The Rock of Gibraltar is located on a peninsula on Spain’s southern Mediterranean coast, just northeast of the Strait of Gibraltar. Rockscapes.net helps you discover all about this iconic landmark, including its location, geology, and significance. Let’s explore the Rock of Gibraltar’s location, formation, and why it holds such a prominent place in history and culture, plus discover how rocks and rock formations are important in landscaping.
1. What Exactly Is the Rock of Gibraltar?
The Rock of Gibraltar is a monolithic limestone promontory that dominates the landscape. This imposing geological formation is not just a rock; it’s a symbol of strategic importance and historical significance.
A Geological Marvel
Composed primarily of limestone, the Rock of Gibraltar’s origins trace back to the Jurassic period. Over millennia, tectonic forces and erosion sculpted this massive structure. The Rock features a network of caves, tunnels, and cliffs, adding to its unique geological appeal.
Strategic Location
Gibraltar’s location at the entrance to the Mediterranean Sea has made it a coveted territory throughout history. Its strategic importance stems from its ability to control maritime traffic between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean. This control has been vital for trade, naval operations, and military strategy.
Historical Significance
The Rock of Gibraltar has a rich history, dating back to ancient times. It has been controlled by various powers, including the Phoenicians, Romans, and Moors. In 1704, it was captured by British forces during the War of the Spanish Succession and has remained a British Overseas Territory ever since.
2. Where Is the Rock of Gibraltar Physically Situated?
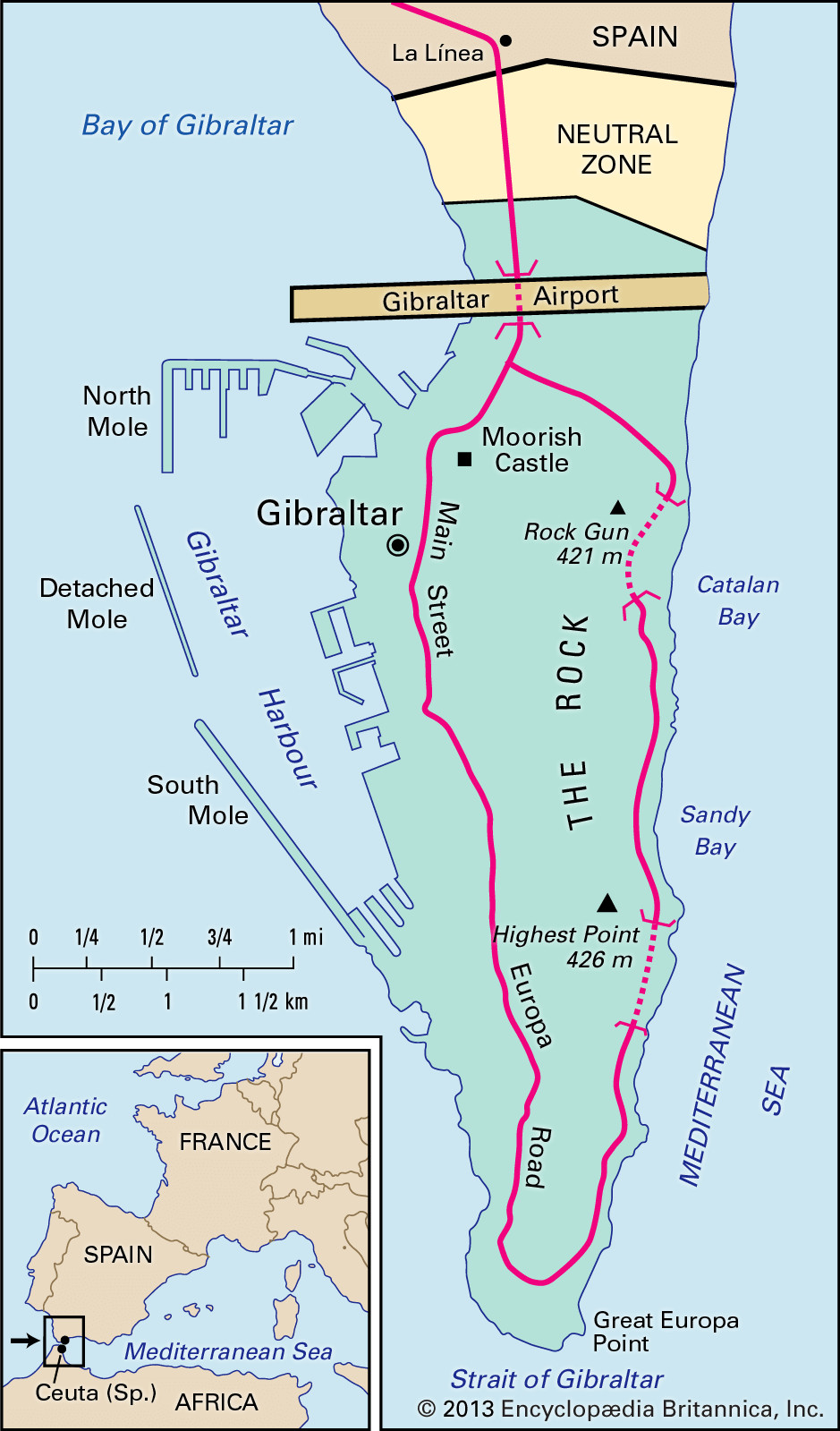
The Rock of Gibraltar is situated on a peninsula that juts out from the southern coast of Spain. Its precise coordinates are approximately 36.1447° N latitude and 5.3533° W longitude.
Geographic Context
The peninsula is located on the eastern side of the Bay of Gibraltar (also known as the Bay of Algeciras) and directly south of the Spanish city of La Línea de la Concepción. The Rock is connected to Spain by a low, sandy isthmus, which is about 1 mile (1.6 km) long.
Proximity to Key Locations
The Rock’s position near the Strait of Gibraltar places it at a critical juncture between Europe and Africa. The Moroccan coast is visible from Gibraltar on clear days, emphasizing its proximity to the African continent. According to research from Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, in July 2025, the visibility between continents can influence regional weather patterns.
Dimensions and Topography
The territory of Gibraltar is relatively small, covering an area of about 2.6 square miles (6.8 square kilometers). The Rock itself is approximately 3 miles (5 km) long and 0.75 miles (1.2 km) wide. It rises dramatically from the isthmus, reaching a height of 1,396 feet (426 meters) at its highest point.
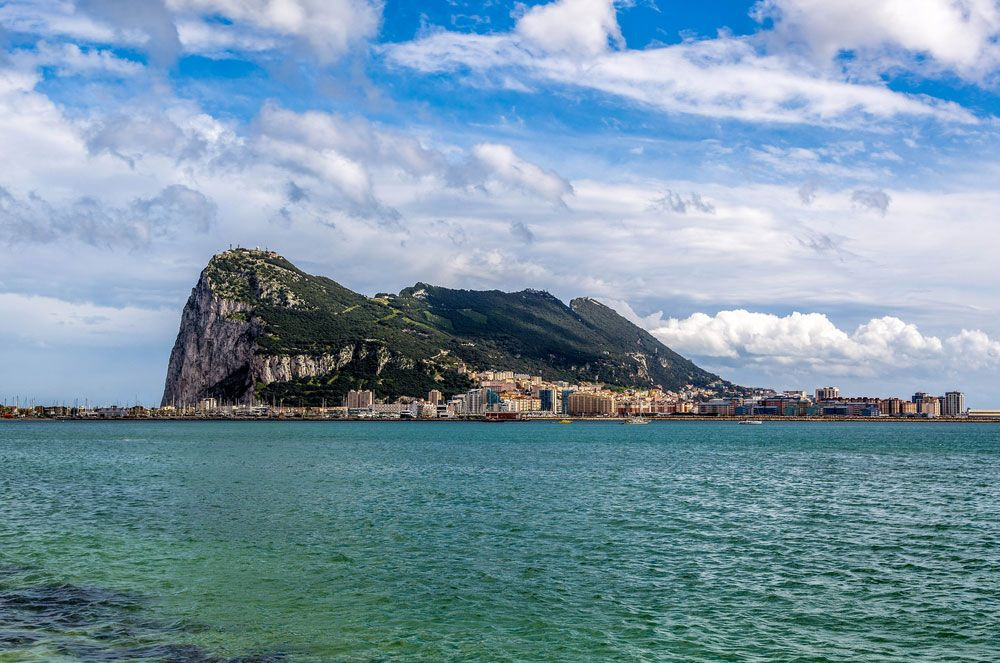 Rock of Gibraltar Overview
Rock of Gibraltar Overview
3. How Was the Rock of Gibraltar Formed?
The geological formation of the Rock of Gibraltar is a story spanning millions of years, involving tectonic activity, sedimentation, and erosion.
Tectonic Origins
The Rock of Gibraltar is primarily composed of Jurassic limestone, which was formed over 200 million years ago when the region was submerged under a shallow sea. Sediments, including the remains of marine organisms, accumulated on the seabed and eventually solidified into limestone.
Uplift and Tilting
The formation of the Rock is closely linked to the collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates. This collision resulted in the uplift and tilting of the limestone layers, creating the prominent ridge that we see today.
Erosion and Weathering
Over millions of years, the Rock has been subjected to extensive erosion and weathering. Wind, rain, and temperature fluctuations have sculpted the limestone, creating its steep cliffs, caves, and other distinctive features.
Cave Systems
One of the most remarkable aspects of the Rock of Gibraltar is its extensive network of caves. St. Michael’s Cave, the most famous, is a series of natural limestone caves adorned with stalactites and stalagmites. These caves were formed by the dissolution of limestone by rainwater over thousands of years.
4. What Is the Strategic Importance of the Rock of Gibraltar?
The Rock of Gibraltar’s strategic importance is rooted in its geographical location, which commands the Strait of Gibraltar. This narrow waterway connects the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, making it a vital maritime passage.
Control of Maritime Traffic
Possession of Gibraltar allows control over the movement of ships between the Atlantic and the Mediterranean. This control has been crucial for trade, naval operations, and military strategy throughout history.
Naval Base and Military Stronghold
Gibraltar has served as a major naval base and military stronghold for centuries. Its fortified position has enabled naval powers to project their influence and protect their interests in the Mediterranean region.
Historical Conflicts
The strategic value of Gibraltar has made it a focal point in numerous historical conflicts. Control of the Rock has been contested by various powers, including Spain, France, and Britain. The territory has withstood sieges and battles, underscoring its resilience and strategic importance.
Modern Significance
Even in the modern era, Gibraltar remains strategically important. It serves as a British naval base and a key monitoring point for maritime activities in the region. Its location also makes it a valuable asset for intelligence gathering and security operations.
5. Who Inhabits the Rock of Gibraltar?
Gibraltar is inhabited by a diverse population with a unique cultural identity. The majority of residents are Gibraltarians, who have a distinct heritage blending Genoese, British, Spanish, Maltese, and Portuguese influences.
Demographics
As of recent estimates, the population of Gibraltar is around 34,000. Gibraltarians make up the largest portion of the population, with smaller communities of British, Spanish, Moroccan, and Indian residents.
Cultural Identity
Gibraltarian culture is a blend of various influences, reflecting the territory’s history and geographical location. English is the official language, but many Gibraltarians also speak Spanish, and a local dialect known as Llanito, which combines elements of both languages.
Religion
The majority of Gibraltarians are Roman Catholic. The territory also has Anglican, Jewish, and Muslim communities, reflecting its diverse population.
Wildlife
In addition to its human inhabitants, Gibraltar is home to a unique wildlife population. The most famous are the Barbary macaques, a species of monkey that roams freely on the Upper Rock. According to legend, British dominion over Gibraltar will persist as long as the macaques remain on the Rock.
6. What Are Some Key Landmarks on the Rock of Gibraltar?
The Rock of Gibraltar is dotted with landmarks that highlight its history, geology, and strategic importance.
St. Michael’s Cave
St. Michael’s Cave is a network of natural limestone caves located in the upper part of the Rock. These caves are adorned with stunning stalactites and stalagmites and have been used for various purposes throughout history, including as shelters, storage areas, and even a military hospital.
Great Siege Tunnels
The Great Siege Tunnels are a series of tunnels carved into the Rock during the Great Siege of Gibraltar in the late 18th century. These tunnels were built to provide access to strategic firing positions and played a crucial role in defending the territory against enemy forces.
Europa Point
Europa Point is the southernmost point of Gibraltar, offering stunning views of the Strait of Gibraltar and the African coast. The area features a lighthouse, a chapel, and several historical military installations.
Moorish Castle
The Moorish Castle is a medieval fortification built during the Moorish rule of Gibraltar. The castle has been modified and expanded over the centuries and offers a glimpse into the territory’s rich history.
Apes’ Den
The Apes’ Den is an area on the Upper Rock where the Barbary macaques can be observed in their natural habitat. This popular tourist attraction provides visitors with the opportunity to see these fascinating primates up close.
7. How Does the Rock of Gibraltar Impact the Local Economy?
The Rock of Gibraltar plays a significant role in the local economy, contributing to various sectors such as tourism, finance, and maritime services.
Tourism
Tourism is a major source of revenue for Gibraltar. The Rock is a popular destination, attracting visitors from around the world who come to explore its landmarks, enjoy its natural beauty, and experience its unique culture.
Finance
Gibraltar has developed a thriving financial services sector, offering banking, insurance, and investment services. The territory’s favorable tax regime and strategic location have attracted international businesses and investors.
Maritime Services
The port of Gibraltar provides a range of maritime services, including ship repair, bunkering, and cargo handling. Its strategic location on a major shipping route makes it a valuable hub for maritime activities.
British Military Garrison
The presence of a British military garrison in Gibraltar also contributes to the local economy. The military provides employment opportunities and supports local businesses through its procurement activities.
8. What Is the Climate Like Near the Rock of Gibraltar?
The climate near the Rock of Gibraltar is characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This Mediterranean climate is influenced by the territory’s geographical location and proximity to the sea.
Summers
Summers in Gibraltar are hot and dry, with average temperatures ranging from 75°F to 85°F (24°C to 29°C). Rainfall is scarce during the summer months, and the sun shines for most of the day.
Winters
Winters are mild and wet, with average temperatures ranging from 50°F to 60°F (10°C to 16°C). Rainfall is more frequent during the winter months, and the territory can experience occasional storms.
Transitional Seasons
The transitional seasons of spring and autumn are generally warm and pleasant, with moderate temperatures and occasional rainfall. These seasons are ideal for outdoor activities and exploring the Rock of Gibraltar.
Winds
Gibraltar is subject to strong easterly winds, known as the Levanter, which can bring humid air and cloud cover. These winds can impact visibility and maritime activities in the area.
9. How Is the Rock of Gibraltar Connected to Other “Rocks” or Geological Formations Worldwide?
While the Rock of Gibraltar is unique, it shares geological similarities with other limestone formations around the world.
Limestone Formations
Limestone is a common sedimentary rock found in many parts of the world. Other notable limestone formations include the White Cliffs of Dover in England, the karst landscapes of Southeast Asia, and the cenotes of the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico.
Coastal Cliffs
The Rock of Gibraltar’s dramatic cliffs are similar to other coastal cliff formations, such as the Cliffs of Moher in Ireland and the Twelve Apostles in Australia. These cliffs are formed by the erosion of rock by wave action and weathering.
Monoliths
As a monolithic structure, the Rock of Gibraltar shares characteristics with other famous monoliths, such as Uluru (Ayers Rock) in Australia and Sugarloaf Mountain in Brazil. These formations are large, single rocks that stand out prominently in their surrounding landscapes.
Geological Processes
The geological processes that formed the Rock of Gibraltar – tectonic uplift, sedimentation, and erosion – are common to many mountain ranges and geological formations around the world. Studying these processes helps geologists understand the Earth’s history and dynamics.
10. Why Is It Important To Preserve The Rock Of Gibraltar?
Preserving the Rock of Gibraltar is essential for several reasons, including its historical, cultural, and environmental significance.
Historical Preservation
The Rock of Gibraltar is a historical landmark that has played a crucial role in the history of Europe and the Mediterranean region. Preserving its historical sites, fortifications, and tunnels is important for understanding and appreciating the past.
Cultural Heritage
The Rock is an integral part of Gibraltarian culture and identity. Protecting its cultural heritage, including its unique blend of British and Mediterranean influences, is vital for maintaining the territory’s distinct character.
Environmental Conservation
The Rock of Gibraltar is home to a diverse range of plant and animal species, including the Barbary macaques and the Gibraltar candytuft, a flower found nowhere else in the world. Preserving its natural environment is essential for protecting these unique species and ecosystems.
Tourism and Economy
The Rock of Gibraltar is a major tourist attraction, contributing significantly to the local economy. Preserving its natural beauty and historical landmarks is important for sustaining tourism and supporting local businesses.
Geopolitical Stability
The Rock’s strategic location makes it a key factor in regional geopolitical stability. Maintaining its security and stability is important for ensuring peace and security in the Mediterranean region.
 Europa Point, Gibraltar
Europa Point, Gibraltar
How Rockscapes.net Can Help You With Your Rock and Landscape Needs
At Rockscapes.net, we understand the beauty and versatility of rocks in landscaping. Whether you’re looking to create a stunning rock garden, build a durable retaining wall, or add unique stone features to your outdoor space, we have the expertise and resources to help you achieve your vision.
Rock Selection and Sourcing
We offer a wide variety of rocks, stones, and boulders to suit any landscaping project. From classic granite and limestone to unique and exotic stones, we can help you find the perfect materials to complement your design.
Design and Installation
Our team of experienced landscape designers and installers can help you create a custom rockscape that enhances the beauty and functionality of your property. We work closely with you to understand your needs and preferences, and we use our expertise to bring your vision to life.
Maintenance and Care
We also provide maintenance and care services to ensure that your rockscapes look their best for years to come. From cleaning and sealing to repair and restoration, we can help you keep your rock features in top condition.
Crafting Your Landscape with Rocks: A Source of Inspiration
Rocks offer unique opportunities to enhance landscaping, blending natural beauty with functional design. Whether you’re looking to create a serene rock garden, a robust retaining wall, or eye-catching stone features, the possibilities are endless. Let’s explore a few inspiring ideas to transform your outdoor space with rocks.
Rock Gardens
A rock garden is a stunning way to showcase a variety of plants and stones in a harmonious arrangement. To create a rock garden:
- Choose a Location: Select a sunny, well-drained area.
- Select Rocks: Use a mix of sizes and types for visual interest.
- Arrange Rocks: Place larger stones first, creating a natural-looking layout.
- Add Plants: Incorporate alpine plants, succulents, and other rock-friendly species.
- Maintenance: Regularly weed and prune plants to maintain the garden’s beauty.
Retaining Walls
Retaining walls are not only functional but can also add aesthetic value to your landscape. They help manage soil erosion and create tiered garden beds.
- Planning: Determine the height and length of the wall.
- Material Selection: Choose durable stones like granite or sandstone.
- Construction: Ensure a solid foundation and proper drainage.
- Backfilling: Use gravel behind the wall for drainage.
- Planting: Add plants on top or in between stones for a natural look.
Stone Pathways
Stone pathways provide a charming and practical way to navigate your garden. They can be designed to complement various garden styles.
- Layout: Plan the path’s route, considering key garden features.
- Stone Selection: Opt for flagstones, pavers, or gravel.
- Installation: Lay stones on a compacted base of sand or gravel.
- Spacing: Leave small gaps for plants like thyme or moss to grow.
- Edging: Use larger stones or edging materials to define the path.
Water Features
Incorporating rocks into water features like ponds, waterfalls, or fountains adds a natural and soothing element to your landscape.
- Pond Construction: Line the pond with rocks of various sizes.
- Waterfall Design: Arrange rocks to create a cascading effect.
- Pump Installation: Ensure proper water circulation with a suitable pump.
- Plant Integration: Add aquatic plants for a balanced ecosystem.
- Maintenance: Regularly clean the pond and pump to keep the water clear.
Decorative Boulders
Large boulders can serve as focal points in your garden, adding drama and character.
- Boulder Selection: Choose boulders that match your garden’s style.
- Placement: Position boulders strategically for visual impact.
- Grouping: Arrange multiple boulders to create a natural formation.
- Planting: Surround boulders with complementary plants.
- Lighting: Highlight boulders with landscape lighting for evening ambiance.
Rock Mulch
Using rock mulch instead of traditional wood mulch offers several benefits, including better drainage, weed control, and a unique aesthetic.
- Preparation: Clear the area and lay down landscape fabric.
- Rock Selection: Choose gravel, pebbles, or crushed stone.
- Application: Spread the rock mulch evenly over the area.
- Depth: Maintain a mulch depth of about 2-3 inches.
- Maintenance: Occasionally rake and replenish the mulch as needed.
Dry Creek Beds
A dry creek bed is an excellent way to manage drainage while adding a visually appealing feature to your landscape.
- Planning: Design the creek bed’s path, mimicking natural water flow.
- Excavation: Dig a shallow trench along the planned route.
- Lining: Line the trench with landscape fabric.
- Rock Placement: Use a mix of river rocks, boulders, and pebbles.
- Planting: Add moisture-loving plants along the creek bed.
Why Choose Rockscapes.net?
Choosing the right partner for your rock and landscape needs is crucial. Rockscapes.net stands out for several compelling reasons:
- Expertise and Experience: With years of experience in the industry, Rockscapes.net brings unparalleled expertise to every project.
- Quality Materials: We source only the highest quality rocks, stones, and landscaping materials.
- Custom Solutions: Our team tailors every project to meet your specific needs and preferences.
- Comprehensive Services: From design and installation to maintenance and care, we offer end-to-end solutions.
- Customer Satisfaction: At Rockscapes.net, customer satisfaction is our top priority.
Ready to Transform Your Landscape?
Are you inspired to transform your landscape with rocks? Contact Rockscapes.net today to explore the possibilities. Our team is ready to help you create a stunning outdoor space that reflects your style and enhances your property’s value.
Contact Information:
- Address: 1151 S Forest Ave, Tempe, AZ 85281, United States
- Phone: +1 (480) 965-9011
- Website: Rockscapes.net
Let rockscapes.net be your partner in creating the landscape of your dreams. Together, we can turn your outdoor space into a breathtaking oasis.
FAQ About The Rock of Gibraltar
1. What type of rock is the Rock of Gibraltar made of?
The Rock of Gibraltar is primarily made of limestone, specifically Jurassic limestone. This type of rock was formed over millions of years from the accumulation and compression of marine sediments.
2. How tall is the Rock of Gibraltar?
The highest point of the Rock of Gibraltar is 1,396 feet (426 meters) above sea level. This height provides strategic advantages for observation and defense.
3. Can you walk to the Rock of Gibraltar from Spain?
Yes, you can walk to the Rock of Gibraltar from Spain via the isthmus that connects the peninsula to the Spanish mainland. However, you will need to pass through a border control checkpoint.
4. Are there monkeys on the Rock of Gibraltar?
Yes, the Rock of Gibraltar is famous for its Barbary macaques, a species of monkey that roams freely on the Upper Rock. They are Europe’s only wild monkey population.
5. How did the Rock of Gibraltar get its name?
The Rock of Gibraltar gets its name from the Arabic name Jabal Ṭāriq (Mount Tarik), which honors Ṭāriq ibn Ziyād, the Muslim general who led the conquest of the Iberian Peninsula in 711 AD.
6. What is the significance of the Strait of Gibraltar?
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow waterway that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea. It is a strategically important passage for maritime trade and naval operations.
7. What is the climate like on the Rock of Gibraltar?
The climate on the Rock of Gibraltar is Mediterranean, with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The territory is also subject to strong easterly winds.
8. What are some popular tourist attractions on the Rock of Gibraltar?
Popular tourist attractions on the Rock of Gibraltar include St. Michael’s Cave, the Great Siege Tunnels, Europa Point, the Moorish Castle, and the Apes’ Den.
9. How does Gibraltar get its freshwater?
Gibraltar used to collect rainwater using a rain-catchment area. Now, most of its freshwater comes from a desalinization plant that converts seawater into potable water.
10. Why is the Rock of Gibraltar considered a British Overseas Territory?
The Rock of Gibraltar became a British Overseas Territory in 1713 under the Treaty of Utrecht. It has remained under British control ever since, despite occasional disputes with Spain.