Are you curious about the stones beneath your feet and how they shape our world? The three major rock types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic, each formed through unique geological processes. At rockscapes.net, we’ll explore these rock types and their surprising roles in everything from home building to backyard landscaping, offering insights into their formation, characteristics, and applications in creating stunning rockscapes.
1. Unveiling the Earth’s Building Blocks: An Introduction to Rock Types
Do you know what rocks are actually made of? Rocks are not just inert objects; they are dynamic materials that reflect Earth’s ever-changing processes. Rocks are composed of one or more minerals, each possessing a unique chemical composition and crystalline structure. According to research from Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, rocks constantly transform through geological processes, highlighting their dynamic nature. Igneous rocks solidify from cooled magma or lava, sedimentary rocks form from accumulated sediments, and metamorphic rocks result from the transformation of existing rocks under intense heat and pressure.
1.1. What Makes a Rock a Rock?
What defines a rock, and how does it differ from a mineral? A rock is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of one or more minerals. Minerals have a specific chemical composition and crystal structure, while rocks are mixtures of minerals or other materials. Rocks can also be made of organic matter, like coal, which contains carbon from ancient plants. This composition determines a rock’s physical properties and influences its role in geological processes.
1.2. How Do the Three Major Rock Types Differ?
What sets apart igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks? Igneous rocks originate from cooled molten rock, sedimentary rocks form from accumulated sediments, and metamorphic rocks are created by the alteration of existing rocks under heat and pressure. Igneous rocks like granite and basalt are known for their hardness and durability. Sedimentary rocks such as sandstone and limestone often display layered structures and may contain fossils. Metamorphic rocks like marble and slate exhibit new mineral compositions and textures due to their transformation.
2. Igneous Rocks: Born of Fire
Have you ever wondered how volcanic eruptions contribute to rock formation? Igneous rocks, derived from the Latin word “ignis” meaning fire, are born from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Magma, molten rock beneath the Earth’s surface, cools slowly, resulting in intrusive igneous rocks. Lava, molten rock erupted onto the surface, cools rapidly, forming extrusive igneous rocks. According to the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), the rate of cooling significantly influences the crystal size and texture of igneous rocks.
2.1. What is the Difference Between Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks?
What are the defining characteristics of intrusive and extrusive rocks? Intrusive igneous rocks, like granite, cool slowly beneath the Earth’s surface, forming large crystals. Extrusive igneous rocks, such as basalt, cool quickly on the surface, resulting in small or no crystals. The slow cooling process of intrusive rocks allows for the development of visible mineral grains, while the rapid cooling of extrusive rocks often leads to a fine-grained or glassy texture.
2.2. What Are Some Common Types of Igneous Rocks?
Can you name a few examples of igneous rocks and where they are found? Granite, diorite, gabbro, and peridotite are common intrusive igneous rocks. Basalt, andesite, rhyolite, and obsidian are typical extrusive igneous rocks. Granite is often used in countertops and buildings due to its durability and aesthetic appeal. Basalt is frequently used in road construction and landscaping because of its strength and resistance to weathering. Obsidian, a volcanic glass, has been used for tools and ornamental purposes for centuries.
2.3. How Are Igneous Rocks Used in Landscaping?
How can you use igneous rocks to enhance your outdoor spaces? Igneous rocks are excellent for creating durable and visually appealing landscape features. Granite boulders can serve as focal points in gardens, while basalt columns can add a modern touch to outdoor designs. According to landscape architects, the use of igneous rocks in landscaping provides a natural, timeless aesthetic that complements various design styles. Crushed granite is also a popular choice for pathways and driveways, offering a stable and attractive surface.
 Granite boulders in a garden
Granite boulders in a garden
2.4. What Are The Physical Properties Of Igneous Rocks?
What gives igneous rocks their distinctive characteristics? Igneous rocks are known for their hardness, density, and resistance to weathering. Granite, for example, has a high compressive strength, making it ideal for structural applications. Basalt is resistant to chemical weathering, which makes it perfect for outdoor use. These physical properties make igneous rocks a reliable and long-lasting choice for both construction and landscaping projects.
3. Sedimentary Rocks: Stories in Stone
Did you know that some rocks are formed from layers of ancient sediments? Sedimentary rocks, formed from the accumulation and cementation of sediments, provide a window into Earth’s past. Sediments, including fragments of other rocks, minerals, and organic matter, are transported by wind, water, and ice and eventually deposited in layers. According to the National Park Service, sedimentary rocks often contain fossils, offering valuable insights into prehistoric life.
3.1. What are the Processes Involved in the Formation of Sedimentary Rocks?
How do loose sediments transform into solid rock? Weathering, erosion, transportation, deposition, and lithification are the key processes in the formation of sedimentary rocks. Weathering breaks down existing rocks into smaller fragments. Erosion transports these sediments to new locations. Deposition involves the accumulation of sediments in layers. Lithification, which includes compaction and cementation, transforms the loose sediments into solid rock.
3.2. What Are the Different Types of Sedimentary Rocks?
Can you describe the main categories of sedimentary rocks and their compositions? Clastic, chemical, and organic sedimentary rocks are the three main types. Clastic sedimentary rocks, like sandstone and shale, are formed from fragments of other rocks. Chemical sedimentary rocks, such as limestone and rock salt, precipitate from solutions. Organic sedimentary rocks, like coal, are formed from the accumulation of organic matter.
3.3. How Are Sedimentary Rocks Used in Construction?
What makes sedimentary rocks a valuable resource in the building industry? Sedimentary rocks are widely used in construction for their versatility and aesthetic appeal. Sandstone is a popular choice for building facades and paving stones. Limestone is used in cement production and as a decorative stone. According to civil engineers, the durability and availability of sedimentary rocks make them cost-effective building materials.
3.4. How Can You Incorporate Sedimentary Rocks Into Your Garden Design?
How can sedimentary rocks enhance the beauty and functionality of your garden? Sedimentary rocks can be used to create natural-looking pathways, retaining walls, and water features. Limestone pavers can add a touch of elegance to garden paths, while sandstone boulders can create a rustic, natural look. Landscape designers often use sedimentary rocks to mimic natural geological formations, enhancing the overall aesthetic of the garden.
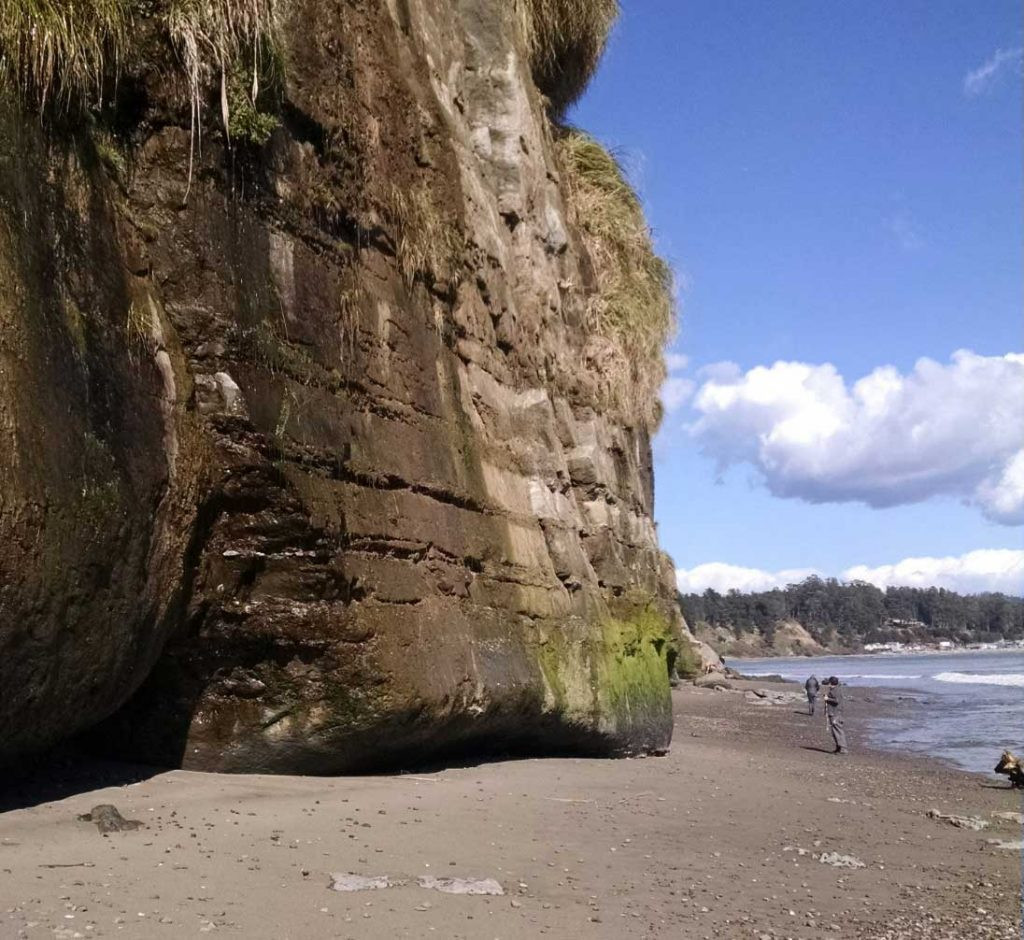 Sedimentary rocks along the California coast
Sedimentary rocks along the California coast
3.5. What Are The Common Uses Of Sedimentary Rocks?
What are the diverse applications of sedimentary rocks in various industries? Sedimentary rocks have numerous uses, including construction, agriculture, and manufacturing. Limestone is used in the production of cement, while sandstone is used in the construction of buildings and roads. Shale is used in the production of shale oil and natural gas. In agriculture, limestone is used to neutralize acidic soils, improving crop yields.
4. Metamorphic Rocks: Transformed by Pressure
Have you heard of rocks that change their form due to extreme conditions? Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing rocks are transformed by heat, pressure, or chemically active fluids. Metamorphism can alter the mineral composition, texture, and structure of the original rock, creating new and unique rock types. According to geologists, metamorphic rocks provide evidence of Earth’s dynamic geological processes.
4.1. What Causes Metamorphism in Rocks?
What are the primary factors that drive the metamorphic process? Heat, pressure, and chemically active fluids are the main agents of metamorphism. Heat increases the rate of chemical reactions, allowing new minerals to form. Pressure causes the alignment of minerals, creating distinct textures. Chemically active fluids facilitate the transport of ions, leading to the formation of new minerals.
4.2. What Are the Two Main Types of Metamorphism?
How does regional metamorphism differ from contact metamorphism? Regional metamorphism occurs over large areas, typically associated with mountain building, while contact metamorphism occurs locally, near igneous intrusions. Regional metamorphism results from the combined effects of heat and pressure, leading to the formation of foliated rocks like schist and gneiss. Contact metamorphism is primarily caused by heat from nearby magma, creating non-foliated rocks like marble and quartzite.
4.3. What Are Some Examples of Metamorphic Rocks and Their Parent Rocks?
Can you match metamorphic rocks with their original rock types? Shale transforms into slate, limestone becomes marble, sandstone becomes quartzite, and granite can turn into gneiss. Slate is commonly used for roofing and flooring due to its durability and ability to be split into thin sheets. Marble is prized for its beauty and is used in sculptures and decorative building elements. Quartzite is valued for its hardness and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for countertops and paving stones.
4.4. How Do Landscapers Use Metamorphic Rocks?
What are some creative ways to use metamorphic rocks in outdoor spaces? Metamorphic rocks add elegance and durability to landscape designs. Slate can be used for pathways, patios, and water features, providing a smooth and sophisticated surface. Marble chips can brighten up garden beds and walkways, adding a touch of luxury. Gneiss boulders can create dramatic focal points, showcasing the unique textures and patterns of metamorphic rocks.
4.5. What Are The Unique Characteristics Of Metamorphic Rocks?
What sets metamorphic rocks apart from other rock types? Metamorphic rocks exhibit a wide range of textures and mineral compositions, reflecting the varying conditions under which they formed. Foliated metamorphic rocks, like schist and gneiss, have a layered or banded appearance due to the alignment of minerals. Non-foliated metamorphic rocks, like marble and quartzite, have a uniform texture. These unique characteristics make metamorphic rocks highly desirable for both functional and aesthetic applications.
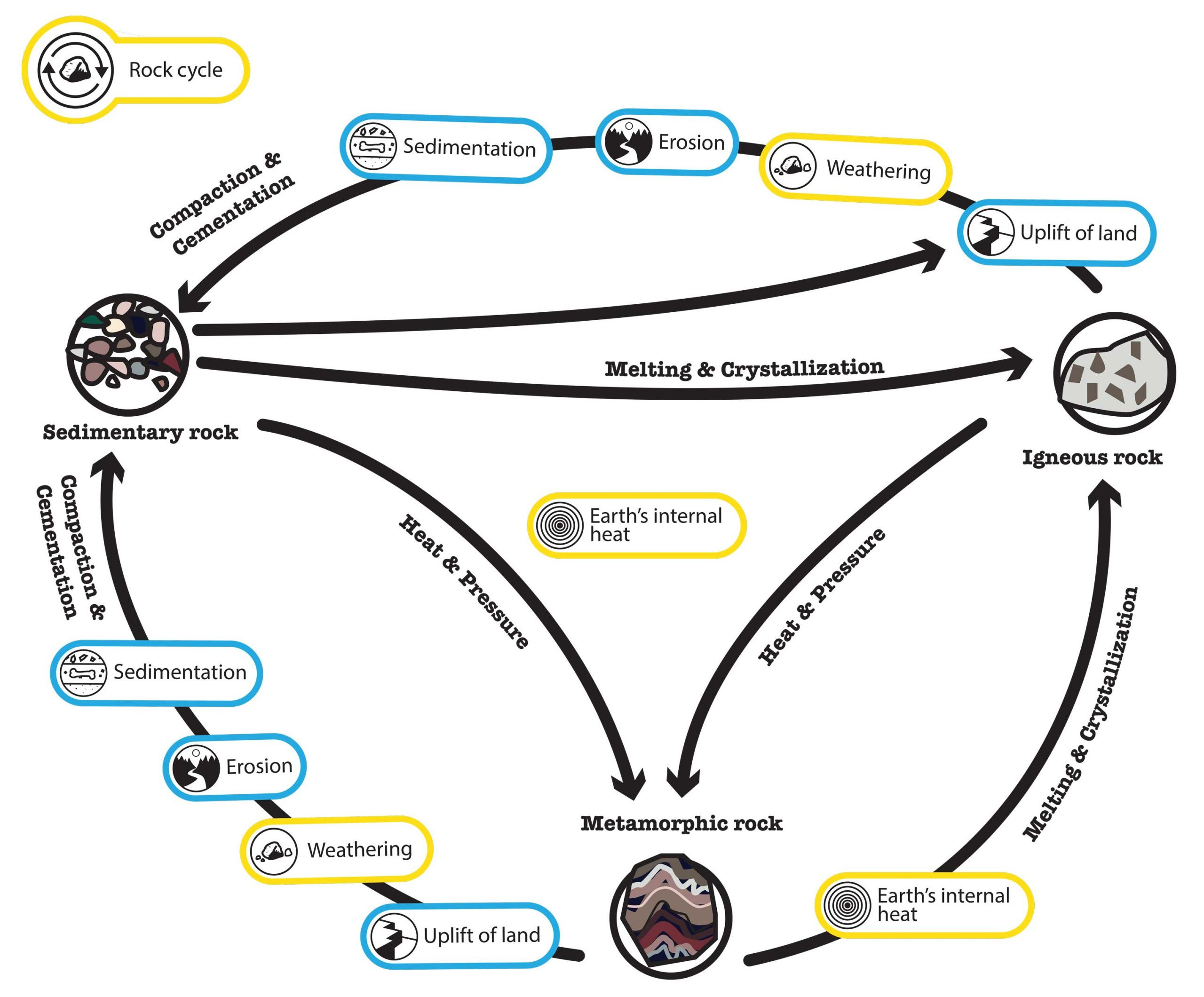
5. The Rock Cycle: A Continuous Transformation
Did you know that rocks are constantly changing from one type to another? The rock cycle describes the continuous processes through which rocks are transformed from one type to another. Igneous rocks can be weathered and eroded into sediments, which form sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks can be metamorphosed into metamorphic rocks. Metamorphic rocks can be melted to form magma, which cools to form igneous rocks, completing the cycle. According to the Geological Society of America, the rock cycle is a fundamental concept in understanding Earth’s dynamic systems.
5.1. What Are the Key Processes That Drive the Rock Cycle?
What forces cause rocks to change and transform over time? Weathering, erosion, sedimentation, lithification, metamorphism, and melting are the key processes that drive the rock cycle. Weathering and erosion break down rocks at the Earth’s surface. Sedimentation involves the accumulation of sediments. Lithification transforms sediments into sedimentary rocks. Metamorphism changes rocks under heat and pressure. Melting turns rocks into magma. These processes ensure that Earth’s materials are constantly recycled and transformed.
5.2. How Do Plate Tectonics Influence the Rock Cycle?
What role do tectonic plates play in the formation and transformation of rocks? Plate tectonics significantly influences the rock cycle by driving processes such as mountain building, volcanism, and subduction. Mountain building exposes rocks to weathering and erosion. Volcanism brings magma to the surface, forming igneous rocks. Subduction zones recycle crustal materials back into the mantle, leading to metamorphism and melting.
5.3. What Role Do Humans Play in the Rock Cycle?
How do human activities impact the natural processes of the rock cycle? Humans significantly impact the rock cycle through activities such as mining, quarrying, and urbanization. Mining and quarrying extract rocks and minerals from the Earth, altering natural landscapes and increasing erosion. Urbanization covers land with impermeable surfaces, increasing runoff and altering sedimentation patterns. According to environmental scientists, these activities can accelerate certain processes in the rock cycle while disrupting others.
5.4. What Are the Environmental Implications of the Rock Cycle?
How does the cycling of rocks affect Earth’s ecosystems and resources? The rock cycle plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate, controlling soil formation, and influencing water quality. Weathering of rocks releases essential nutrients into soils, supporting plant growth. Sedimentation patterns affect the distribution of water resources and the formation of sedimentary basins. The rock cycle also helps to sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating climate change.
5.5. How Can You Study the Rock Cycle in Your Own Backyard?
What can you learn about geology by observing rocks in your local environment? By examining rocks in your backyard, you can learn about local geological history and the processes that have shaped the landscape. Identifying the different types of rocks, observing their textures and compositions, and researching their origins can provide valuable insights into the rock cycle. Visit local parks and geological sites to see larger-scale examples of rock formations and geological processes.
6. Applications of the 3 Major Rock Types in Landscaping and Construction
How can you use the three major rock types to create beautiful and functional spaces? The three major rock types—igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic—offer a diverse range of applications in landscaping and construction, each bringing unique aesthetic and functional qualities. According to landscape architects, understanding the properties of these rocks is crucial for creating sustainable and visually appealing designs.
6.1. Igneous Rocks: Strength and Durability in Design
How do igneous rocks provide stability and longevity to landscape and construction projects? Igneous rocks, known for their strength and resistance to weathering, are ideal for structural elements and high-traffic areas. Granite is commonly used for countertops, paving stones, and building facades. Basalt is frequently used in retaining walls, pathways, and water features. Their durability ensures that these features will withstand the elements and maintain their appearance for years.
6.2. Sedimentary Rocks: Adding Texture and Character to Spaces
What unique aesthetic qualities do sedimentary rocks bring to landscaping and construction? Sedimentary rocks, with their layered textures and earthy tones, add character and natural beauty to any space. Sandstone is a popular choice for building veneers, garden walls, and decorative stones. Limestone is used in garden paths, patios, and as a component in cement. The presence of fossils and other sedimentary structures can add unique visual interest.
6.3. Metamorphic Rocks: Elegance and Sophistication in Outdoor Designs
How do metamorphic rocks elevate the aesthetic appeal of landscape and construction projects? Metamorphic rocks, with their elegant textures and refined appearances, bring a touch of sophistication to outdoor designs. Slate is commonly used for roofing, paving, and water features, providing a sleek and modern look. Marble chips can brighten up garden beds and walkways, adding a touch of luxury. Gneiss boulders can create dramatic focal points, showcasing the unique patterns and textures of metamorphic rocks.
6.4. How to Choose the Right Rock Type for Your Project
What factors should you consider when selecting rocks for your landscaping or construction needs? When selecting rocks for your project, consider the climate, soil conditions, intended use, and desired aesthetic. In areas with harsh weather, choose durable and weather-resistant rocks like granite or quartzite. For pathways and patios, select rocks with a smooth surface and good traction, such as sandstone or slate. Consider the color and texture of the rocks to ensure they complement the overall design.
6.5. Sustainable Rock Sourcing: Protecting the Environment
How can you ensure that your rock choices are environmentally responsible? Opt for locally sourced rocks to reduce transportation costs and environmental impact. Choose suppliers who follow sustainable quarrying practices and minimize habitat disruption. Consider using recycled or reclaimed rocks to conserve natural resources. By making informed choices, you can enjoy the beauty of natural stone while protecting the environment.
7. Inspiring Landscape Design Ideas with the 3 Major Rock Types
Ready to transform your outdoor space with the beauty of natural stone? From rustic rock gardens to elegant stone pathways, the possibilities are endless. Let’s explore some inspiring design ideas that showcase the versatility of the three major rock types. Discover how you can incorporate these geological wonders into your landscape to create stunning and sustainable outdoor spaces.
7.1. Creating a Serene Rock Garden with Igneous Boulders
How can you use igneous rocks to design a peaceful and low-maintenance rock garden? Arrange granite boulders of varying sizes to create a natural-looking rock garden. Plant drought-tolerant plants like succulents, sedums, and ornamental grasses between the rocks. Add gravel or crushed stone to improve drainage and suppress weeds. The combination of rugged rocks and resilient plants will create a serene and low-maintenance landscape.
7.2. Building a Rustic Retaining Wall with Sedimentary Stones
How can sedimentary stones provide both functionality and aesthetic appeal in a retaining wall? Construct a retaining wall using sandstone or limestone blocks. Choose stones with a variety of shapes and sizes to create a natural, rustic look. Backfill the wall with gravel to improve drainage. Plant cascading plants like creeping thyme or sedum along the top of the wall to soften the edges and add visual interest.
7.3. Designing an Elegant Pathway with Metamorphic Pavers
How can metamorphic pavers elevate the look and feel of your garden pathway? Install slate or quartzite pavers to create an elegant and durable pathway. Arrange the pavers in a pattern that complements the style of your garden. Fill the gaps between the pavers with gravel or polymeric sand to prevent weed growth. Line the pathway with ornamental grasses or flowering plants to create a welcoming and inviting entrance.
7.4. Constructing a Natural Water Feature with a Variety of Rock Types
How can you combine different rock types to create a dynamic and visually appealing water feature? Combine igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks to create a natural-looking waterfall or pond. Use large boulders to form the structure of the water feature. Line the bottom of the pond with gravel and small stones. Add aquatic plants to create a thriving ecosystem. The combination of different rock types will create a dynamic and visually appealing water feature.
7.5. Enhancing Garden Beds with Decorative Rock Mulch
How can rock mulch improve the health and appearance of your garden beds? Replace traditional organic mulch with decorative rock mulch, such as granite chips or marble pebbles. Rock mulch helps to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Choose a rock color that complements the plants and other elements in your garden. The addition of rock mulch will create a clean and polished look while providing numerous benefits for your plants.
8. Maintaining the Beauty and Longevity of Your Rock Features
How can you ensure that your rock landscapes remain beautiful and functional for years to come? Proper maintenance is essential for preserving the beauty and longevity of your rock features. Regular cleaning, occasional repairs, and preventative measures will help to keep your rock landscapes looking their best. According to landscape maintenance experts, a little effort can go a long way in extending the life of your rock features.
8.1. Cleaning and Sealing Rock Surfaces
What are the best practices for cleaning and protecting rock surfaces from stains and damage? Clean rock surfaces regularly with a mild soap and water solution. Use a soft brush to remove dirt and debris. For stubborn stains, use a specialized stone cleaner. Apply a sealant to protect the rock from moisture and stains. Reapply the sealant every one to two years, or as needed, to maintain its effectiveness.
8.2. Preventing Weed Growth in Rock Landscapes
How can you minimize weed growth and keep your rock features looking tidy? Install a weed barrier fabric beneath the rocks to prevent weed growth. Regularly inspect the rock landscape for weeds and remove them by hand or with a weeding tool. Apply a pre-emergent herbicide to prevent weed seeds from germinating. Use a post-emergent herbicide to kill existing weeds. Mulch around plants with rocks or gravel to suppress weed growth.
8.3. Repairing Cracks and Damage in Rock Structures
How can you address cracks and damage to ensure the structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of your rock features? Inspect rock structures regularly for cracks and damage. Repair small cracks with a mortar mix that matches the color of the rock. For larger cracks, consider consulting a professional stone mason. Replace damaged stones with new ones that match the existing rock. Ensure that the repairs are structurally sound and aesthetically pleasing.
8.4. Protecting Rocks from Weathering and Erosion
What measures can you take to safeguard your rock features from the elements? Protect rock features from excessive moisture by ensuring proper drainage. Avoid using de-icing salts on rock surfaces, as they can cause damage. Apply a water repellent sealant to protect the rock from moisture and freeze-thaw cycles. Stabilize slopes and embankments with vegetation or retaining walls to prevent erosion.
8.5. Enhancing the Natural Beauty of Rocks with Lighting
How can lighting transform the look of your rock landscapes at night? Install landscape lighting to highlight the textures and colors of your rocks. Use spotlights to illuminate large boulders or rock formations. Place path lights along pathways to provide safety and visibility. Install underwater lights in water features to create a magical effect. Choose energy-efficient LED lights to minimize energy consumption.
9. The Expertise of Rockscapes.net: Your Partner in Landscape Design
Looking for expert advice and high-quality materials for your next rockscape project? At rockscapes.net, we offer a wide range of services to help you create the landscape of your dreams. From design consultation to material selection and installation, our team of experienced professionals is here to guide you every step of the way. Explore our website today to discover the beauty and versatility of natural stone!
9.1. Comprehensive Landscape Design Services
What landscape design services does rockscapes.net offer to help you bring your vision to life? At rockscapes.net, we offer comprehensive landscape design services tailored to your unique needs and preferences. Our experienced designers will work closely with you to create a customized plan that incorporates your favorite rock types, plants, and features. We will consider factors such as site conditions, budget, and maintenance requirements to ensure that your landscape is both beautiful and sustainable.
9.2. High-Quality Rock and Stone Materials
What types of rock and stone materials does rockscapes.net provide for your landscaping projects? We offer a wide selection of high-quality rock and stone materials, including granite, sandstone, slate, limestone, and more. Our materials are sourced from reputable quarries and are available in a variety of sizes, shapes, and colors. Whether you are looking for large boulders, small pebbles, or paving stones, we have the perfect materials to bring your vision to life.
9.3. Professional Installation Services
How can rockscapes.net assist you with the installation of your landscape features? Our team of skilled installers will ensure that your landscape features are installed correctly and efficiently. We have the expertise and equipment to handle projects of all sizes, from small rock gardens to large retaining walls. We will work closely with you to ensure that the installation process is smooth and hassle-free.
9.4. Expert Advice and Guidance
What expert advice and guidance can you expect from rockscapes.net? Our team of experienced professionals is here to provide you with expert advice and guidance on all aspects of landscape design and installation. We can help you choose the right rock types for your project, design a landscape that meets your needs and preferences, and provide tips on maintaining the beauty and longevity of your rock features.
9.5. Contact Us Today to Get Started
How can you get in touch with rockscapes.net to begin your landscape transformation? Ready to transform your outdoor space with the beauty of natural stone? Contact us today to schedule a consultation with one of our experienced designers. We will work closely with you to create a customized plan that meets your needs, preferences, and budget. Let us help you bring your vision to life!
Address: 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States.
Phone: +1 (480) 965-9011.
Website: rockscapes.net.
10. FAQs About the Three Major Rock Types
Do you have more questions about the three major rock types and their applications? Here are some frequently asked questions to help you deepen your understanding of these fascinating geological materials.
10.1. What Are the Three Major Rock Types?
The three major rock types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic, each formed through unique geological processes.
10.2. How Are Igneous Rocks Formed?
Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
10.3. What Are Sedimentary Rocks Made Of?
Sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and cementation of sediments, including fragments of other rocks, minerals, and organic matter.
10.4. What Causes Metamorphism in Rocks?
Metamorphism in rocks is caused by heat, pressure, or chemically active fluids, which alter the mineral composition, texture, and structure of the original rock.
10.5. How Can I Identify Different Types of Rocks?
You can identify different types of rocks by observing their color, texture, mineral composition, and the presence of fossils or other distinctive features.
10.6. What Are Some Common Uses for Granite?
Granite is commonly used for countertops, paving stones, and building facades due to its strength and durability.
10.7. How Is Limestone Used in Construction?
Limestone is used in cement production, building facades, and garden paths due to its versatility and aesthetic appeal.
10.8. What Is Slate Typically Used For?
Slate is typically used for roofing, paving, and water features due to its durability and ability to be split into thin sheets.
10.9. How Does the Rock Cycle Work?
The rock cycle describes the continuous processes through which rocks are transformed from one type to another, involving weathering, erosion, sedimentation, lithification, metamorphism, and melting.
10.10. Where Can I Learn More About Rocks and Geology?
You can learn more about rocks and geology by visiting rockscapes.net, exploring resources from organizations like the U.S. Geological Survey and the Geological Society of America, and visiting local geological sites and museums.
By understanding the three major rock types and their applications, you can create stunning and sustainable landscapes that celebrate the beauty and power of nature. Visit rockscapes.net for inspiration, high-quality materials, and expert advice to bring your vision to life.
