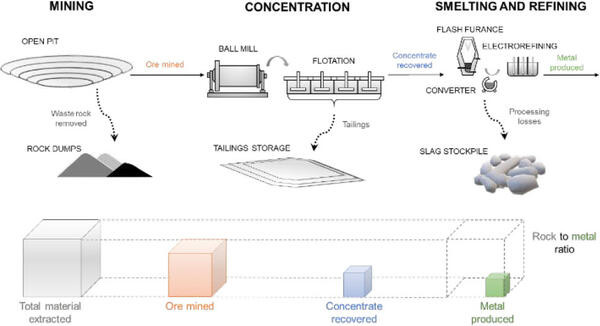 A graphic showing the rock to metal ration from rock and ore being mined to the final, refined product.
A graphic showing the rock to metal ration from rock and ore being mined to the final, refined product.
How Can This Knowledge Impact Landscape Design?
For landscape designers and homeowners, understanding the rock-to-metal ratio can influence choices in several ways:
- Sustainable Sourcing: Prioritizing materials with lower rock-to-metal ratios supports more sustainable mining practices.
- Material Selection: Considering the environmental impact of different materials helps in making eco-conscious decisions.
- Recycled Materials: Utilizing recycled materials reduces the demand for newly mined resources, lowering the overall environmental footprint.
- Design Choices: Creating designs that minimize material waste and maximize the use of local resources can promote sustainability.
By understanding the rock-to-metal ratio, individuals and businesses can make more informed and responsible choices when it comes to material selection and usage, contributing to more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
2. Factors Influencing Gold Concentration in Rocks: Why Does It Vary?
The concentration of gold in rocks varies significantly based on several geological and environmental factors. This variation affects the economic viability of gold mining operations and is crucial for understanding where to find gold deposits.
Several factors influence how much gold is present in mined rock:
- Geological Formation: Gold is often found in specific geological formations, such as hydrothermal veins and placer deposits.
- Ore Grade: The grade of the ore, measured in grams of gold per ton of rock (g/t), directly affects the amount of gold that can be extracted.
- Mining Techniques: Different mining methods can influence the amount of gold recovered from the rock.
- Location: The geographical location of the mine plays a significant role, as certain regions are known for higher gold concentrations.
- Mineral Composition: The presence of other minerals in the rock can either enhance or hinder gold extraction.
How Does Ore Grade Affect Gold Extraction?
Ore grade is a critical factor in gold mining. It refers to the concentration of gold within the ore, typically measured in grams per ton (g/t) or ounces per ton (oz/t). Higher ore grades mean more gold can be extracted from a given amount of rock, making the mining operation more economically viable.
- High-Grade Ore: Ore with a high gold concentration (e.g., above 8 g/t) is highly sought after because it requires less processing to extract a significant amount of gold.
- Low-Grade Ore: Low-grade ore (e.g., below 1 g/t) requires processing vast amounts of rock to obtain a worthwhile quantity of gold, increasing costs and environmental impact.
The decision to mine a particular deposit depends heavily on the ore grade, as it directly impacts the profitability and sustainability of the operation.
What Are the Different Types of Gold Deposits?
Gold deposits can be classified into several types, each with unique characteristics and gold concentrations:
- Hydrothermal Veins: These deposits form when hot, aqueous solutions circulate through fractures in rocks, depositing gold and other minerals.
- Placer Deposits: Formed by the erosion of gold-bearing rocks, with gold particles accumulating in riverbeds and alluvial fans due to their density.
- Porphyry Deposits: Large-scale deposits associated with intrusive igneous rocks, often containing lower gold concentrations but significant overall quantities.
- Skarn Deposits: Formed at the contact between intrusive rocks and carbonate rocks, resulting in the deposition of gold and other metals.
- Sedimentary Deposits: Gold can also be found in sedimentary rocks, where it has been transported and deposited along with other sediments.
Each type of deposit presents different challenges and opportunities for gold extraction, influencing the mining techniques and processing methods used.
What Role Does Location Play in Gold Concentration?
The geographical location of a mine is a critical determinant of gold concentration. Certain regions are known for their rich gold deposits due to their unique geological history and formations.
- Regions with High Gold Concentrations:
- Witwatersrand Basin, South Africa: Historically, the world’s largest gold-producing region.
- Nevada, USA: Home to numerous large gold mines, with significant Carlin-type deposits.
- Australia: Known for its gold-rich deposits in Western Australia and other regions.
- Canada: Significant gold production in Ontario, Quebec, and British Columbia.
- Russia: Increasing gold production in Siberia and other areas.
These regions have favorable geological conditions that have led to the formation of substantial gold deposits over millions of years.
How Does Mineral Composition Affect Gold Extraction?
The mineral composition of the rock matrix can significantly affect the ease and efficiency of gold extraction. Certain minerals can interfere with the extraction process, while others may enhance it.
- Interfering Minerals:
- Arsenopyrite: An arsenic-bearing mineral that can complicate gold extraction and require specialized processing techniques.
- Pyrite: Also known as “fool’s gold,” pyrite can encapsulate gold particles, making them difficult to recover.
- Tellurides: Minerals containing tellurium can bind with gold, requiring specific methods to break down and extract the gold.
- Enhancing Minerals:
- Quartz: Often associated with gold in hydrothermal veins, quartz is relatively easy to process.
- Calcite: Can indicate favorable conditions for gold deposition in certain geological settings.
Understanding the mineral composition of the ore is crucial for selecting the appropriate extraction methods and optimizing gold recovery.
3. Average Gold Content in Mined Rock: What to Realistically Expect?
Determining the average gold content in mined rock is essential for assessing the viability of gold mining operations. While the rock-to-metal ratio suggests a very low concentration, actual gold content can vary widely based on the factors discussed earlier.
What can one realistically expect from a ton of mined rock? Here are the key points:
- Typical Gold Content: The average gold content in mined rock is quite low, often less than 1 gram per ton.
- Economic Viability: For a gold mine to be economically viable, the ore grade needs to be high enough to offset the costs of mining and processing.
- Variability: Gold content varies significantly based on location, geological conditions, and mining techniques.
How Is Gold Content Measured?
Gold content in mined rock is typically measured in grams per ton (g/t) or ounces per ton (oz/t). This measurement, known as ore grade, is determined through various sampling and assaying techniques.
- Sampling Methods:
- Core Sampling: Involves extracting cylindrical rock samples from drill cores to analyze gold content.
- Channel Sampling: Cutting channels into rock faces to collect representative samples.
- Grab Sampling: Collecting random rock samples for a preliminary assessment (less accurate).
- Assaying Techniques:
- Fire Assay: A traditional method involving melting the sample with fluxes to separate gold and other precious metals.
- Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS): Measures the concentration of gold in a solution by analyzing the absorption of light.
- Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS): A highly sensitive technique for detecting trace elements, including gold.
These methods provide accurate measurements of gold content, which are crucial for resource estimation and mine planning.
What Are Considered High, Medium, and Low Ore Grades?
Classifying ore grades helps in evaluating the economic potential of a gold deposit. Here’s a general guideline for categorizing ore grades:
| Ore Grade Category | Gold Content (g/t) | Economic Viability |
|---|---|---|
| High Grade | > 8 g/t | Highly profitable, requires less processing. |
| Medium Grade | 2 – 8 g/t | Economically viable with efficient mining techniques. |
| Low Grade | < 2 g/t | Marginally viable, requires large-scale operations. |
These classifications can vary depending on the specific mining operation, location, and processing costs.
How Do Mining Techniques Influence Gold Recovery?
The choice of mining technique significantly impacts the amount of gold recovered from the rock. Different methods are suited for different types of deposits and ore grades.
- Open-Pit Mining: Used for large, low-grade deposits, involving the extraction of ore from a large open pit.
- Underground Mining: Used for high-grade deposits, involving the excavation of tunnels and shafts to access the ore.
- Placer Mining: Used for alluvial deposits, involving the separation of gold particles from sand and gravel using gravity concentration methods.
Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, efficiency, and environmental impact.
What Technologies Are Used to Improve Gold Extraction?
Advancements in technology have led to improved gold extraction methods, enhancing recovery rates and reducing environmental impact.
- Heap Leaching: Involves stacking ore in large heaps and applying a cyanide solution to dissolve gold, which is then recovered from the solution.
- Carbon-in-Pulp (CIP): A process where activated carbon is added to the ore pulp to adsorb gold, which is then stripped from the carbon.
- Carbon-in-Leach (CIL): Similar to CIP, but leaching and adsorption occur simultaneously.
- Bio-Oxidation: Uses microorganisms to oxidize sulfide minerals, liberating gold for easier extraction.
- Pressure Oxidation: Oxidizes sulfide minerals under high pressure and temperature, improving gold recovery.
These technologies have made it possible to extract gold from previously uneconomic deposits, contributing to increased gold production worldwide.
4. Environmental Impact of Gold Mining: Understanding the Costs
Gold mining, while economically significant, can have substantial environmental impacts. Understanding these costs is crucial for promoting sustainable mining practices and minimizing harm to the environment.
What are the primary environmental concerns associated with gold mining?
- Deforestation: Clearing forests to create mines and infrastructure can lead to habitat loss and soil erosion.
- Water Pollution: The use of cyanide and other chemicals in gold extraction can contaminate water sources, harming aquatic life and human health.
- Soil Degradation: Mining activities can disrupt soil structure, leading to erosion and loss of fertility.
- Air Pollution: Dust and emissions from mining operations can contribute to air pollution, affecting local communities and ecosystems.
- Habitat Destruction: Mining can destroy or fragment habitats, impacting biodiversity and wildlife populations.
How Does Cyanide Use Affect the Environment?
Cyanide is commonly used in gold mining to dissolve gold from ore, but it poses significant environmental risks.
- Toxicity: Cyanide is highly toxic to humans and wildlife, and accidental releases can have devastating consequences.
- Water Contamination: Cyanide spills can contaminate rivers, lakes, and groundwater, harming aquatic organisms and rendering water unusable.
- Soil Contamination: Cyanide can also contaminate soil, affecting plant growth and soil health.
- Regulations: Strict regulations are in place to manage cyanide use and prevent environmental damage, but accidents can still occur.
Alternatives to cyanide, such as thiosulfate and glycine, are being explored to reduce the environmental impact of gold mining.
What Are the Effects of Deforestation and Soil Erosion?
Deforestation and soil erosion are significant consequences of gold mining, with long-lasting effects on ecosystems.
- Deforestation:
- Habitat Loss: Clearing forests destroys habitats for numerous species, leading to biodiversity loss.
- Climate Change: Forests play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, and deforestation contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Water Cycle Disruption: Forests help regulate the water cycle, and deforestation can lead to increased runoff and flooding.
- Soil Erosion:
- Loss of Fertility: Erosion removes topsoil, which is rich in nutrients and organic matter, reducing soil fertility.
- Sedimentation: Eroded soil can be transported into rivers and lakes, causing sedimentation and harming aquatic life.
- Land Degradation: Erosion can lead to land degradation, making it difficult to rehabilitate mined areas.
Sustainable mining practices, such as reforestation and erosion control, are essential to mitigate these effects.
How Can Mining Companies Minimize Environmental Impact?
Mining companies can take several steps to minimize the environmental impact of their operations.
- Environmental Impact Assessments: Conducting thorough assessments before starting mining operations to identify potential environmental risks.
- Sustainable Mining Practices: Implementing best practices in waste management, water conservation, and energy efficiency.
- Rehabilitation: Restoring mined areas to their original state or creating new habitats for wildlife.
- Community Engagement: Working with local communities to address concerns and ensure that mining operations benefit the region.
- Technology Adoption: Using advanced technologies to improve gold extraction efficiency and reduce chemical usage.
By prioritizing environmental stewardship, mining companies can reduce their footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
What Role Does Regulation Play in Environmental Protection?
Government regulations play a crucial role in protecting the environment from the adverse effects of gold mining.
- Environmental Laws: Setting standards for water and air quality, waste disposal, and land rehabilitation.
- Permitting: Requiring mining companies to obtain permits before starting operations, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
- Monitoring: Monitoring mining operations to ensure they are adhering to regulations and taking corrective action when necessary.
- Enforcement: Enforcing environmental laws through fines, penalties, and other measures to deter non-compliance.
- International Agreements: Participating in international agreements to promote sustainable mining practices and protect shared resources.
Effective regulation is essential for ensuring that gold mining is conducted in an environmentally responsible manner.
5. Sustainable Gold Mining Practices: A Path Forward
Sustainable gold mining practices aim to balance the economic benefits of gold production with the need to protect the environment and support local communities. These practices focus on reducing environmental impact, promoting responsible resource management, and ensuring social well-being.
What are the key principles of sustainable gold mining?
- Environmental Stewardship: Minimizing environmental impact through responsible mining practices and effective rehabilitation.
- Social Responsibility: Engaging with local communities and respecting their rights and cultural heritage.
- Economic Viability: Ensuring that mining operations are economically sustainable and contribute to local development.
- Transparency and Accountability: Operating in a transparent and accountable manner, providing information to stakeholders and addressing concerns.
- Innovation and Technology: Adopting new technologies and innovative approaches to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
How Can Mining Companies Reduce Water Consumption?
Water is a critical resource in gold mining, and reducing water consumption is essential for sustainable operations.
- Water Recycling: Recycling water used in processing operations to reduce the need for freshwater.
- Dry Stacking: Using dry stacking methods for tailings disposal to minimize water loss and reduce the risk of water contamination.
- Water Harvesting: Collecting rainwater and stormwater for use in mining operations.
- Efficient Irrigation: Using efficient irrigation techniques for dust suppression and vegetation.
- Leak Detection and Repair: Implementing programs to detect and repair leaks in water pipelines and storage facilities.
By implementing these measures, mining companies can significantly reduce their water footprint and contribute to water conservation.
What Are the Best Practices for Waste Management?
Effective waste management is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of gold mining.
- Tailings Management: Storing tailings in secure and well-managed facilities to prevent water and soil contamination.
- Waste Rock Management: Properly disposing of waste rock to prevent acid mine drainage and other environmental problems.
- Hazardous Waste Management: Handling and disposing of hazardous waste materials, such as cyanide, in a safe and responsible manner.
- Waste Reduction: Reducing waste generation through efficient mining and processing techniques.
- Recycling: Recycling materials, such as scrap metal and used equipment, to reduce the need for new resources.
By adopting these best practices, mining companies can minimize waste generation and reduce the risk of environmental contamination.
How Can Mining Benefit Local Communities?
Gold mining can provide economic and social benefits to local communities, but it is essential to ensure that these benefits are shared equitably.
- Job Creation: Providing employment opportunities for local residents.
- Local Procurement: Purchasing goods and services from local businesses.
- Infrastructure Development: Investing in infrastructure, such as roads, schools, and hospitals.
- Community Development Programs: Supporting community development programs, such as education, health, and environmental conservation.
- Revenue Sharing: Sharing a portion of mining revenues with local communities.
By working in partnership with local communities, mining companies can create lasting benefits and contribute to sustainable development.
What Certifications Promote Sustainable Mining?
Several certifications promote sustainable mining practices and provide assurance to consumers and investors that gold is produced responsibly.
- Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC): Certifies companies that meet ethical, social, and environmental standards in the gold and jewelry supply chain.
- Fairmined: Certifies artisanal and small-scale mining organizations that meet strict environmental, social, and labor standards.
- Alliance for Responsible Mining (ARM): Promotes responsible mining practices and supports the development of sustainable mining communities.
- International Council on Mining and Metals (ICMM): A global organization that promotes sustainable development in the mining and metals industry.
By supporting certified gold, consumers and investors can encourage responsible mining practices and contribute to a more sustainable future.
6. Gold in Landscape Design: Adding Value Beyond Monetary Worth
While the extraction of gold has significant environmental considerations, incorporating rocks with even trace amounts of gold or minerals that complement gold tones can add unique aesthetic value to landscape designs. Gold-colored stones and minerals can enhance the beauty and elegance of outdoor spaces, creating visually stunning environments.
How can gold or gold-toned elements be used in landscape design?
- Accent Stones: Incorporating gold-colored stones as accent pieces in rock gardens or pathways.
- Water Features: Using stones with gold flecks or minerals to enhance the shimmer and sparkle of water features.
- Decorative Gravel: Adding gold-toned gravel to flower beds or walkways for a touch of elegance.
- Mineral Displays: Showcasing rocks with interesting mineral formations or gold inclusions as focal points.
- Color Complement: Pairing gold-toned elements with complementary colors in plants and other landscape features to create visual harmony.
What Types of Rocks and Minerals Complement Gold Tones?
Several types of rocks and minerals can complement gold tones in landscape design, enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal.
- Quartz: Clear or milky quartz can provide a neutral backdrop that highlights the warmth of gold tones.
- Pyrite: Known as “fool’s gold,” pyrite has a metallic gold luster that can add visual interest.
- Mica: Mica flakes can add shimmer and sparkle to rocks and soil, complementing gold tones.
- Granite: Certain types of granite contain gold-colored minerals, such as feldspar and mica, that can add warmth and texture.
- Sandstone: Sandstone with iron oxide staining can exhibit warm, earthy tones that complement gold.
By carefully selecting rocks and minerals that complement gold tones, designers can create visually stunning and harmonious landscapes.
How Can Gold-Toned Elements Enhance Water Features?
Water features are a popular element in landscape design, and incorporating gold-toned elements can enhance their beauty and appeal.
- Shimmer and Sparkle: Stones with gold flecks or minerals can add shimmer and sparkle to water features, creating a mesmerizing effect.
- Reflections: Gold-toned surfaces can reflect sunlight, enhancing the brightness and vibrancy of the water.
- Contrast: Pairing gold-toned elements with darker stones or plants can create a striking contrast, drawing attention to the water feature.
- Natural Look: Using natural stones with gold tones can create a more organic and authentic look for water features.
- Focal Point: A large gold-toned stone or mineral formation can serve as a focal point in a water feature, adding visual interest.
By incorporating gold-toned elements into water features, designers can create captivating and visually stunning landscapes.
What Are Some Design Ideas for Incorporating Gold in Landscapes?
Here are some creative design ideas for incorporating gold in landscapes:
- Rock Garden: Create a rock garden with a variety of gold-toned stones, minerals, and plants that complement each other.
- Pathway: Line a pathway with gold-colored gravel or stones to add a touch of elegance.
- Focal Point: Use a large gold-toned stone or mineral formation as a focal point in a garden bed or lawn.
- Water Feature Accent: Add gold-toned stones around a water feature to enhance its beauty.
- Container Garden: Plant flowers in gold-colored pots or containers to add a touch of luxury to a patio or deck.
These design ideas can help you incorporate gold into your landscape in a creative and visually appealing way.
Where Can You Find Gold-Toned Rocks and Minerals for Landscaping?
Finding the right materials is essential for incorporating gold tones into your landscape design.
- Local Stone Suppliers: Check with local stone suppliers for gold-toned rocks and minerals.
- Rock and Mineral Shows: Attend rock and mineral shows to find unique specimens.
- Online Retailers: Browse online retailers for a wide selection of gold-toned rocks and minerals.
- Landscape Supply Stores: Visit landscape supply stores for decorative gravel and stones with gold tones.
- Rockscapes.net: Explore the selection at rockscapes.net for unique and high-quality landscape materials.
By exploring these sources, you can find the perfect materials to add a touch of gold to your landscape.
7. Exploring the Geology of Gold: From Earth’s Depths to Your Backyard
Understanding the geology of gold provides valuable insights into how it forms, where it is found, and how it can be incorporated into landscape design. Gold’s unique properties and geological origins make it a fascinating element to explore, both in its natural state and as a design element.
How does gold form in the earth?
- Hydrothermal Processes: Gold often forms through hydrothermal processes, where hot, aqueous fluids circulate through fractures in rocks, depositing gold and other minerals.
- Magmatic Processes: Gold can also form through magmatic processes, where it crystallizes from molten rock as it cools.
- Placer Deposits: Gold can be eroded from its original source and transported by water, accumulating in placer deposits in riverbeds and alluvial fans.
What Are the Different Types of Gold Deposits?
Different types of gold deposits have unique characteristics and geological settings.
- Vein Deposits: These deposits form when gold-bearing fluids fill fractures in rocks, creating veins of gold and other minerals.
- Porphyry Deposits: Large-scale deposits associated with intrusive igneous rocks, often containing lower gold concentrations but significant overall quantities.
- Skarn Deposits: Formed at the contact between intrusive rocks and carbonate rocks, resulting in the deposition of gold and other metals.
- Placer Deposits: Formed by the erosion of gold-bearing rocks, with gold particles accumulating in riverbeds and alluvial fans due to their density.
- Sedimentary Deposits: Gold can also be found in sedimentary rocks, where it has been transported and deposited along with other sediments.
Each type of deposit presents different challenges and opportunities for gold extraction.
Where Are the Major Gold-Producing Regions in the World?
Certain regions are known for their rich gold deposits due to their unique geological history and formations.
- South Africa: Historically, the world’s largest gold-producing region, particularly the Witwatersrand Basin.
- Australia: Known for its gold-rich deposits in Western Australia and other regions.
- Russia: Increasing gold production in Siberia and other areas.
- United States: Significant gold production in Nevada and other western states.
- Canada: Significant gold production in Ontario, Quebec, and British Columbia.
These regions have favorable geological conditions that have led to the formation of substantial gold deposits over millions of years.
How Does Gold’s Geology Influence Landscape Design?
Understanding gold’s geology can influence landscape design in several ways.
- Material Selection: Choosing rocks and minerals that are associated with gold deposits can add authenticity and visual interest.
- Design Inspiration: Drawing inspiration from geological formations and landscapes to create natural-looking designs.
- Educational Value: Incorporating geological elements into landscape design to educate visitors about the earth’s history and processes.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Prioritizing materials from sustainable mining operations to minimize environmental impact.
By incorporating geological knowledge into landscape design, you can create unique and educational outdoor spaces.
What Resources Can You Use to Learn More About Gold Geology?
Several resources can help you learn more about gold geology.
- Geological Surveys: Consult geological surveys for information on gold deposits in your region.
- Universities: Take geology courses at local universities or community colleges.
- Books and Publications: Read books and publications on gold geology and mining.
- Online Resources: Explore online resources, such as websites, articles, and videos, to learn more about gold geology.
- Museums: Visit natural history museums to see displays of gold specimens and learn about their geological origins.
By utilizing these resources, you can gain a deeper understanding of gold geology and its significance in landscape design.
8. The Allure of Gold: Why Are We So Fascinated?
Gold has captivated humanity for millennia, symbolizing wealth, power, and beauty. Its unique properties and cultural significance make it a fascinating element to explore, both in its natural state and as a design element.
What makes gold so special?
- Rarity: Gold is a relatively rare element, making it valuable and desirable.
- Durability: Gold is highly resistant to corrosion and tarnish, making it a long-lasting and durable material.
- Beauty: Gold has a unique color and luster that is highly prized for jewelry and decorative purposes.
- Conductivity: Gold is an excellent conductor of electricity, making it useful in electronics.
- Malleability: Gold is highly malleable, meaning it can be easily shaped and formed into various objects.
How Has Gold Been Used Throughout History?
Gold has been used for various purposes throughout history, reflecting its cultural and economic significance.
- Currency: Gold has been used as a form of currency for thousands of years.
- Jewelry: Gold has been used to create jewelry and adornments since ancient times.
- Decoration: Gold has been used to decorate buildings, furniture, and other objects.
- Religious Objects: Gold has been used to create religious objects and symbols.
- Technology: Gold is used in various technological applications, such as electronics and medicine.
Gold’s versatility and enduring appeal have made it a valuable and sought-after material throughout history.
What Is the Cultural Significance of Gold in Different Societies?
Gold holds different cultural meanings in different societies, reflecting their unique values and traditions.
- Ancient Egypt: Gold was associated with the sun god Ra and was used to adorn pharaohs and create elaborate burial objects.
- Ancient Greece: Gold was associated with wealth and power and was used to create coins, jewelry, and statues.
- Inca Empire: Gold was considered the “sweat of the sun” and was used to create elaborate ornaments and religious objects.
- Modern Western Societies: Gold is associated with wealth, luxury, and status and is used to create jewelry, coins, and investments.
These cultural meanings reflect gold’s enduring appeal and its role in shaping human societies.
How Does Gold’s Allure Influence Landscape Design?
Gold’s allure can influence landscape design by adding a touch of luxury, elegance, and sophistication to outdoor spaces.
- Focal Points: Using gold-toned elements as focal points to draw attention and create visual interest.
- Accent Elements: Adding gold-toned accents to complement other landscape features.
- Color Palette: Incorporating gold tones into a color palette to create a warm and inviting atmosphere.
- Material Selection: Choosing materials with gold tones to add richness and texture to the landscape.
- Symbolism: Using gold-toned elements to symbolize wealth, prosperity, and good fortune.
By incorporating gold’s allure into landscape design, you can create outdoor spaces that are both beautiful and meaningful.
Where Can You Find Inspiration for Gold-Themed Landscapes?
Several sources can provide inspiration for gold-themed landscapes.
- Gardens: Visit gardens that feature gold-toned elements and plants.
- Design Magazines: Browse design magazines for ideas on incorporating gold into landscapes.
- Online Resources: Explore online resources, such as websites, articles, and images, for inspiration.
- Travel: Visit regions known for their gold deposits and geological formations.
- Rockscapes.net: Explore the design ideas and material selections at rockscapes.net for inspiration on creating gold-themed landscapes.
By exploring these sources, you can gather ideas and inspiration for creating unique and captivating gold-themed landscapes.
9. The Future of Gold Mining: Innovations and Challenges
The future of gold mining is shaped by innovations in technology, growing environmental concerns, and evolving social expectations. Addressing these challenges while harnessing the potential of new technologies will be crucial for ensuring a sustainable and responsible gold mining industry.
What are the major trends shaping the future of gold mining?
- Technological Advancements: The adoption of new technologies, such as automation, robotics, and data analytics, is transforming the gold mining industry.
- Environmental Sustainability: Growing pressure to reduce the environmental impact of gold mining is driving the development of more sustainable practices.
- Social Responsibility: Increasing focus on social responsibility and community engagement is shaping how mining companies operate.
- Resource Depletion: The depletion of high-grade gold deposits is driving the search for new deposits and the development of more efficient extraction methods.
- Regulatory Changes: Evolving regulations are influencing mining practices and environmental standards.
How Will Technology Transform Gold Mining?
Technology is poised to revolutionize gold mining in several ways.
- Automation: Automated equipment and processes can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance safety in mining operations.
- Robotics: Robotic systems can be used to perform tasks in hazardous or difficult-to-access environments.
- Data Analytics: Data analytics can be used to optimize mining operations, improve resource estimation, and reduce waste.
- Remote Sensing: Remote sensing technologies, such as drones and satellites, can be used to monitor mining operations and assess environmental impact.
- Virtual Reality: Virtual reality can be used for training, planning, and simulating mining operations.
These technologies have the potential to transform gold mining into a more efficient, sustainable, and responsible industry.
What Are the Challenges Facing the Gold Mining Industry?
The gold mining industry faces several significant challenges.
- Environmental Impact: Minimizing the environmental impact of gold mining remains a major challenge.
- Social Issues: Addressing social issues, such as community displacement and human rights abuses, is crucial for maintaining a social license to operate.
- Resource Depletion: Finding new gold deposits and developing more efficient extraction methods is essential for sustaining production.
- Regulatory Compliance: Complying with increasingly stringent environmental and social regulations can be costly and time-consuming.
- Price Volatility: Fluctuations in gold prices can impact the economic viability of mining operations.
Addressing these challenges will require innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to sustainable and responsible mining practices.
How Can the Gold Mining Industry Become More Sustainable?
The gold mining industry can become more sustainable by adopting best practices in environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic viability.
- Reduce Environmental Impact: Minimize water consumption, reduce waste generation, and prevent pollution.
- Engage with Communities: Respect community rights, provide economic benefits, and address social concerns.
- Promote Transparency: Operate in a transparent and accountable manner, providing information to stakeholders and addressing concerns.
- Invest in Technology: Adopt new technologies to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability.
- Support Certification: Support certification programs that promote sustainable mining practices.
By prioritizing sustainability, the gold mining industry can contribute to a more environmentally and socially responsible future.
What Role Do Consumers Play in Promoting Sustainable Gold Mining?
Consumers play a crucial role in promoting sustainable gold mining by making informed purchasing decisions and supporting certified gold products.
- Buy Certified Gold: Choose gold products that are certified by organizations such as the Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC) and Fairmined.
- Support Responsible Companies: Purchase gold from companies that are committed to sustainable mining practices.
- Ask Questions: Ask retailers and manufacturers about their gold sourcing practices.
- Recycle Gold: Recycle old gold jewelry and electronics to reduce the need for new mining.
- Spread Awareness: Educate others about the importance of sustainable gold mining.
By making conscious choices, consumers can encourage responsible mining practices and contribute to a more sustainable gold industry.
10. Rockscapes.net: Your Partner in Landscape Design and Sustainable Material Sourcing
At rockscapes.net, we understand the importance of sustainable material sourcing and responsible landscape design. We are committed to providing our customers with high-quality materials and expert advice to create beautiful and environmentally friendly outdoor spaces.
How can rockscapes.net help you with your landscape design needs?
- Wide Selection of Materials: We offer a wide selection of rocks, minerals, and other landscape materials to suit any design style.
- Sustainable Sourcing: We prioritize sustainable sourcing practices to minimize our environmental impact.
- Expert Advice: Our team of experienced landscape designers can provide expert advice and guidance to help you create the perfect outdoor space.
- **Design Ideas
